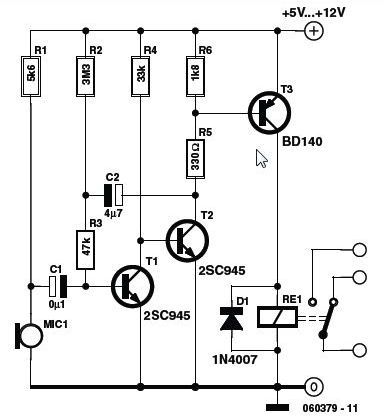
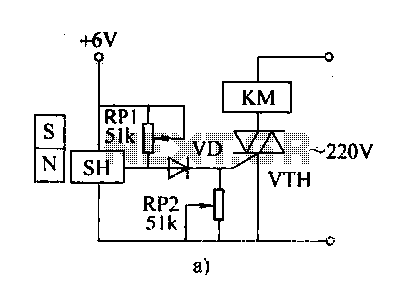
Automatic Brightness Switch
Driving the highway with your high-beam headlights can really increase your visibility, but can be a blinding hazard for other drivers. This simple circuit can be wired into your headlight switch to provide automatic switching between high and low beam headlights when there is oncoming traffic. It does this by sensing the lights of that traffic. In this way, you can drive safely with your high-beams on without blinding other drivers.
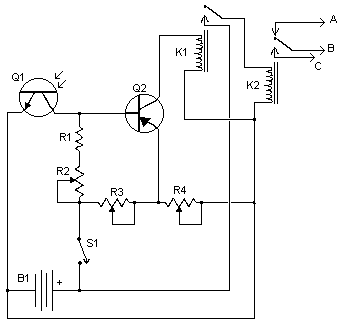
The described circuit functions as an automatic high-low beam headlight switch, enhancing driving safety by preventing glare to oncoming vehicles. The core components of this circuit typically include a light sensor (photoresistor), a comparator (operational amplifier), and a relay or transistor to switch the headlight beams.
The light sensor detects ambient light levels, particularly the headlights of oncoming vehicles. When the sensor detects a certain threshold of light intensity—indicating the presence of oncoming traffic—the comparator processes this input and activates the relay. The relay serves as a switch that toggles the headlights from high beam to low beam.
The circuit can be integrated into the vehicle's existing headlight switch wiring. When the driver engages the high beams, the circuit takes over the control based on the light sensor's readings. This automatic switching occurs without driver intervention, providing a seamless transition between high and low beams.
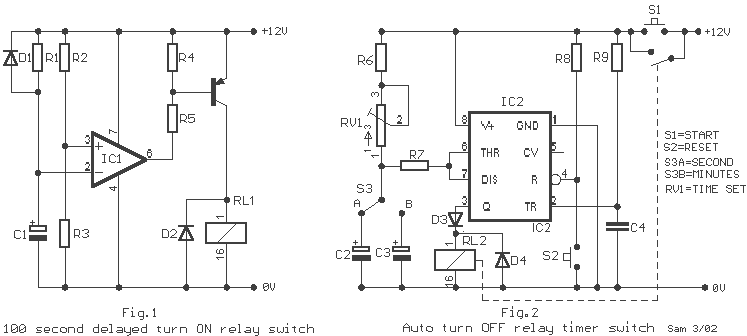
To ensure reliability, the circuit should include a time delay feature to prevent rapid switching in situations where the sensor may detect fleeting light sources, such as streetlights or reflective signs. This can be achieved using an RC (resistor-capacitor) timing circuit that introduces a delay before the relay is activated.
In summary, this automatic headlight switching circuit enhances road safety by allowing drivers to utilize high beams without the risk of blinding other drivers, thereby improving overall visibility during nighttime driving conditions. Proper design and implementation of this circuit can significantly contribute to safer driving practices.Driving the highway with your high-beam headlights can really increase your visibility, but can be a blinding hazard for other drivers. This simple circuit can be wired into your headlight switch to provide automatic switching between high and low beam headlights when there is oncoming traffic.
It does this by sensing the lights of that traffic. In this way, you can drive safely with your high-beams on without blinding other drivers. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as an automatic high-low beam headlight switch, enhancing driving safety by preventing glare to oncoming vehicles. The core components of this circuit typically include a light sensor (photoresistor), a comparator (operational amplifier), and a relay or transistor to switch the headlight beams.
The light sensor detects ambient light levels, particularly the headlights of oncoming vehicles. When the sensor detects a certain threshold of light intensity—indicating the presence of oncoming traffic—the comparator processes this input and activates the relay. The relay serves as a switch that toggles the headlights from high beam to low beam.
The circuit can be integrated into the vehicle's existing headlight switch wiring. When the driver engages the high beams, the circuit takes over the control based on the light sensor's readings. This automatic switching occurs without driver intervention, providing a seamless transition between high and low beams.
To ensure reliability, the circuit should include a time delay feature to prevent rapid switching in situations where the sensor may detect fleeting light sources, such as streetlights or reflective signs. This can be achieved using an RC (resistor-capacitor) timing circuit that introduces a delay before the relay is activated.
In summary, this automatic headlight switching circuit enhances road safety by allowing drivers to utilize high beams without the risk of blinding other drivers, thereby improving overall visibility during nighttime driving conditions. Proper design and implementation of this circuit can significantly contribute to safer driving practices.Driving the highway with your high-beam headlights can really increase your visibility, but can be a blinding hazard for other drivers. This simple circuit can be wired into your headlight switch to provide automatic switching between high and low beam headlights when there is oncoming traffic.
It does this by sensing the lights of that traffic. In this way, you can drive safely with your high-beams on without blinding other drivers. 🔗 External reference