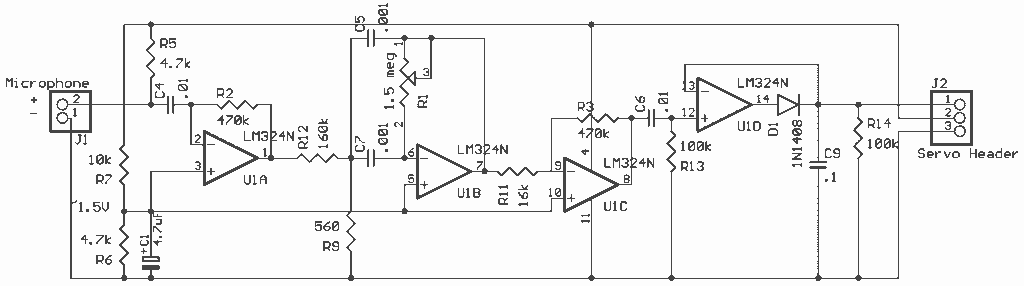
AUDIO NOTCH FILTER FOR SHORTWAVE RECEIVERS
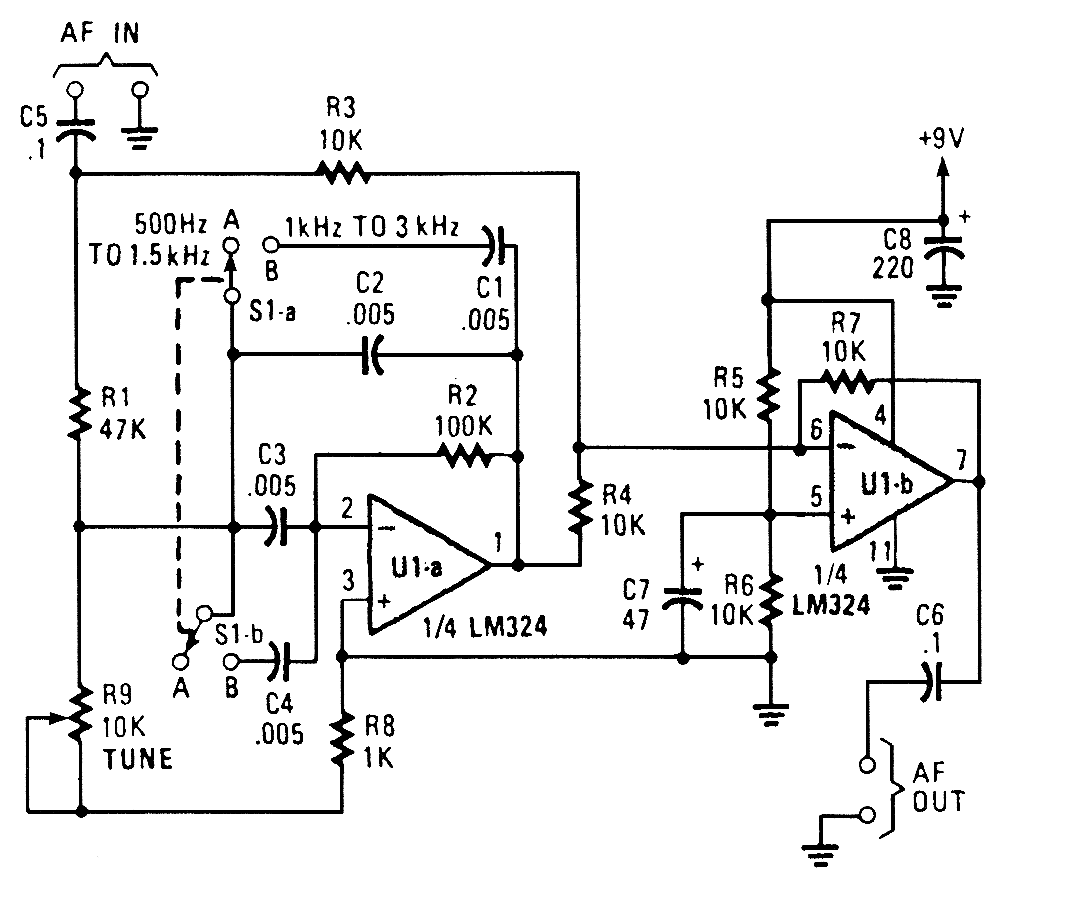
The notch filter can be integrated into nearly any receiver to attenuate a specific frequency by more than 30 dB. This filter is particularly useful for diminishing heterodynes and whistles.
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop or band-reject filter, is designed to eliminate a narrow band of frequencies while allowing all other frequencies to pass through with minimal attenuation. The primary application of a notch filter in a receiver setup is to target and significantly reduce unwanted signals, such as heterodynes and whistles, which can interfere with the desired audio or radio signal.
In practical terms, a notch filter can be constructed using various electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers. The design typically involves creating a parallel resonant circuit that is tuned to the frequency to be attenuated. This circuit can be implemented using passive components for simpler applications or active components for more complex designs requiring higher performance.
The performance of the notch filter is characterized by its quality factor (Q), which defines the bandwidth of the notch. A higher Q factor results in a narrower notch, allowing for precise attenuation of a specific frequency. Conversely, a lower Q factor results in a wider notch, affecting a broader range of frequencies.
In receiver applications, the notch filter can be placed strategically within the signal path. It can be implemented before the demodulation stage to prevent unwanted frequencies from interfering with the desired signal processing. Alternatively, it can be placed after initial amplification to refine the signal further.
To ensure optimal performance, careful consideration must be given to the design parameters, including the frequency to be attenuated, the desired level of attenuation, and the overall impact on the signal integrity. Proper testing and tuning of the filter are essential to achieving the desired results, ensuring that the receiver operates effectively in the presence of unwanted signals.The notch filter can be added to just about any receiver to attenuate a single frequency by more Lhan 30 dB. This filter should be handy for reducing heterodynes and whistles. 🔗 External reference
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop or band-reject filter, is designed to eliminate a narrow band of frequencies while allowing all other frequencies to pass through with minimal attenuation. The primary application of a notch filter in a receiver setup is to target and significantly reduce unwanted signals, such as heterodynes and whistles, which can interfere with the desired audio or radio signal.
In practical terms, a notch filter can be constructed using various electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers. The design typically involves creating a parallel resonant circuit that is tuned to the frequency to be attenuated. This circuit can be implemented using passive components for simpler applications or active components for more complex designs requiring higher performance.
The performance of the notch filter is characterized by its quality factor (Q), which defines the bandwidth of the notch. A higher Q factor results in a narrower notch, allowing for precise attenuation of a specific frequency. Conversely, a lower Q factor results in a wider notch, affecting a broader range of frequencies.
In receiver applications, the notch filter can be placed strategically within the signal path. It can be implemented before the demodulation stage to prevent unwanted frequencies from interfering with the desired signal processing. Alternatively, it can be placed after initial amplification to refine the signal further.
To ensure optimal performance, careful consideration must be given to the design parameters, including the frequency to be attenuated, the desired level of attenuation, and the overall impact on the signal integrity. Proper testing and tuning of the filter are essential to achieving the desired results, ensuring that the receiver operates effectively in the presence of unwanted signals.The notch filter can be added to just about any receiver to attenuate a single frequency by more Lhan 30 dB. This filter should be handy for reducing heterodynes and whistles. 🔗 External reference