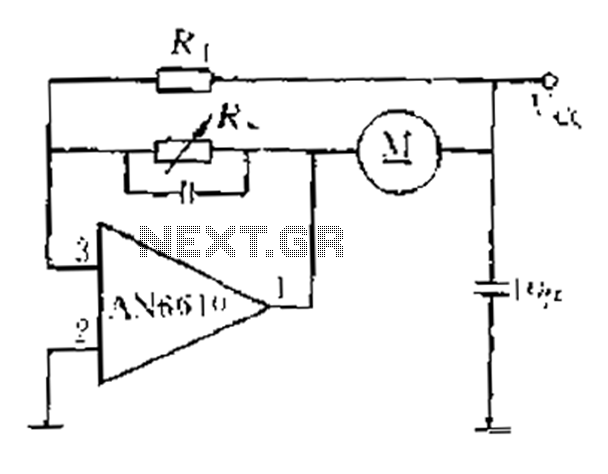
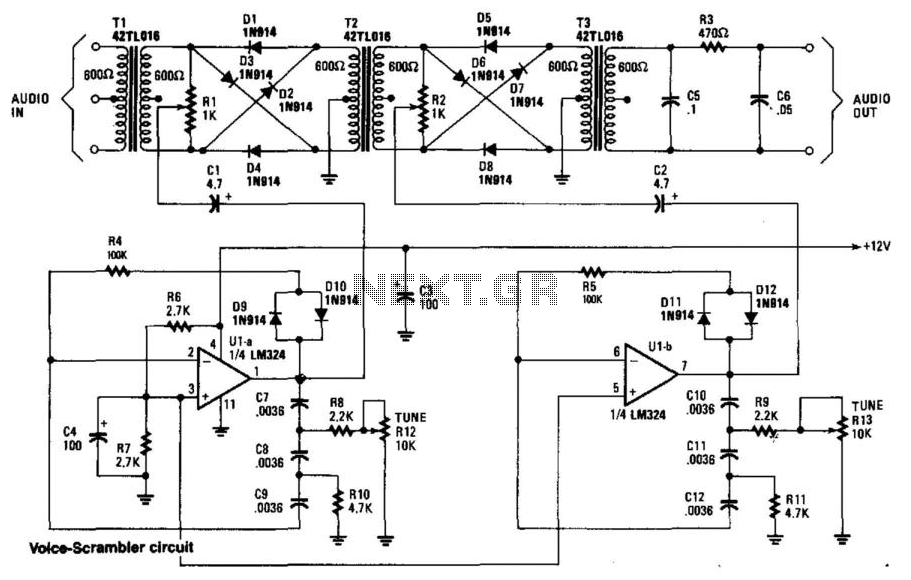
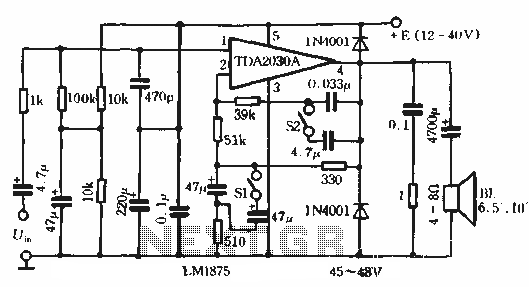
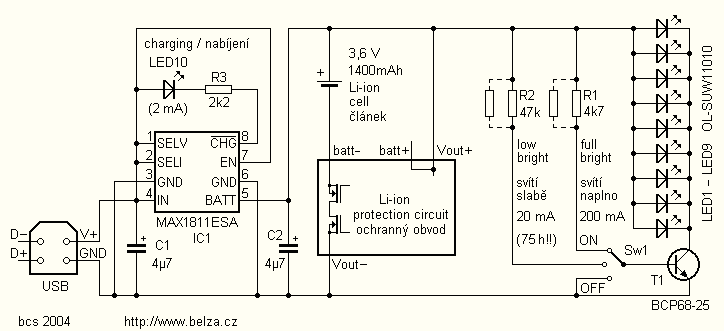
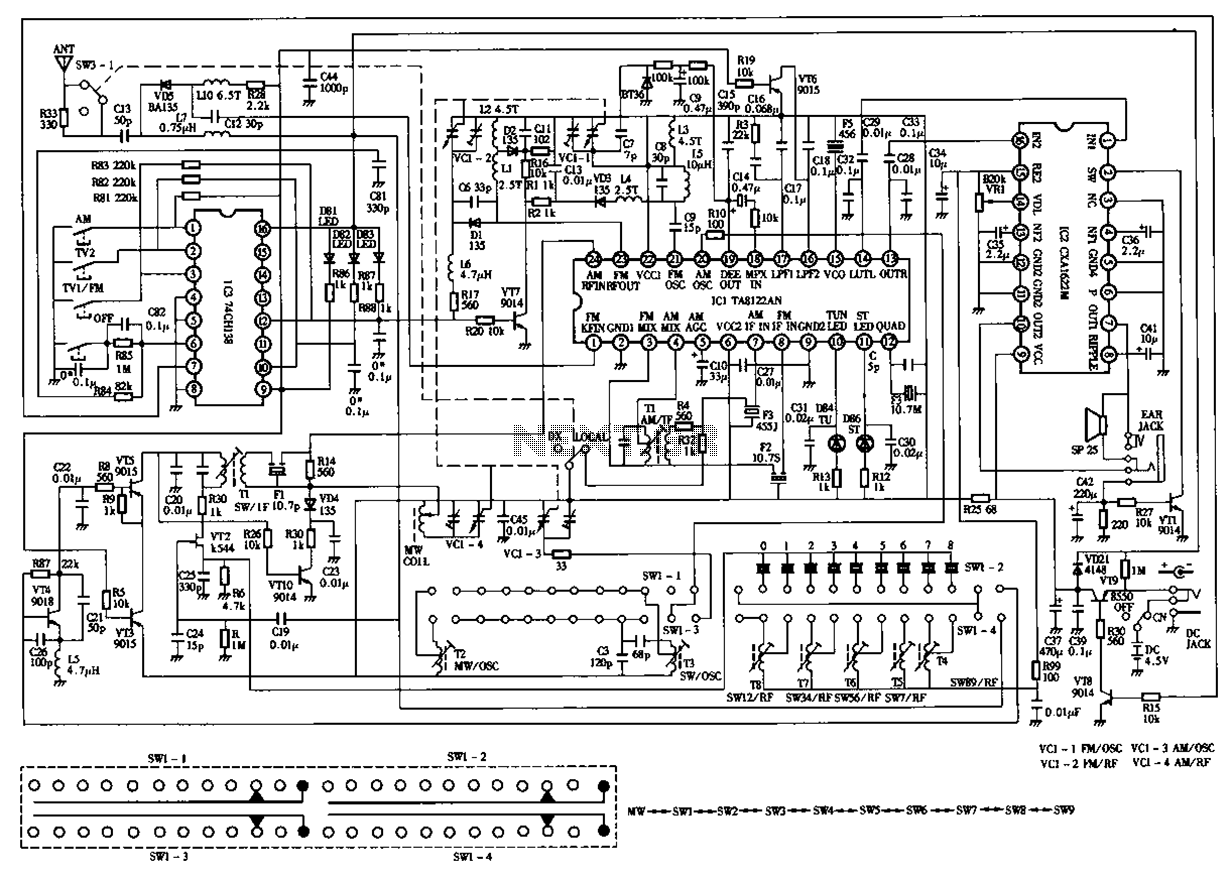
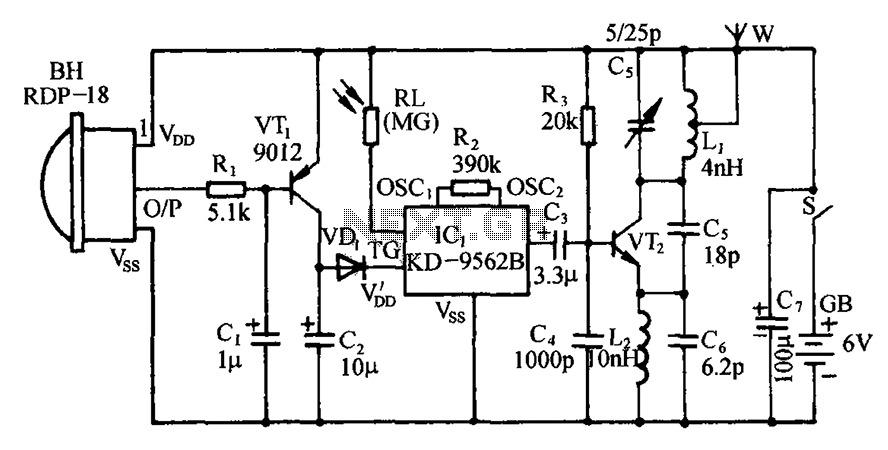
Balanced mixer circuit consisting of two dual-gate field effect transistor formed
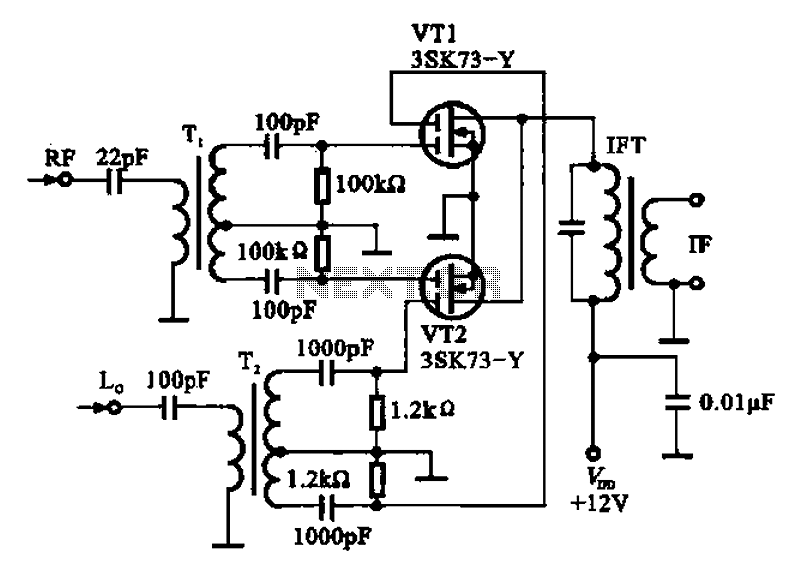
A balanced mixer circuit is illustrated using two dual-gate field effect transistors (FETs). The RF signal is coupled to the gates of these transistors through an input signal transformer (T1). Additionally, a local oscillation signal is introduced to the gates of the two FETs via a coupling transformer (T2). The drain outputs of the two field-effect transistors (VT1, VT2) are connected to an intermediate frequency transformer (IFT), which selects the 10.7 MHz intermediate frequency (IF) signal output.
The balanced mixer circuit employs two dual-gate field effect transistors to achieve effective mixing of signals. The RF signal is first fed into the circuit through an input transformer (T1), which ensures proper impedance matching and signal integrity. Each FET has two gates, allowing for improved control over the mixing process and enhanced linearity.
The local oscillation signal, which is crucial for the mixing operation, is coupled to the gates of the FETs using a second transformer (T2). This coupling ensures that the oscillation signal is appropriately phase-aligned with the RF input, facilitating optimal signal processing. The advantage of using dual-gate FETs in this configuration is the ability to handle higher frequency signals while minimizing distortion and improving overall performance.
The drain outputs of the FETs, labeled as VT1 and VT2, are connected to an intermediate frequency transformer (IFT). This transformer is responsible for selecting and amplifying the desired intermediate frequency signal, which in this design is set to 10.7 MHz. The choice of this frequency is common in various RF applications, particularly in FM demodulation and communications systems.
The balanced mixer configuration enhances signal isolation and minimizes interference, making it suitable for applications where high fidelity and low noise are critical. The circuit's design allows for efficient signal processing, ensuring that the resulting output maintains the integrity of the original RF signal while providing the necessary frequency conversion. Balanced mixer circuit is shown by the two dual-gate field effect transistor. RF signal by the input signal transformer Tl effect transistors coupled to the gate of the two, th e local oscillation signal by the coupling transformer Tz added two additional field effect transistor gates, two field-effect transistors (VT1, VT2) drain pole outputs the intermediate frequency transformer din (IFT), select the 10.7 MHz IF signal output.
The balanced mixer circuit employs two dual-gate field effect transistors to achieve effective mixing of signals. The RF signal is first fed into the circuit through an input transformer (T1), which ensures proper impedance matching and signal integrity. Each FET has two gates, allowing for improved control over the mixing process and enhanced linearity.
The local oscillation signal, which is crucial for the mixing operation, is coupled to the gates of the FETs using a second transformer (T2). This coupling ensures that the oscillation signal is appropriately phase-aligned with the RF input, facilitating optimal signal processing. The advantage of using dual-gate FETs in this configuration is the ability to handle higher frequency signals while minimizing distortion and improving overall performance.
The drain outputs of the FETs, labeled as VT1 and VT2, are connected to an intermediate frequency transformer (IFT). This transformer is responsible for selecting and amplifying the desired intermediate frequency signal, which in this design is set to 10.7 MHz. The choice of this frequency is common in various RF applications, particularly in FM demodulation and communications systems.
The balanced mixer configuration enhances signal isolation and minimizes interference, making it suitable for applications where high fidelity and low noise are critical. The circuit's design allows for efficient signal processing, ensuring that the resulting output maintains the integrity of the original RF signal while providing the necessary frequency conversion. Balanced mixer circuit is shown by the two dual-gate field effect transistor. RF signal by the input signal transformer Tl effect transistors coupled to the gate of the two, th e local oscillation signal by the coupling transformer Tz added two additional field effect transistor gates, two field-effect transistors (VT1, VT2) drain pole outputs the intermediate frequency transformer din (IFT), select the 10.7 MHz IF signal output.