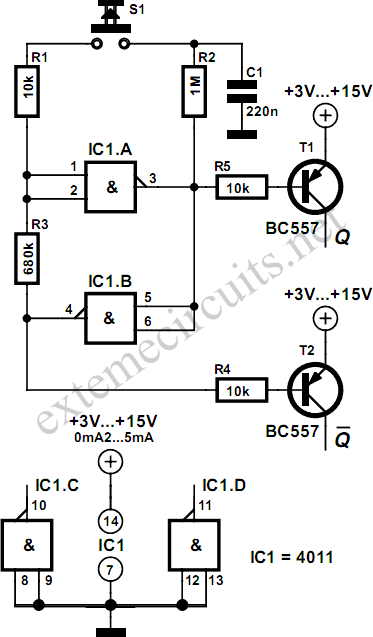
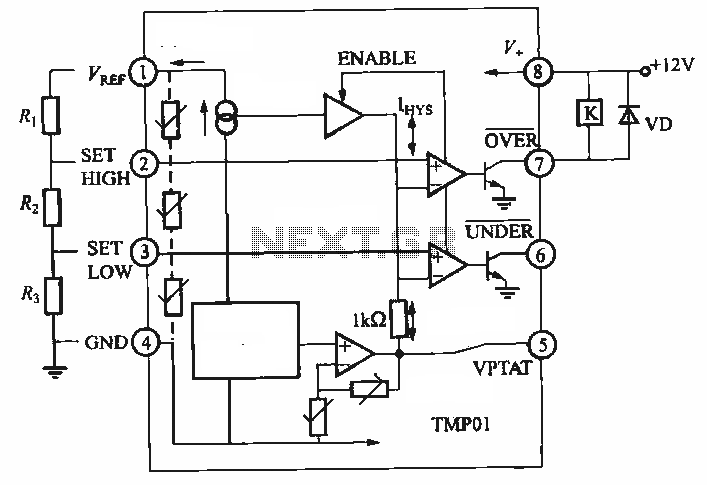
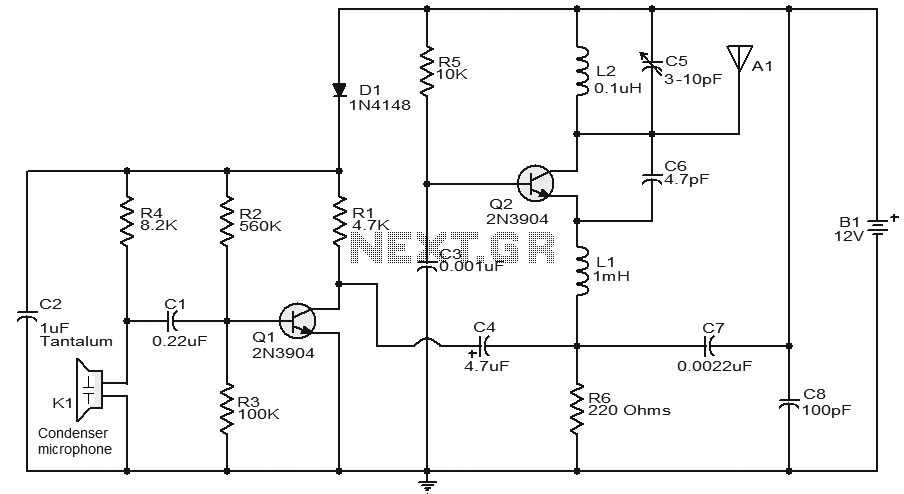
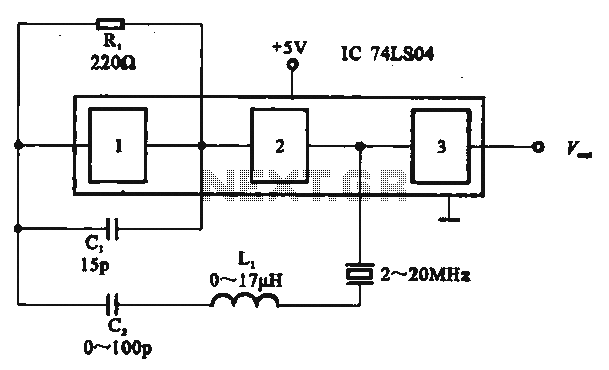
Basic Logic Gate with PNP Transistor
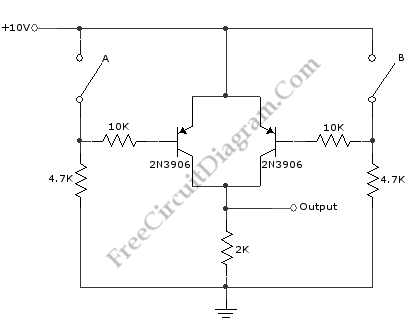
This schematic diagram illustrates a basic logic gate circuit. This PNP transistor circuit can function as either an OR gate or an AND gate, depending on the input states.
The described circuit employs PNP transistors to create a versatile logic gate configuration. In digital electronics, logic gates are fundamental building blocks used to perform logical operations on one or more binary inputs to produce a single binary output.
In this specific schematic, the PNP transistor can be configured to operate as an OR gate when the inputs are connected in such a way that if either input is activated (i.e., brought to a low state), the output will also be activated (high state). Conversely, when configured as an AND gate, the circuit will only output a high state when both inputs are in a low state.
The operation of the PNP transistor is based on the principle that it conducts when the base is at a lower potential than the emitter. Therefore, the arrangement of resistors and the connections to the inputs are critical to achieving the desired logical functionality.
The transistor's biasing must be carefully considered to ensure that the desired logic levels are correctly interpreted. Resistors may be used to limit the current flowing into the base of the transistor and to establish the necessary voltage levels for proper operation.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various digital systems, including simple calculators, alarm systems, and other devices requiring basic logical decision-making capabilities. The simplicity of the PNP transistor circuit allows for easy integration into larger systems while providing reliable performance.
Overall, this schematic serves as a foundational example of how PNP transistors can be employed in digital logic design, showcasing their versatility and importance in electronic circuit design.This schematic diagram shows a circuit of basic logic gate circuit. This PNP transistor circuit can act as OR gate or AND gate. If the input is closing of. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs PNP transistors to create a versatile logic gate configuration. In digital electronics, logic gates are fundamental building blocks used to perform logical operations on one or more binary inputs to produce a single binary output.
In this specific schematic, the PNP transistor can be configured to operate as an OR gate when the inputs are connected in such a way that if either input is activated (i.e., brought to a low state), the output will also be activated (high state). Conversely, when configured as an AND gate, the circuit will only output a high state when both inputs are in a low state.
The operation of the PNP transistor is based on the principle that it conducts when the base is at a lower potential than the emitter. Therefore, the arrangement of resistors and the connections to the inputs are critical to achieving the desired logical functionality.
The transistor's biasing must be carefully considered to ensure that the desired logic levels are correctly interpreted. Resistors may be used to limit the current flowing into the base of the transistor and to establish the necessary voltage levels for proper operation.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various digital systems, including simple calculators, alarm systems, and other devices requiring basic logical decision-making capabilities. The simplicity of the PNP transistor circuit allows for easy integration into larger systems while providing reliable performance.
Overall, this schematic serves as a foundational example of how PNP transistors can be employed in digital logic design, showcasing their versatility and importance in electronic circuit design.This schematic diagram shows a circuit of basic logic gate circuit. This PNP transistor circuit can act as OR gate or AND gate. If the input is closing of. 🔗 External reference