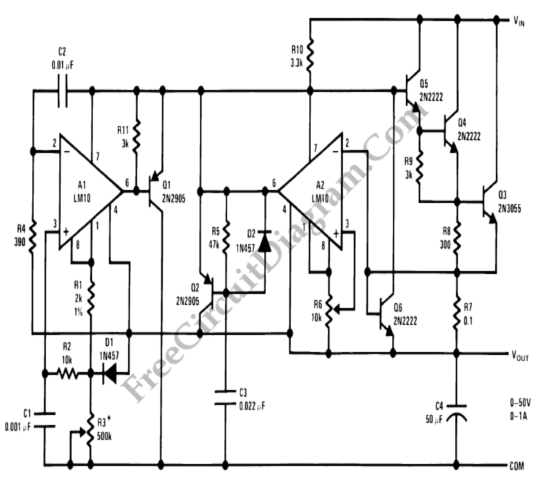
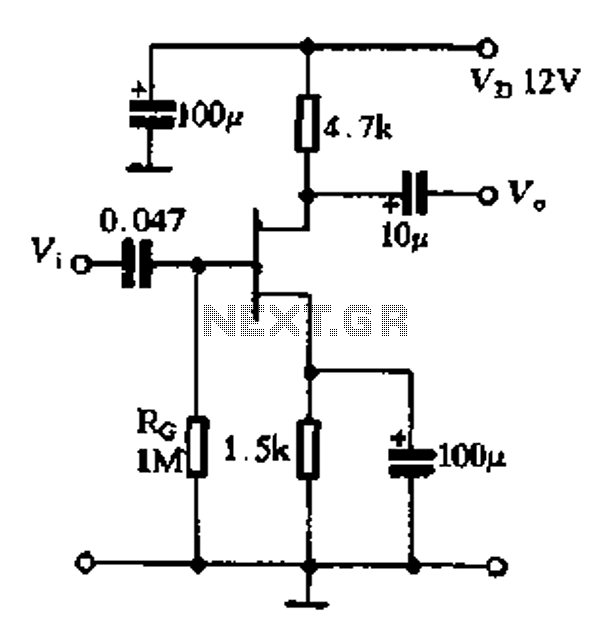
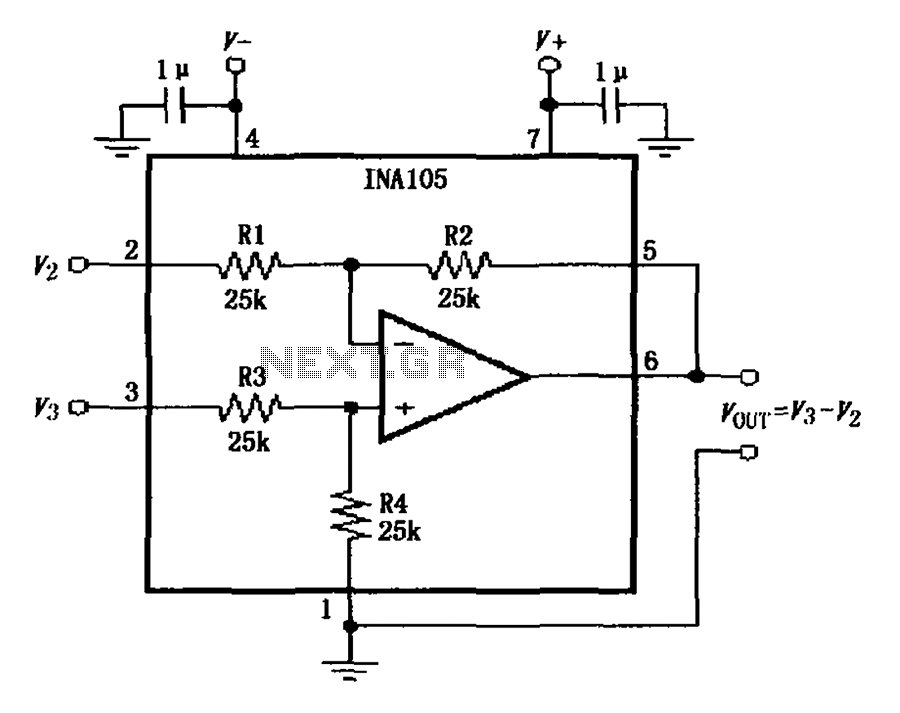
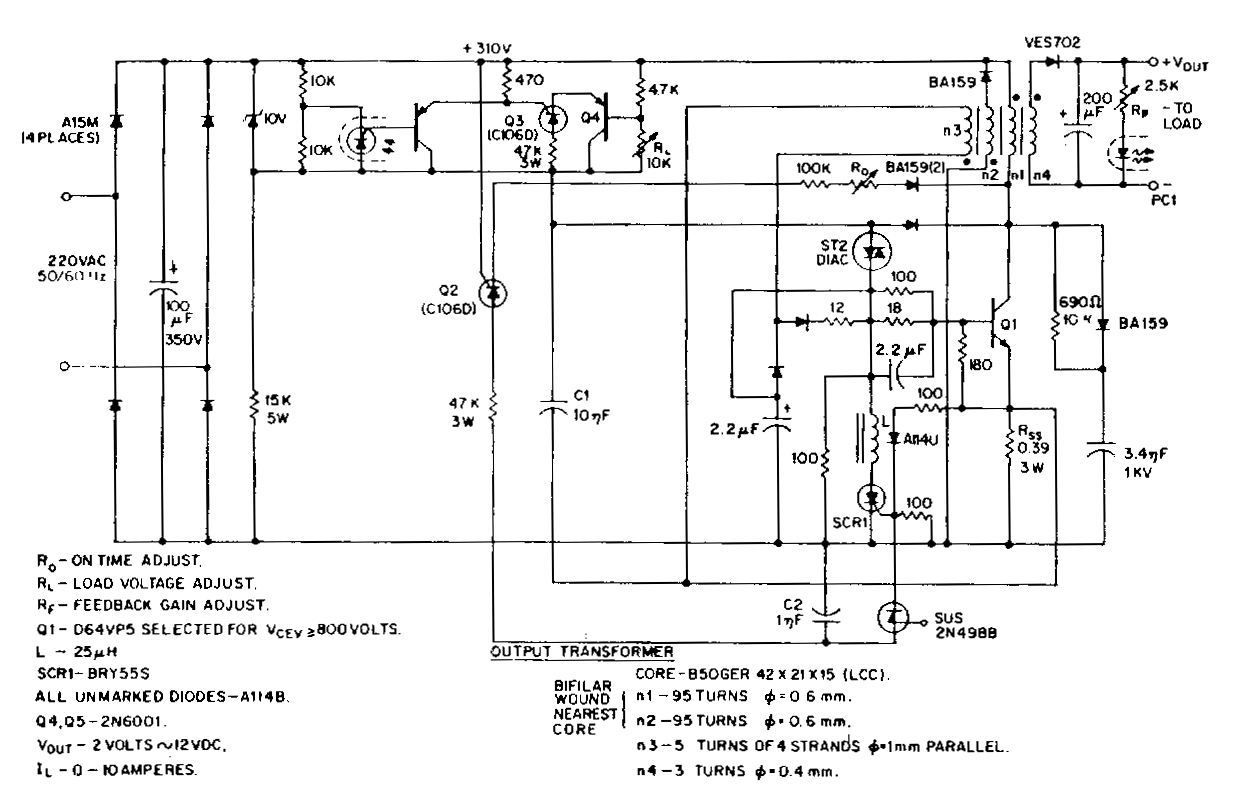
Basic Flash Memory Programming Voltage Supply
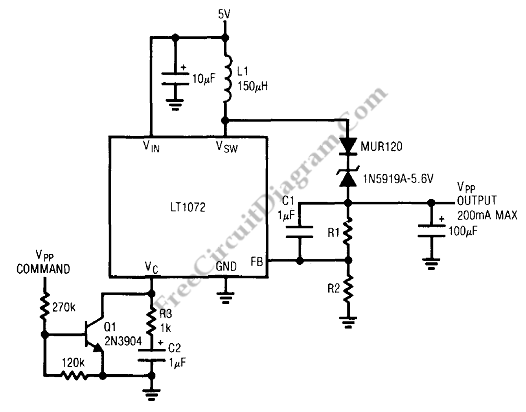
This is a basic flash memory programming voltage supply circuit. This circuit utilizes the LT1072 switching regulator to generate high voltage by driving the inductor L1 and resistor R2.
The basic flash memory programming voltage supply circuit is designed to provide the necessary high voltage for programming flash memory devices. The core component of this circuit is the LT1072, a high-efficiency switching regulator that is capable of stepping up low input voltages to higher levels required for programming operations.
In this configuration, the LT1072 operates in a boost converter mode. When the circuit is powered on, the LT1072 begins to switch on and off rapidly, controlling the current flow through the inductor L1. As the inductor stores energy during the "on" phase, it generates a magnetic field. When the LT1072 switches to the "off" phase, the magnetic field collapses, and the energy stored in the inductor is released. This energy transfer results in a higher voltage output, which is essential for the flash memory programming process.
Resistor R2 plays a crucial role in regulating the output voltage level. By selecting an appropriate resistance value, R2 helps to determine the output voltage that will be delivered to the flash memory device. This output voltage needs to be carefully controlled to prevent damage to the memory components while ensuring reliable programming.
Additional components may include input and output capacitors to stabilize the voltage levels and filter out any noise that could affect the performance of the circuit. A diode may also be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, which could potentially damage the LT1072 or other components in the circuit.
Overall, this flash memory programming voltage supply circuit is a vital tool for applications requiring high voltage for programming flash memory devices, ensuring efficient and safe operation during the programming process.This is a Basic Flash Memory Programming Voltage Supply circuit. This circuit uses LT1072 switching regulator to generate high voltage by driving the L1. R2 and. 🔗 External reference
The basic flash memory programming voltage supply circuit is designed to provide the necessary high voltage for programming flash memory devices. The core component of this circuit is the LT1072, a high-efficiency switching regulator that is capable of stepping up low input voltages to higher levels required for programming operations.
In this configuration, the LT1072 operates in a boost converter mode. When the circuit is powered on, the LT1072 begins to switch on and off rapidly, controlling the current flow through the inductor L1. As the inductor stores energy during the "on" phase, it generates a magnetic field. When the LT1072 switches to the "off" phase, the magnetic field collapses, and the energy stored in the inductor is released. This energy transfer results in a higher voltage output, which is essential for the flash memory programming process.
Resistor R2 plays a crucial role in regulating the output voltage level. By selecting an appropriate resistance value, R2 helps to determine the output voltage that will be delivered to the flash memory device. This output voltage needs to be carefully controlled to prevent damage to the memory components while ensuring reliable programming.
Additional components may include input and output capacitors to stabilize the voltage levels and filter out any noise that could affect the performance of the circuit. A diode may also be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, which could potentially damage the LT1072 or other components in the circuit.
Overall, this flash memory programming voltage supply circuit is a vital tool for applications requiring high voltage for programming flash memory devices, ensuring efficient and safe operation during the programming process.This is a Basic Flash Memory Programming Voltage Supply circuit. This circuit uses LT1072 switching regulator to generate high voltage by driving the L1. R2 and. 🔗 External reference