Audio Voice-Over Circuit using LM380
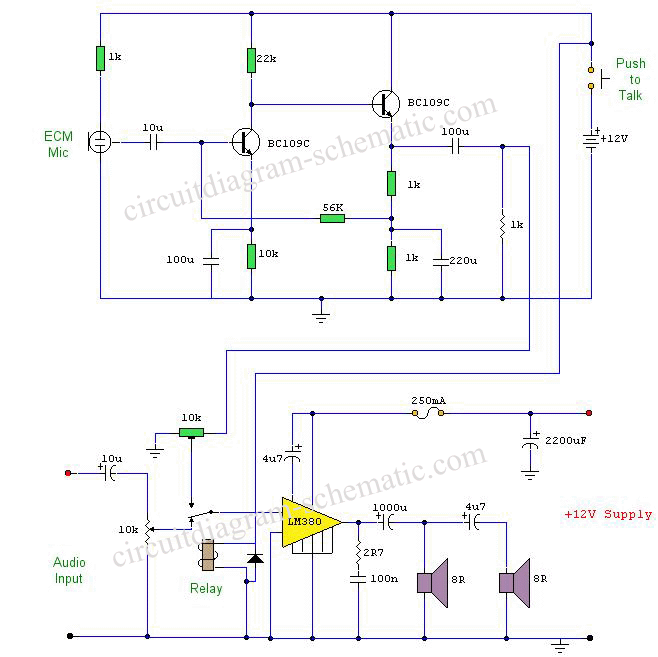
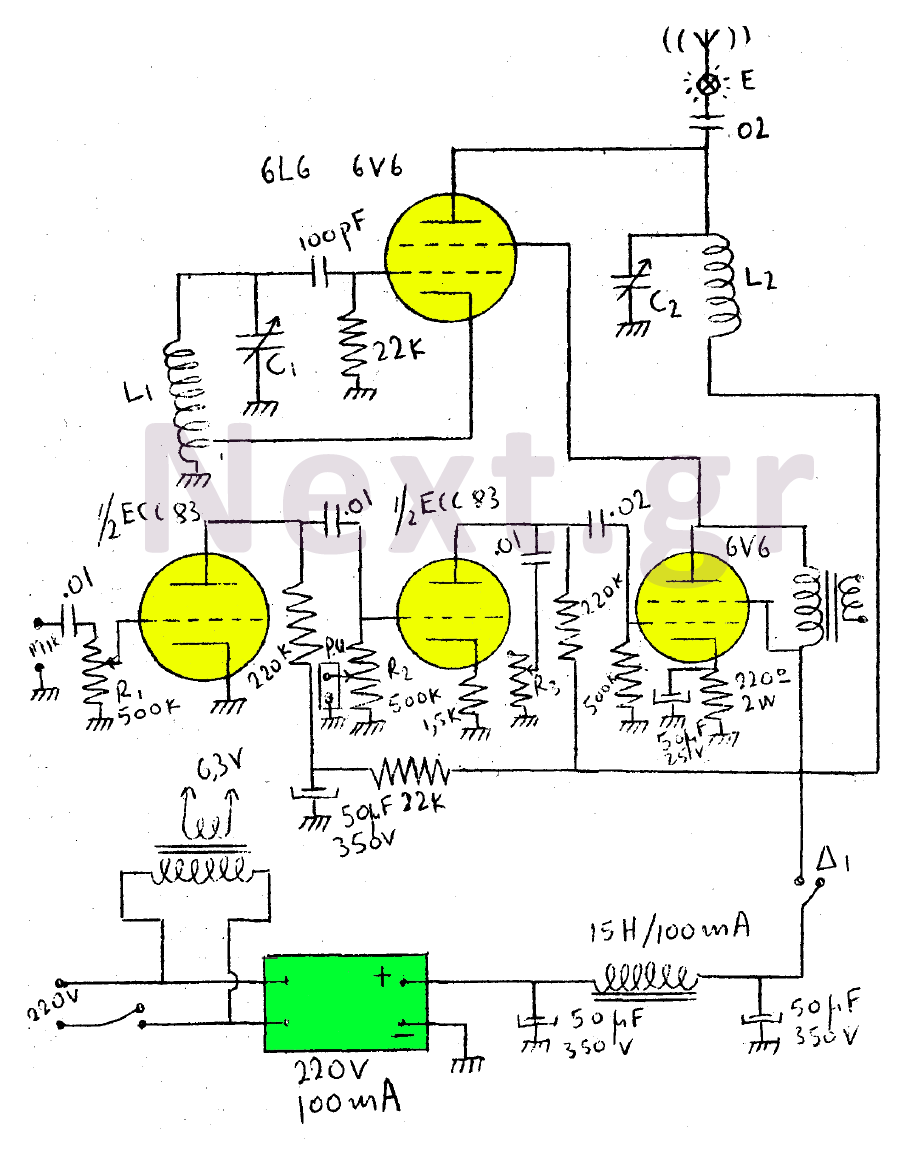
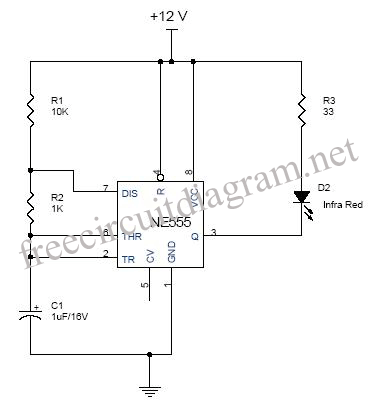
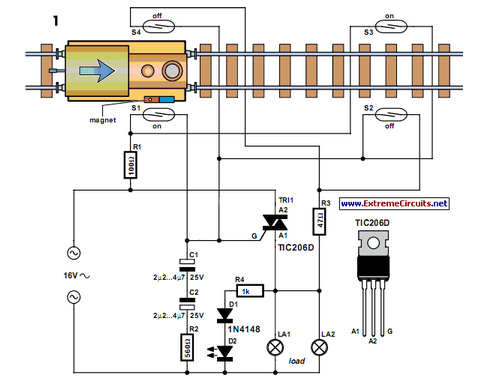
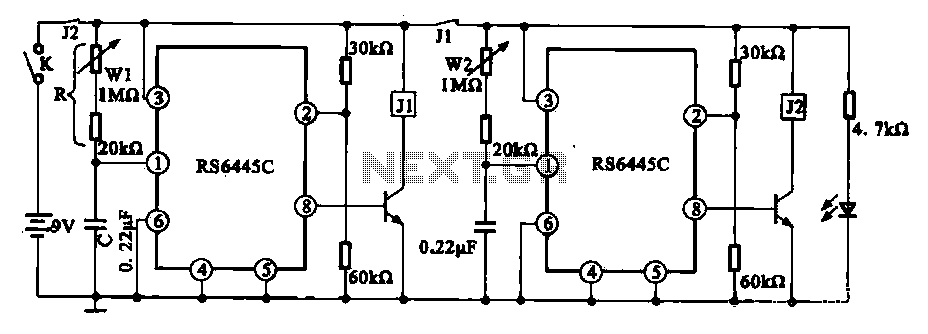
This circuit diagram represents a microphone preamplifier, specifically designed to prioritize voice signals over other audio inputs. In its basic configuration, the circuit includes a microphone unit and a change-over switch that connects to an amplifier. When the push-to-talk switch is activated, the output from the microphone takes precedence over the audio signal from the amplifier.
The microphone preamp circuit is essential in applications where clear voice communication is critical, such as in intercom systems, public address systems, and two-way radios. The circuit typically consists of a microphone, an operational amplifier (op-amp), resistors, capacitors, and a push-to-talk (PTT) switch.
In operation, the microphone captures sound waves and converts them into an electrical signal. This weak signal is then fed into the op-amp, which amplifies it to a usable level. The change-over switch allows the user to select between the microphone input and other audio sources. When the PTT switch is pressed, it activates the microphone circuit, ensuring that the voice signal is prioritized and clearly transmitted over any background audio.
The design may include additional components such as low-pass filters to eliminate high-frequency noise and ensure a clean audio output. Furthermore, careful consideration must be given to the power supply requirements of the op-amp to maintain optimal performance. Overall, this microphone preamp circuit is a vital component in achieving effective voice communication in various electronic systems.This circuit is a circuit diagram of a microphone preamp and circuits (voice circuit) has priority over any other audio signal. In its simplest form, the voice-over only the microphone unit and the change-over switch eating an amplifier, the output of the microphone has priority over the amplifiers audio signal when the push-to-talk switch is pressed
🔗 External reference
The microphone preamp circuit is essential in applications where clear voice communication is critical, such as in intercom systems, public address systems, and two-way radios. The circuit typically consists of a microphone, an operational amplifier (op-amp), resistors, capacitors, and a push-to-talk (PTT) switch.
In operation, the microphone captures sound waves and converts them into an electrical signal. This weak signal is then fed into the op-amp, which amplifies it to a usable level. The change-over switch allows the user to select between the microphone input and other audio sources. When the PTT switch is pressed, it activates the microphone circuit, ensuring that the voice signal is prioritized and clearly transmitted over any background audio.
The design may include additional components such as low-pass filters to eliminate high-frequency noise and ensure a clean audio output. Furthermore, careful consideration must be given to the power supply requirements of the op-amp to maintain optimal performance. Overall, this microphone preamp circuit is a vital component in achieving effective voice communication in various electronic systems.This circuit is a circuit diagram of a microphone preamp and circuits (voice circuit) has priority over any other audio signal. In its simplest form, the voice-over only the microphone unit and the change-over switch eating an amplifier, the output of the microphone has priority over the amplifiers audio signal when the push-to-talk switch is pressed
🔗 External reference