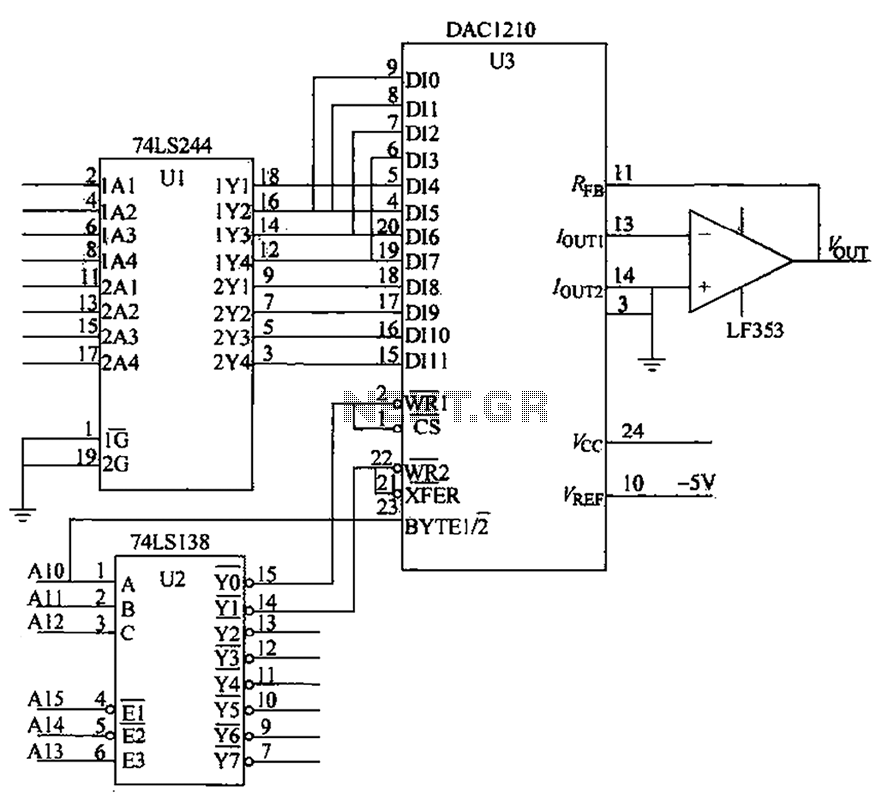
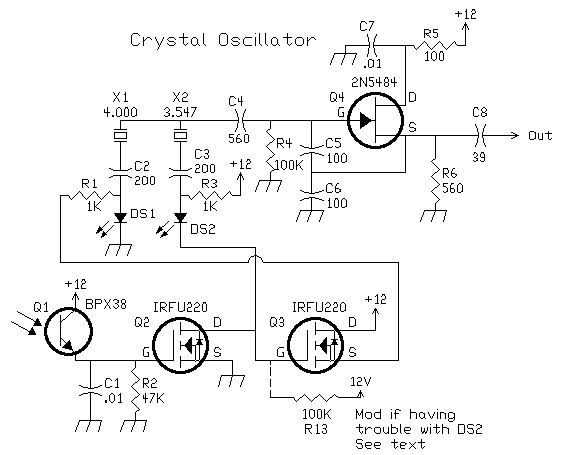
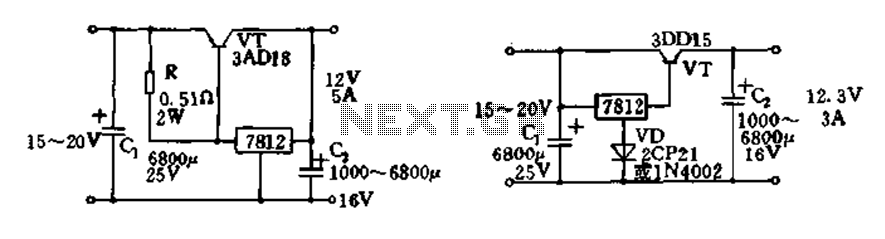
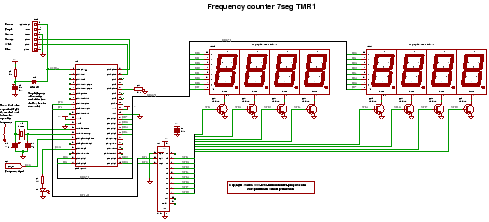
Voice Scrambler/Disguiser Circuit
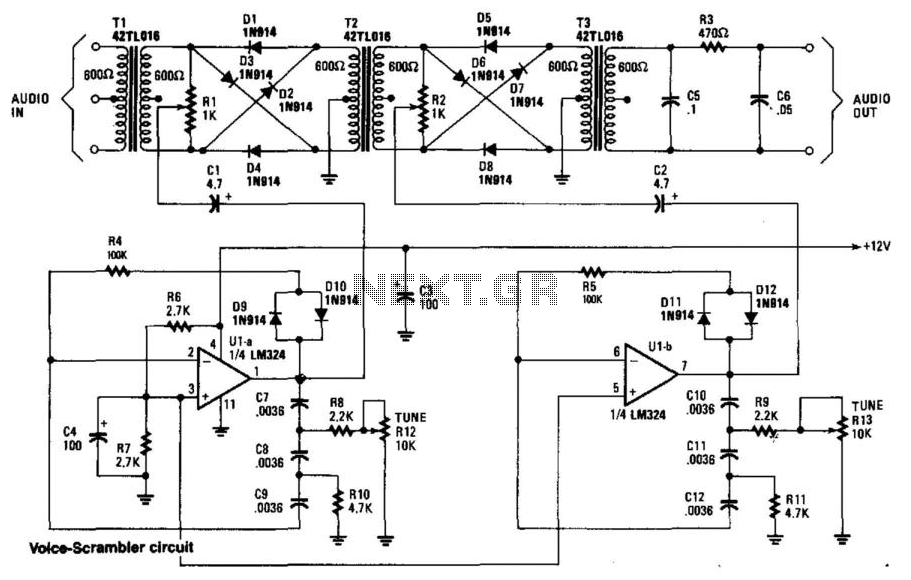
This circuit employs two balanced modulators to generate a Double Sideband (DSB) signal, followed by the reinsertion of a carrier frequency that differs from the original. This alteration leads to distortion of the input signal. While a voice signal can be recognized with this circuit, the original speaker's voice may not be distinguishable even with proper adjustments. Two LM324 operational amplifiers function as oscillators, tunable from 2 to 3.5 kHz, with the frequency settings determined by resistors R12 and R13. T2 and T3 are 600 CT/600 audio transformers, which can be sourced from Mouser Electronics, Inc.
This circuit design utilizes two balanced modulators to create a Double Sideband (DSB) amplitude modulation signal. The DSB signal is characterized by its two sidebands, which carry the same information as the original input signal but without the carrier frequency. The reinsertion of a carrier at a different frequency introduces a level of distortion to the original signal, which can alter the intelligibility of the transmitted voice signal.
In this configuration, the LM324 operational amplifiers serve a dual purpose. They are configured as oscillators, allowing for frequency tuning within a range of 2 kHz to 3.5 kHz. The tuning is achieved through the adjustment of resistors R12 and R13, which set the frequency of oscillation. The choice of the LM324 is significant due to its versatility and ability to drive the required signal levels for modulation.
The circuit also incorporates two 600 CT/600 audio transformers, designated as T2 and T3. These transformers are essential for impedance matching and signal coupling, ensuring that the modulated signal can be efficiently transmitted without significant loss. The transformers are readily available from suppliers such as Mouser Electronics, Inc., making them accessible for implementation in similar circuit designs.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a method for modulating audio signals while demonstrating the effects of frequency manipulation on signal clarity and intelligibility. The design highlights the importance of component selection and configuration in achieving desired audio processing outcomes. This circuit uses two balanced modulators to produce a DSB signal and then reinsert the carrier, except t he carrier now has a different frequency. This causes an input signal to be distorted. A voice signal will be recognizable with this circuit, but the original speakers" voice will not be identifiable with correct adjustments. Two LM324 op amps act as oscillators that are tuneable from 2 to 3.5 kHz. The frequencies are set with R12 and R13., T2, and T3 are 600 CT/600 audio transformers—available from Mouser Electronics, Inc.
This circuit design utilizes two balanced modulators to create a Double Sideband (DSB) amplitude modulation signal. The DSB signal is characterized by its two sidebands, which carry the same information as the original input signal but without the carrier frequency. The reinsertion of a carrier at a different frequency introduces a level of distortion to the original signal, which can alter the intelligibility of the transmitted voice signal.
In this configuration, the LM324 operational amplifiers serve a dual purpose. They are configured as oscillators, allowing for frequency tuning within a range of 2 kHz to 3.5 kHz. The tuning is achieved through the adjustment of resistors R12 and R13, which set the frequency of oscillation. The choice of the LM324 is significant due to its versatility and ability to drive the required signal levels for modulation.
The circuit also incorporates two 600 CT/600 audio transformers, designated as T2 and T3. These transformers are essential for impedance matching and signal coupling, ensuring that the modulated signal can be efficiently transmitted without significant loss. The transformers are readily available from suppliers such as Mouser Electronics, Inc., making them accessible for implementation in similar circuit designs.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a method for modulating audio signals while demonstrating the effects of frequency manipulation on signal clarity and intelligibility. The design highlights the importance of component selection and configuration in achieving desired audio processing outcomes. This circuit uses two balanced modulators to produce a DSB signal and then reinsert the carrier, except t he carrier now has a different frequency. This causes an input signal to be distorted. A voice signal will be recognizable with this circuit, but the original speakers" voice will not be identifiable with correct adjustments. Two LM324 op amps act as oscillators that are tuneable from 2 to 3.5 kHz. The frequencies are set with R12 and R13., T2, and T3 are 600 CT/600 audio transformers—available from Mouser Electronics, Inc.