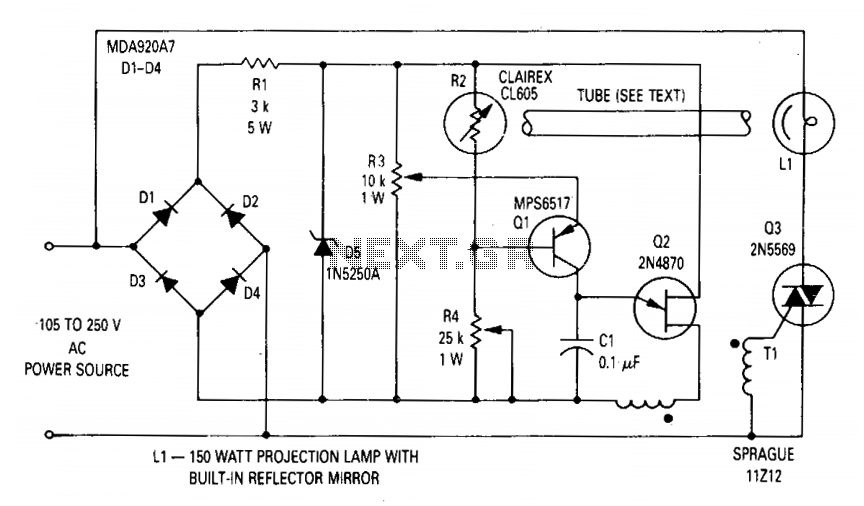
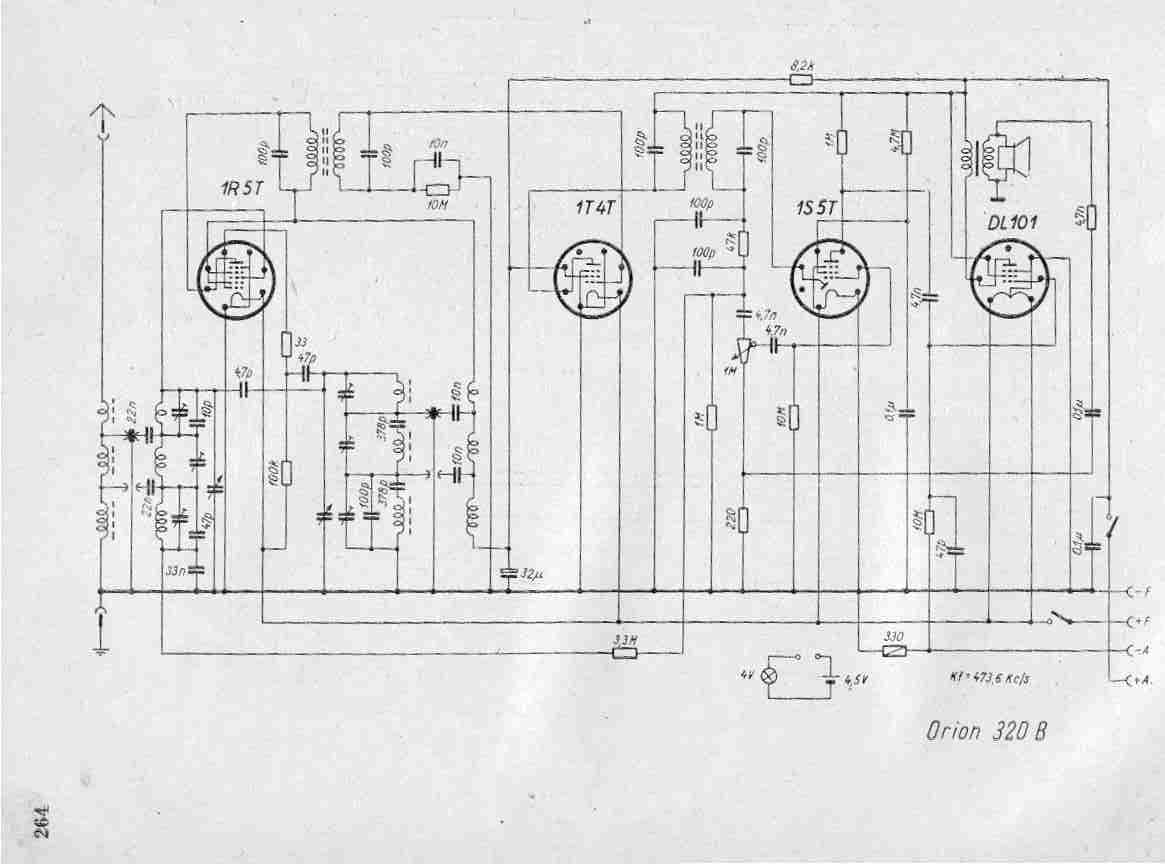
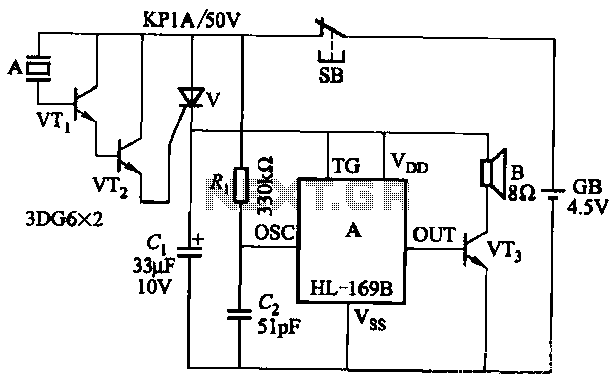
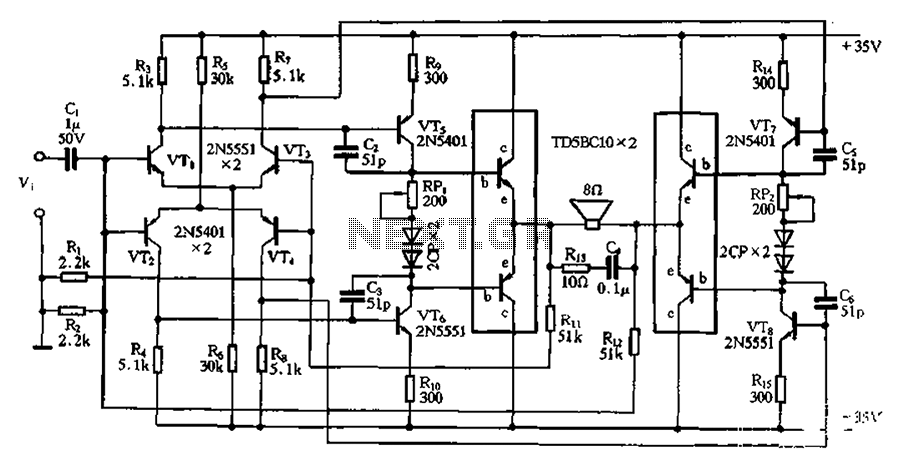
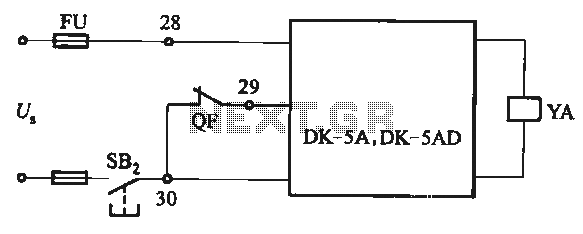
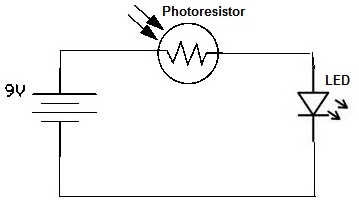
Basic reference bias circuit transistor - negative voltage feedback
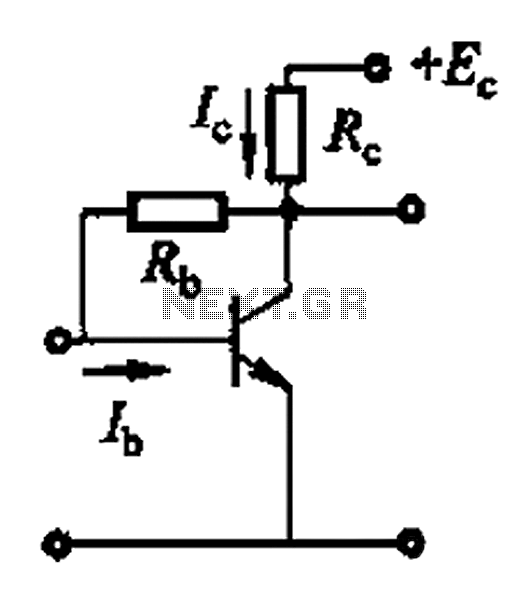
Basic reference bias circuit using a transistor with negative voltage feedback.
The basic reference bias circuit utilizing a transistor with negative voltage feedback is designed to provide a stable output voltage or current that is largely independent of variations in temperature and power supply. The circuit typically consists of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) configured in a feedback arrangement, where a portion of the output is fed back to the input to maintain stability.
In this configuration, the transistor operates in the active region, where it can amplify the input signal. The negative voltage feedback is achieved by connecting a resistor from the output to the base of the transistor. This resistor forms a voltage divider with the base-emitter junction, effectively reducing the base voltage as the output voltage increases, which in turn decreases the collector current. This feedback mechanism stabilizes the output by counteracting any changes in the load or supply voltage.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for filtering and resistors to set the biasing conditions. The use of bypass capacitors can help to filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring a clean and stable reference voltage. The values of the resistors and capacitors must be carefully selected to achieve the desired response time and stability of the circuit.
Overall, this basic reference bias circuit is essential in various electronic applications where a reliable and constant reference voltage is required, such as in amplifiers, oscillators, and other analog circuits. It serves as a foundational element in designing more complex electronic systems. Basic reference bias circuit transistor - negative voltage feedback
The basic reference bias circuit utilizing a transistor with negative voltage feedback is designed to provide a stable output voltage or current that is largely independent of variations in temperature and power supply. The circuit typically consists of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) configured in a feedback arrangement, where a portion of the output is fed back to the input to maintain stability.
In this configuration, the transistor operates in the active region, where it can amplify the input signal. The negative voltage feedback is achieved by connecting a resistor from the output to the base of the transistor. This resistor forms a voltage divider with the base-emitter junction, effectively reducing the base voltage as the output voltage increases, which in turn decreases the collector current. This feedback mechanism stabilizes the output by counteracting any changes in the load or supply voltage.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for filtering and resistors to set the biasing conditions. The use of bypass capacitors can help to filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring a clean and stable reference voltage. The values of the resistors and capacitors must be carefully selected to achieve the desired response time and stability of the circuit.
Overall, this basic reference bias circuit is essential in various electronic applications where a reliable and constant reference voltage is required, such as in amplifiers, oscillators, and other analog circuits. It serves as a foundational element in designing more complex electronic systems. Basic reference bias circuit transistor - negative voltage feedback