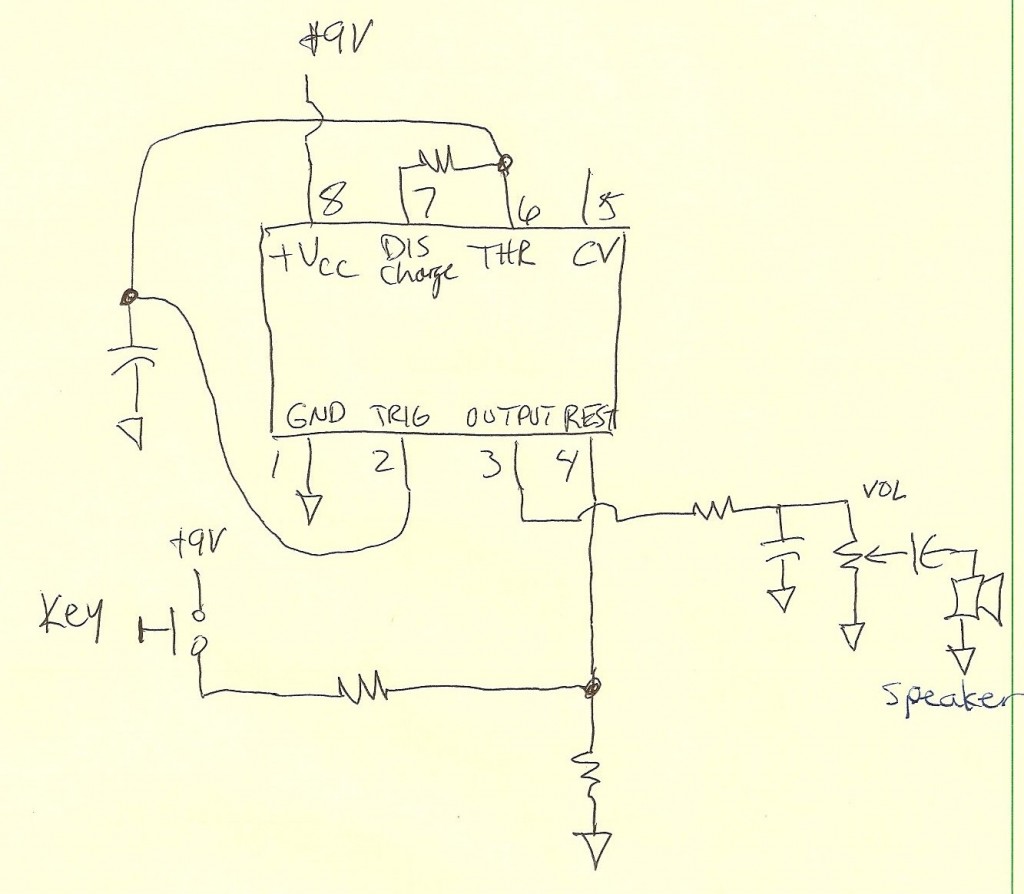
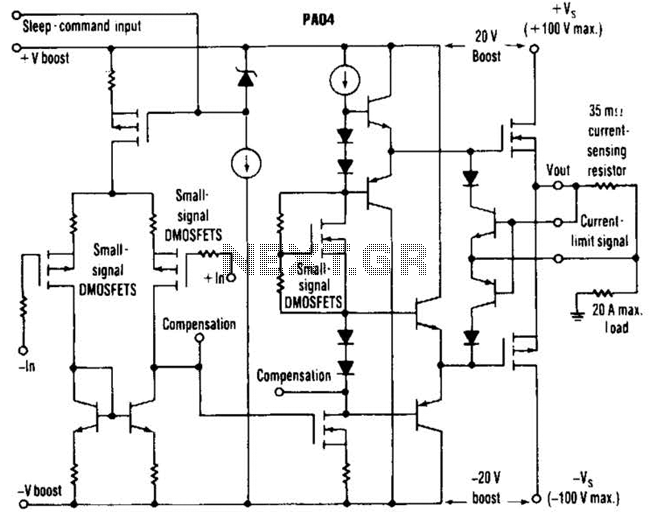
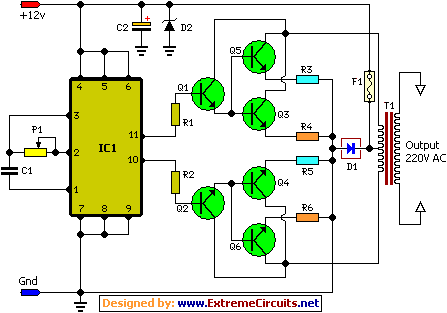
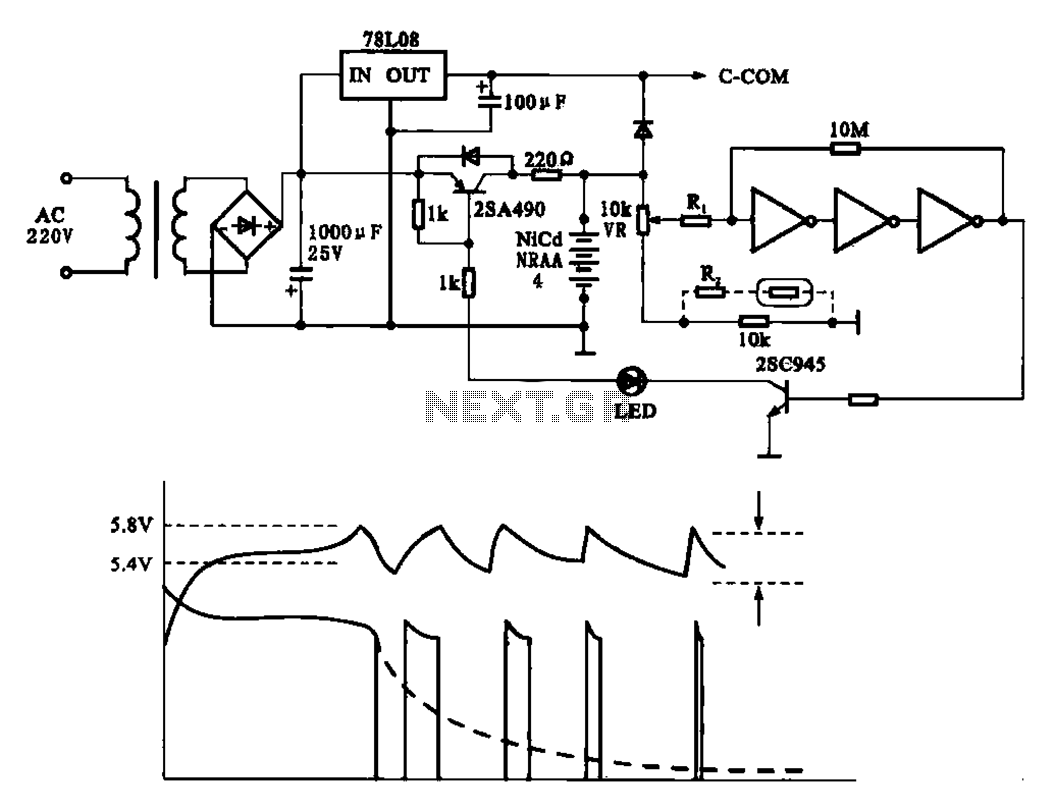
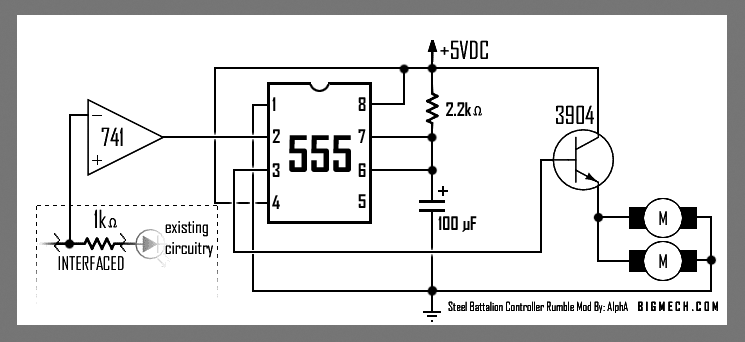
Band decoder circuit diagram
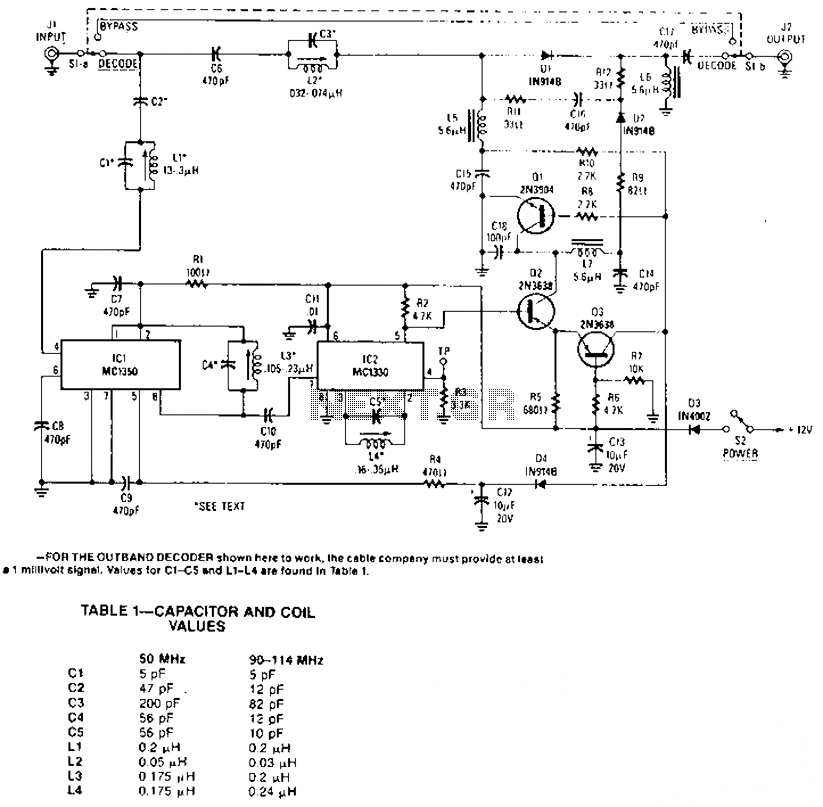
The circuit amplifier and attenuator control video detector consists of a composition for the synchronization channel. The synchronization interval is where the gain circuit is increased.
The described circuit involves an amplifier and an attenuator that work together to control a video detector, specifically tailored for synchronization channels. In this configuration, the synchronization channel is crucial for maintaining the timing and integrity of the video signal. The amplifier is responsible for boosting the signal strength, while the attenuator adjusts the signal level to prevent distortion or saturation in the video processing stage.
Within the synchronization interval, the gain circuit plays a pivotal role. It is designed to dynamically adjust the amplification based on the incoming signal's characteristics. This ensures that the video signal remains within optimal levels for processing, particularly during periods of high activity or signal fluctuations. By increasing the gain during these intervals, the circuit enhances the clarity and reliability of the synchronization signal, which is essential for proper video decoding and display.
In practical applications, this circuit can be integrated into various video processing systems, including television receivers, video conferencing equipment, and broadcast transmission systems. The design should incorporate feedback mechanisms to monitor the output and adjust the gain accordingly, ensuring consistent performance across different operating conditions. Additionally, careful selection of components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors is necessary to achieve the desired frequency response and signal integrity.
Overall, this amplifier and attenuator configuration is critical for effective video signal management, ensuring that synchronization is maintained and that the resultant video output is of high quality.The circuit amplifier and an attenuator control video detector consists of a composition for synchronization channel, the synchronization interval, the gain circuit is increased.
The described circuit involves an amplifier and an attenuator that work together to control a video detector, specifically tailored for synchronization channels. In this configuration, the synchronization channel is crucial for maintaining the timing and integrity of the video signal. The amplifier is responsible for boosting the signal strength, while the attenuator adjusts the signal level to prevent distortion or saturation in the video processing stage.
Within the synchronization interval, the gain circuit plays a pivotal role. It is designed to dynamically adjust the amplification based on the incoming signal's characteristics. This ensures that the video signal remains within optimal levels for processing, particularly during periods of high activity or signal fluctuations. By increasing the gain during these intervals, the circuit enhances the clarity and reliability of the synchronization signal, which is essential for proper video decoding and display.
In practical applications, this circuit can be integrated into various video processing systems, including television receivers, video conferencing equipment, and broadcast transmission systems. The design should incorporate feedback mechanisms to monitor the output and adjust the gain accordingly, ensuring consistent performance across different operating conditions. Additionally, careful selection of components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors is necessary to achieve the desired frequency response and signal integrity.
Overall, this amplifier and attenuator configuration is critical for effective video signal management, ensuring that synchronization is maintained and that the resultant video output is of high quality.The circuit amplifier and an attenuator control video detector consists of a composition for synchronization channel, the synchronization interval, the gain circuit is increased.