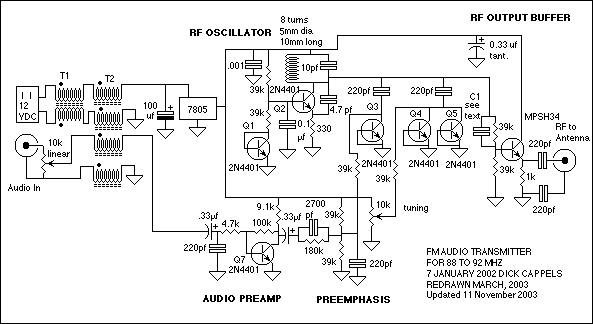
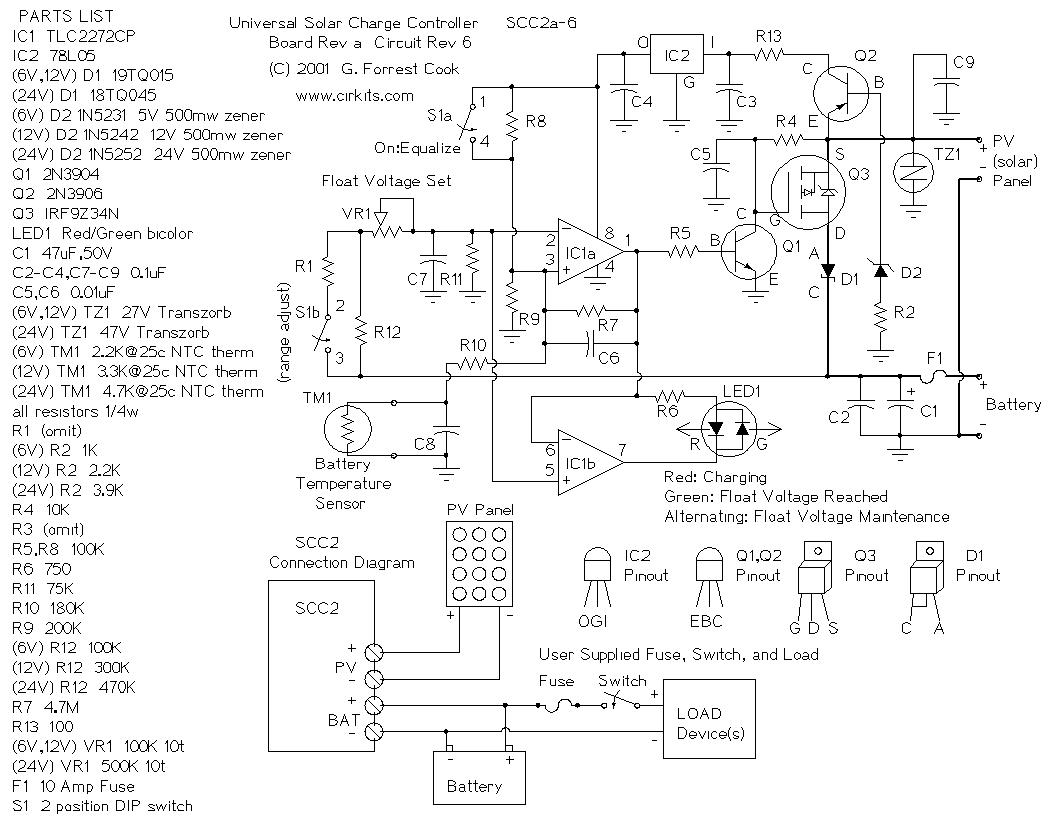
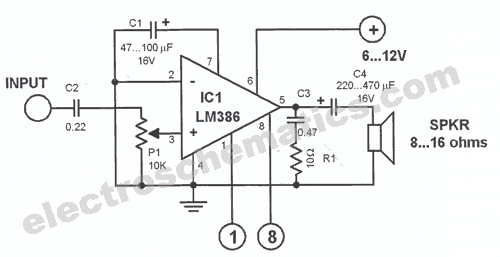
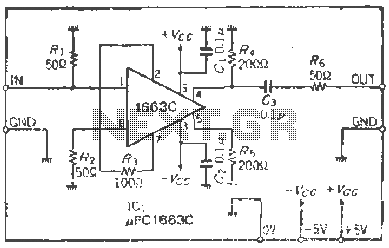
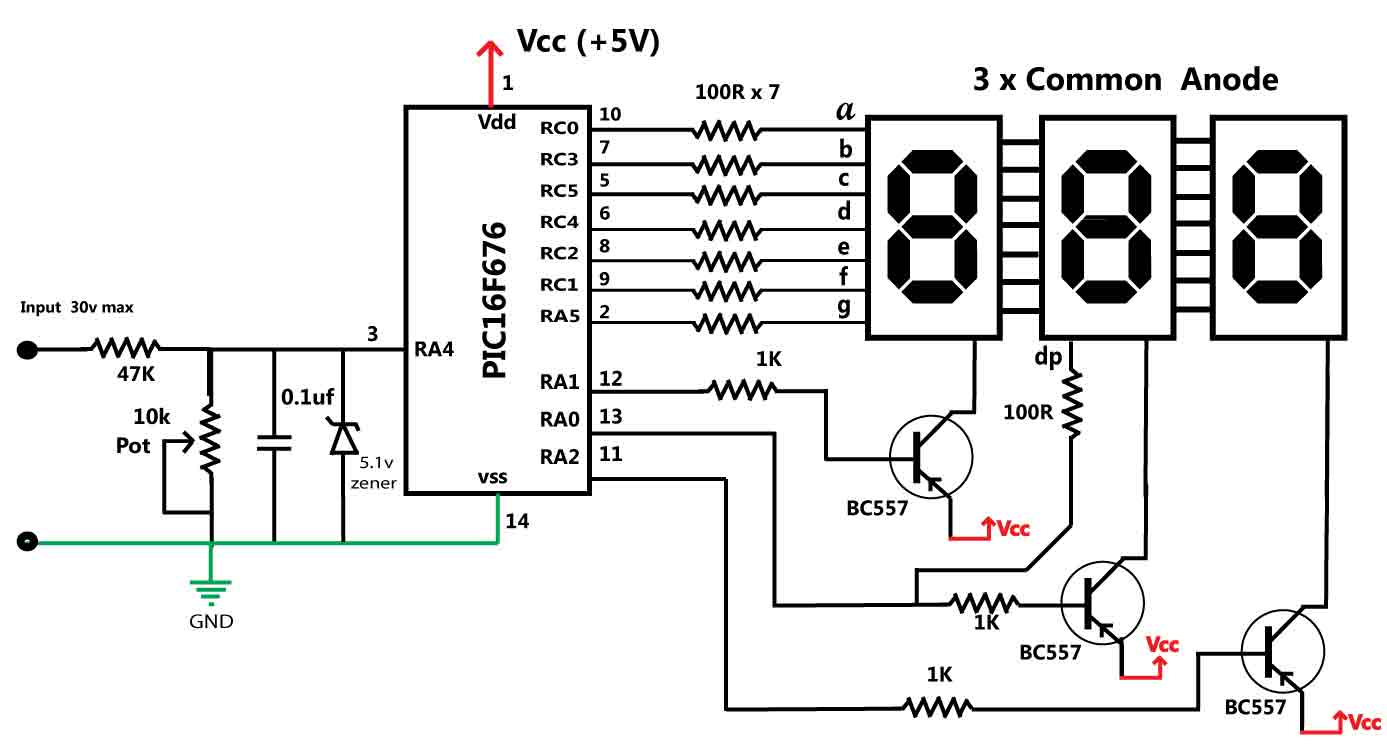
PWM Motor Speed Control Using Class D Audio Amplifier
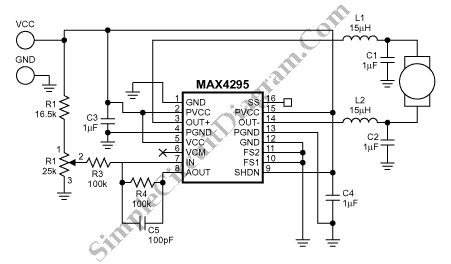
This is a Class D audio amplifier circuit that is used to control PWM motor speed. This circuit has two advantages for battery-powered portable devices. First,
The Class D audio amplifier circuit is designed to efficiently manage the speed of a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) motor, making it particularly suitable for battery-operated portable devices. Class D amplifiers are known for their high efficiency, often exceeding 90%, which is crucial for extending battery life in portable applications.
In this circuit, the input audio signal is first processed and converted into a PWM signal. This conversion is achieved using a comparator that compares the input signal with a triangular waveform. The resulting PWM signal is then used to drive a power stage, typically consisting of MOSFETs or IGBTs, which switch on and off rapidly to control the power delivered to the motor.
The advantages of using a Class D amplifier for PWM motor control include reduced heat generation and improved battery efficiency. Since the switching elements operate in saturation and cutoff regions, power loss due to heat is minimized. This is particularly beneficial in applications where thermal management is critical.
Additionally, the circuit can incorporate feedback mechanisms to ensure precise control of motor speed and torque, enhancing the overall performance of the device. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the speed of the motor can be finely tuned, allowing for smooth operation across a range of speeds.
In summary, the Class D audio amplifier circuit for PWM motor speed control provides an effective solution for managing power in battery-powered devices, combining efficiency, performance, and the ability to maintain compact designs.This is class D audio amplifier circuit that is used to control PWM motor speed. This circuit has two advantages for battery-powered portable devices. First, . 🔗 External reference
The Class D audio amplifier circuit is designed to efficiently manage the speed of a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) motor, making it particularly suitable for battery-operated portable devices. Class D amplifiers are known for their high efficiency, often exceeding 90%, which is crucial for extending battery life in portable applications.
In this circuit, the input audio signal is first processed and converted into a PWM signal. This conversion is achieved using a comparator that compares the input signal with a triangular waveform. The resulting PWM signal is then used to drive a power stage, typically consisting of MOSFETs or IGBTs, which switch on and off rapidly to control the power delivered to the motor.
The advantages of using a Class D amplifier for PWM motor control include reduced heat generation and improved battery efficiency. Since the switching elements operate in saturation and cutoff regions, power loss due to heat is minimized. This is particularly beneficial in applications where thermal management is critical.
Additionally, the circuit can incorporate feedback mechanisms to ensure precise control of motor speed and torque, enhancing the overall performance of the device. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the speed of the motor can be finely tuned, allowing for smooth operation across a range of speeds.
In summary, the Class D audio amplifier circuit for PWM motor speed control provides an effective solution for managing power in battery-powered devices, combining efficiency, performance, and the ability to maintain compact designs.This is class D audio amplifier circuit that is used to control PWM motor speed. This circuit has two advantages for battery-powered portable devices. First, . 🔗 External reference