Audio Reproduction on HCS12 Microcontrollers with Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Capability
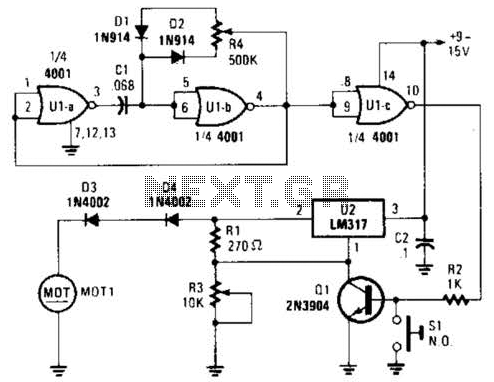
The HCS12 series of microcontrollers does not include dedicated internal digital-to-analog conversion hardware. Therefore, external hardware, such as a digital-to-analog conversion integrated circuit (IC), is required.
To implement digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) in systems utilizing the HCS12 microcontroller, an external DAC IC must be integrated into the circuit. The choice of DAC IC will depend on several factors, including the required resolution, output voltage range, and communication interface.
For example, a commonly used DAC is the MCP4725, which is a 12-bit DAC that communicates via the I2C protocol. It allows for easy interfacing with the HCS12 microcontroller, enabling the microcontroller to send digital signals to the DAC, which then converts these signals into corresponding analog voltages.
The typical connection scheme involves connecting the I2C data (SDA) and clock (SCL) lines from the HCS12 to the corresponding pins on the MCP4725. Additionally, the power supply pins of the DAC must be connected to the appropriate voltage levels, typically 3.3V or 5V, depending on the specifications of both the microcontroller and the DAC.
Furthermore, a bypass capacitor may be placed close to the power pins of the DAC to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation. The output of the DAC can be connected to an analog load, such as an audio amplifier or a control circuit, depending on the application requirements.
In summary, while the HCS12 microcontroller lacks built-in DAC capabilities, it can effectively utilize external DAC ICs to achieve desired analog output functionality, thereby enhancing its versatility in various electronic applications.The HCS12 series of microcontrollers does not support dedicated internal digital-to-analogue conversion hardware, and thus external hardware, perhaps in the form of a digital-to-analogue conversion IC. 🔗 External reference
To implement digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) in systems utilizing the HCS12 microcontroller, an external DAC IC must be integrated into the circuit. The choice of DAC IC will depend on several factors, including the required resolution, output voltage range, and communication interface.
For example, a commonly used DAC is the MCP4725, which is a 12-bit DAC that communicates via the I2C protocol. It allows for easy interfacing with the HCS12 microcontroller, enabling the microcontroller to send digital signals to the DAC, which then converts these signals into corresponding analog voltages.
The typical connection scheme involves connecting the I2C data (SDA) and clock (SCL) lines from the HCS12 to the corresponding pins on the MCP4725. Additionally, the power supply pins of the DAC must be connected to the appropriate voltage levels, typically 3.3V or 5V, depending on the specifications of both the microcontroller and the DAC.
Furthermore, a bypass capacitor may be placed close to the power pins of the DAC to filter out any noise and ensure stable operation. The output of the DAC can be connected to an analog load, such as an audio amplifier or a control circuit, depending on the application requirements.
In summary, while the HCS12 microcontroller lacks built-in DAC capabilities, it can effectively utilize external DAC ICs to achieve desired analog output functionality, thereby enhancing its versatility in various electronic applications.The HCS12 series of microcontrollers does not support dedicated internal digital-to-analogue conversion hardware, and thus external hardware, perhaps in the form of a digital-to-analogue conversion IC. 🔗 External reference