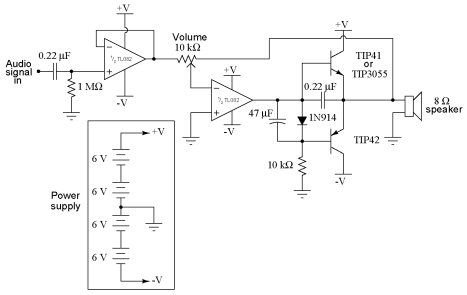
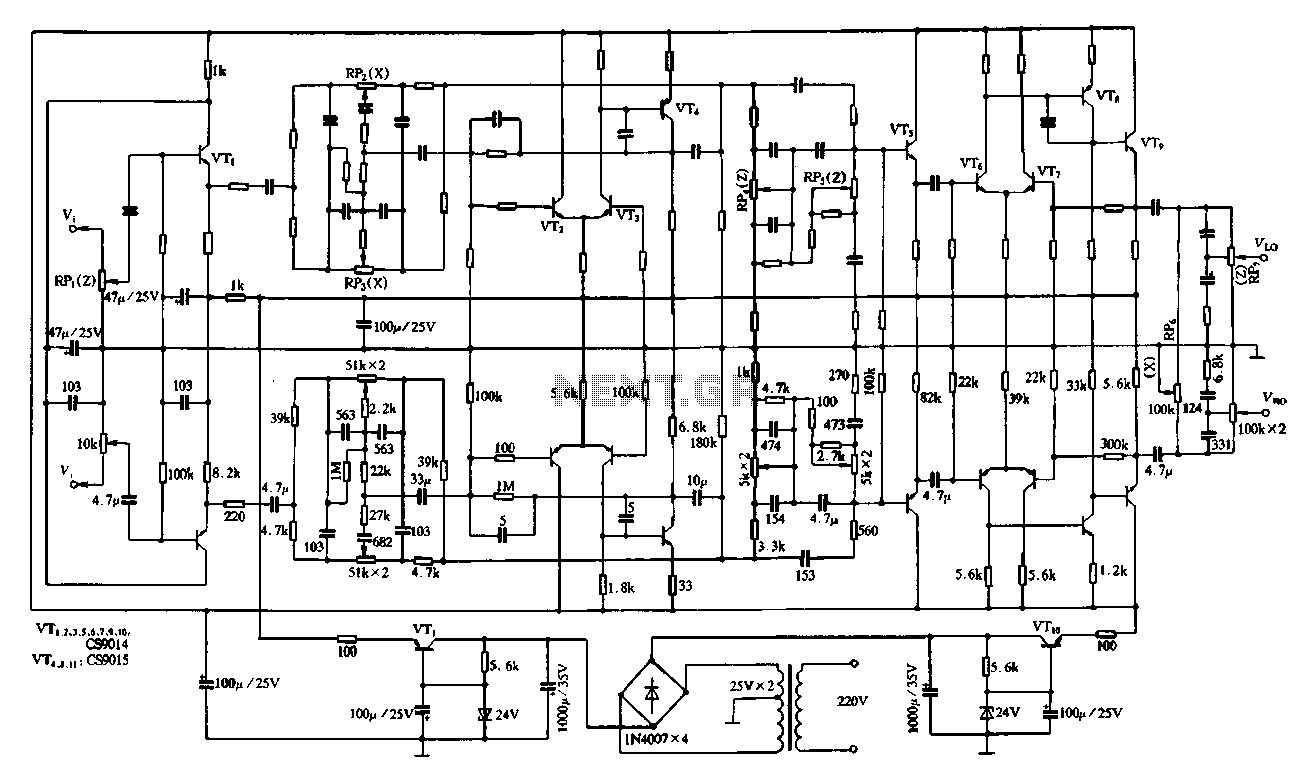
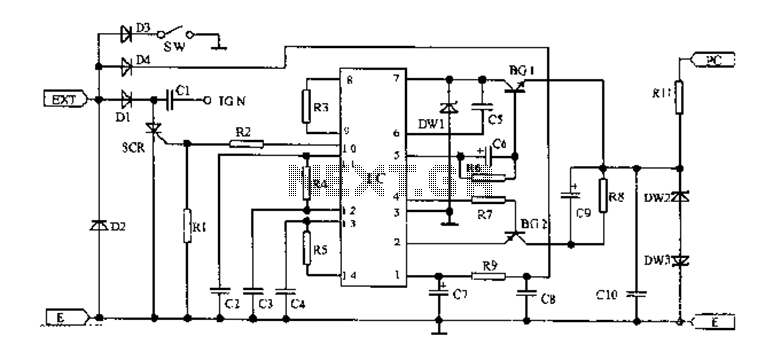
DC bridge amplifier circuit
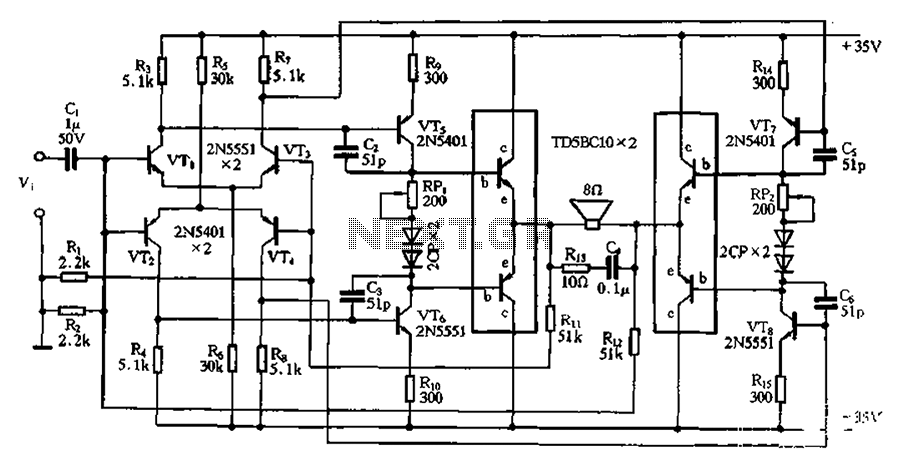
The bridge is a low-frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit with a simple structure, capable of delivering an output power of up to 1W. It can be utilized as an external amplifier for devices such as Walkmans, phones, doorbells, alarms, and other power amplification applications. The circuit, as illustrated in Figure 2-46, features a straightforward design, excellent performance, high output power, and ease of debugging, making it suitable for amateur hobbyists. The transistor stages VTi to VT4 form a complementary symmetry dual differential input stage, while the output stage employs a BTL (Bridge-Tied Load) structure. The voltage amplifier stage utilizes a double push-pull configuration for voltage amplification, which is compatible with the BTL amplifier output stage. The amplifier output stage incorporates a small amplifier consistency pairing module, TD5BC10, simplifying the debugging process. Alternatively, other high-power transistors with similar performance characteristics may also be used in a matched configuration.
The described low-frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit is designed for versatility and ease of use. Its output stage employs a BTL configuration, which effectively drives speakers by providing higher output power while minimizing distortion. The complementary symmetry dual differential input stage enhances the linearity of the amplifier, ensuring that the signal remains faithful to the input. By utilizing a double push-pull voltage amplification method, the circuit maximizes efficiency and power handling capabilities, making it suitable for various applications, from personal audio devices to alarm systems.
The choice of the TD5BC10 module for the output stage is particularly advantageous, as it is designed for consistency and reliability in small amplifier applications. This module simplifies the debugging process, allowing hobbyists and engineers to focus on fine-tuning the amplifier's performance rather than grappling with complex configurations. Furthermore, the design allows for the substitution of other high-power transistors, providing flexibility for those who may have specific performance requirements or component availability considerations.
Overall, this low-frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit exemplifies a well-thought-out design that balances simplicity, performance, and adaptability, making it an ideal choice for both amateur and professional applications in the field of audio amplification. Bridge is a low frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit, its structure is very simple, output power up to 1W. Walkman used as an external amplifier, it can serve as phone, doorbell, alarm and other power amplifier o circuit as shown in Figure 2-46. The simple circuit structure, excellent performance, high output power, easy debugging, it is suitable for amateur homemade. VTi ~ VT4 composed of complementary symmetry dual differential input stage, the output stage of BTL structure, the voltage amplifier stage with double push-pull voltage amplification so and BTL amplifier output stage adaptation.
Amplifier output stage uses a small amplifier consistency pairing module TD5BC10, make debugging very simple o may also be similar to this performance of other high-power tube, paired.
The described low-frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit is designed for versatility and ease of use. Its output stage employs a BTL configuration, which effectively drives speakers by providing higher output power while minimizing distortion. The complementary symmetry dual differential input stage enhances the linearity of the amplifier, ensuring that the signal remains faithful to the input. By utilizing a double push-pull voltage amplification method, the circuit maximizes efficiency and power handling capabilities, making it suitable for various applications, from personal audio devices to alarm systems.
The choice of the TD5BC10 module for the output stage is particularly advantageous, as it is designed for consistency and reliability in small amplifier applications. This module simplifies the debugging process, allowing hobbyists and engineers to focus on fine-tuning the amplifier's performance rather than grappling with complex configurations. Furthermore, the design allows for the substitution of other high-power transistors, providing flexibility for those who may have specific performance requirements or component availability considerations.
Overall, this low-frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit exemplifies a well-thought-out design that balances simplicity, performance, and adaptability, making it an ideal choice for both amateur and professional applications in the field of audio amplification. Bridge is a low frequency push-pull power amplifier circuit, its structure is very simple, output power up to 1W. Walkman used as an external amplifier, it can serve as phone, doorbell, alarm and other power amplifier o circuit as shown in Figure 2-46. The simple circuit structure, excellent performance, high output power, easy debugging, it is suitable for amateur homemade. VTi ~ VT4 composed of complementary symmetry dual differential input stage, the output stage of BTL structure, the voltage amplifier stage with double push-pull voltage amplification so and BTL amplifier output stage adaptation.
Amplifier output stage uses a small amplifier consistency pairing module TD5BC10, make debugging very simple o may also be similar to this performance of other high-power tube, paired.