Common emitter amplifier circuit resistance and capacitance coupled basic

Common emitter amplifier circuit with resistance and capacitance coupling.
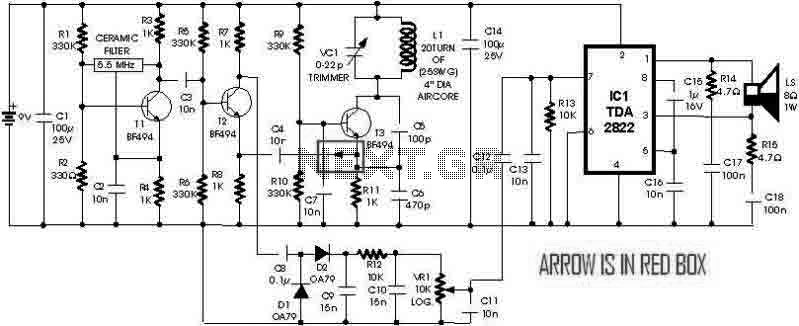
The common emitter amplifier circuit is a fundamental configuration in analog electronics, widely utilized for its ability to amplify voltage signals. This circuit employs a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) as the active component, where the emitter terminal is common to both the input and output circuits.
In this configuration, the input signal is applied between the base and emitter terminals, while the output is taken from the collector terminal. The use of resistors and capacitors in this circuit is crucial for establishing the desired operating point and frequency response.
Typically, the circuit includes a biasing network composed of resistors that set the DC operating point of the transistor, ensuring that it remains in the active region during operation. Capacitors are employed for coupling and bypassing purposes; coupling capacitors allow AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, and bypass capacitors enhance the gain by providing a low-impedance path to ground for AC signals at high frequencies.
The design parameters, such as resistor values and capacitor sizes, must be carefully selected based on the desired gain, input and output impedance, and frequency response. The common emitter amplifier is characterized by its high voltage gain, moderate input impedance, and low output impedance, making it suitable for various applications in audio and RF amplification.
In summary, the common emitter amplifier circuit, with its resistance and capacitance coupling, serves as a versatile and essential building block in electronic circuit design, providing effective signal amplification across a range of frequencies. Common emitter amplifier circuit resistance and capacitance coupled basic
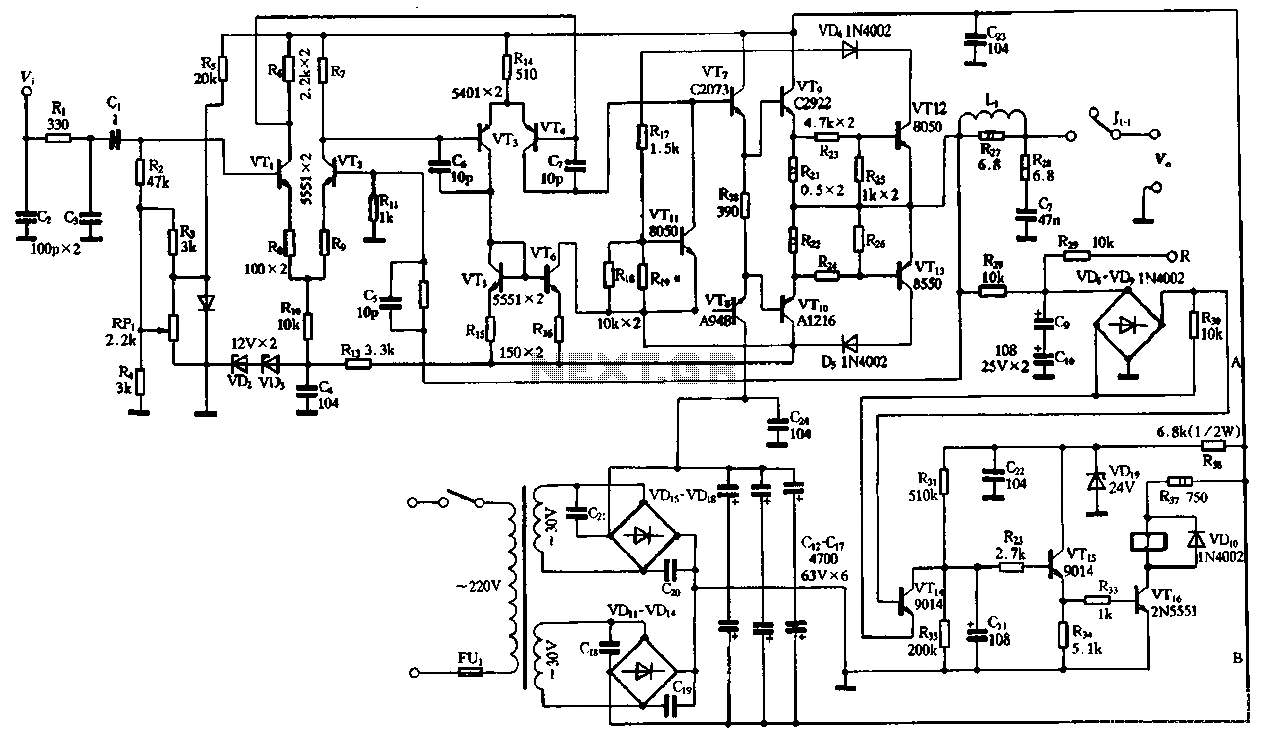
The common emitter amplifier circuit is a fundamental configuration in analog electronics, widely utilized for its ability to amplify voltage signals. This circuit employs a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) as the active component, where the emitter terminal is common to both the input and output circuits.
In this configuration, the input signal is applied between the base and emitter terminals, while the output is taken from the collector terminal. The use of resistors and capacitors in this circuit is crucial for establishing the desired operating point and frequency response.
Typically, the circuit includes a biasing network composed of resistors that set the DC operating point of the transistor, ensuring that it remains in the active region during operation. Capacitors are employed for coupling and bypassing purposes; coupling capacitors allow AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, and bypass capacitors enhance the gain by providing a low-impedance path to ground for AC signals at high frequencies.
The design parameters, such as resistor values and capacitor sizes, must be carefully selected based on the desired gain, input and output impedance, and frequency response. The common emitter amplifier is characterized by its high voltage gain, moderate input impedance, and low output impedance, making it suitable for various applications in audio and RF amplification.
In summary, the common emitter amplifier circuit, with its resistance and capacitance coupling, serves as a versatile and essential building block in electronic circuit design, providing effective signal amplification across a range of frequencies. Common emitter amplifier circuit resistance and capacitance coupled basic