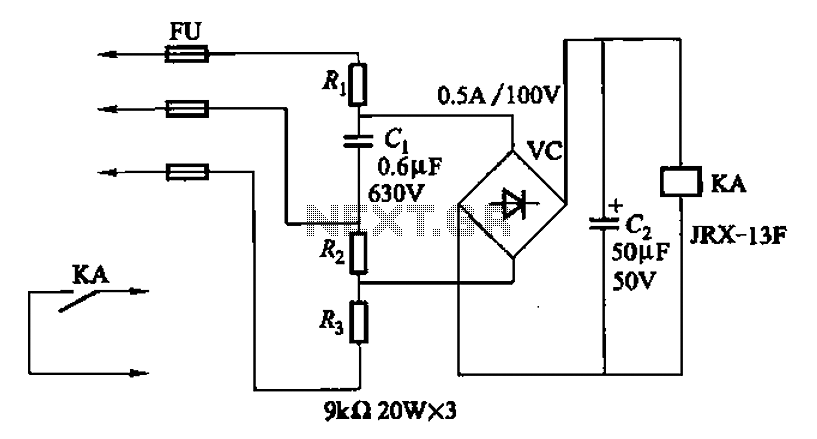
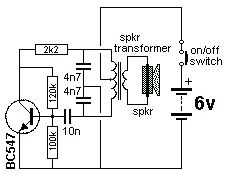
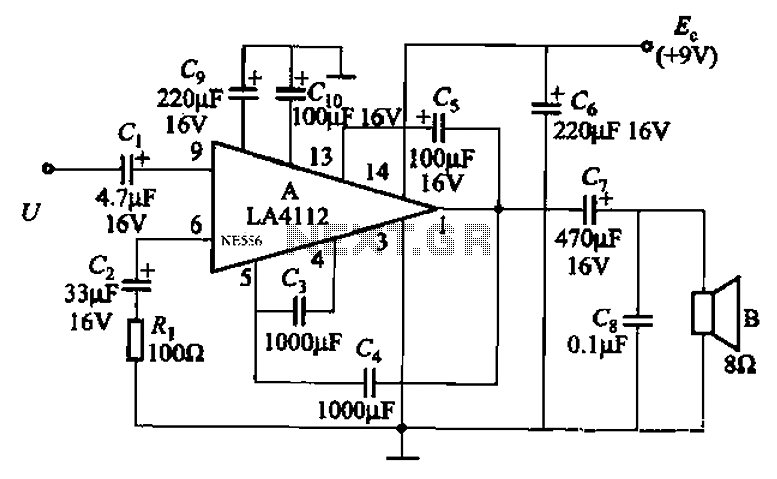
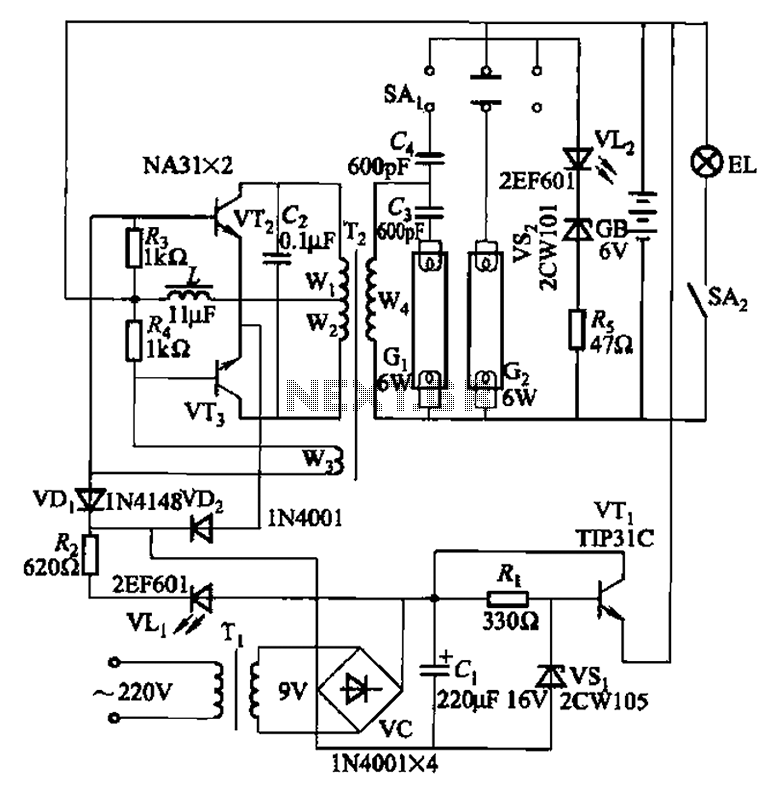
battery backup circuit
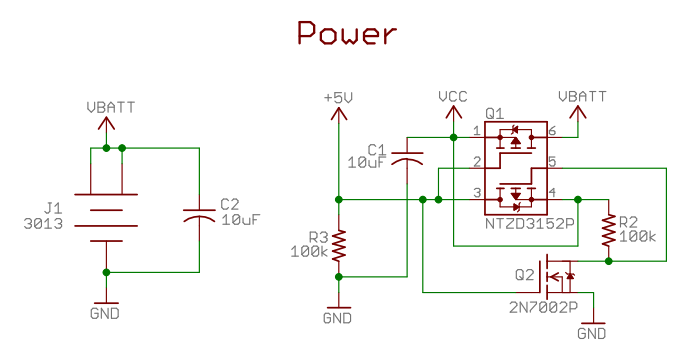
A two-diode selector circuit is utilized when the primary voltage source exceeds both the diodes' turn-on voltage and the input voltage of the second diode. Schottky diodes are preferred due to their low turn-on voltage (typically 0.4V) and high switching speed. The circuit is effective when all voltages fall within the transistor's operational range. In the accompanying schematic, a PNP transistor is employed. It is important to consider the voltage drop across the diodes. An alternative approach involves using complementary FETs, as illustrated in the power source switching section of the schematic, which toggles between +5V and +3V sources. However, the circuit has limitations: it is designed for low-power applications and requires that the battery backup voltage be lower than the external power source. The circuit also includes a configuration for switching between a battery and an adapter for an LCD backlight driver, utilizing a PNP MOSFET to prevent current draw from the battery when voltage is supplied by the adapter to the gate.
The two-diode selector circuit is an efficient solution for applications requiring automatic switching between power sources while ensuring optimal performance and reliability. The use of Schottky diodes is advantageous due to their low forward voltage drop and rapid switching capabilities, which minimize power loss and enhance circuit responsiveness.
In this configuration, when the primary voltage source is present and exceeds the turn-on voltage of the diodes, the circuit allows current to flow through the selected diode, powering the load. If the primary source fails or drops below the necessary voltage, the second diode can take over, ensuring continuous power supply.
The inclusion of a PNP transistor in the circuit serves to manage the flow of current effectively, preventing reverse current from the load back into the power sources. The design also accounts for the voltage drop across the diodes, which is critical in low-voltage applications where even minor losses can impact performance.
For applications that require flexibility in power source selection, the complementary FETs can be employed as an alternative to diodes. This approach can provide improved efficiency and is particularly suitable for higher power applications, although it necessitates careful consideration of the voltage levels between the power sources.
The schematic's power source switching section demonstrates a practical implementation of this concept, allowing the circuit to switch seamlessly between different voltage levels (e.g., +5V and +3V) based on availability. This feature is essential for devices like LCD backlight drivers, where consistent power supply is crucial for operation.
Overall, this two-diode selector circuit design is well-suited for applications requiring reliable power management with minimal losses, making it a valuable addition to low-power electronic systems.A 2 diode selector circuit if your primary voltage source is greater than the diodes turn on voltage and the input voltage of the second diode. Schottky diodes are recommended for both their low lower turn on voltage (typically 0. 4v) and high switching speed. You can use a 2 diode selector circuit if your primary voltage source is grea ter than the diodes turn on voltage and the input voltage of the second diode. Schottky diodes are recommended for both their low lower turn on voltage (typically 0. 4v) and high switching speed. Yes provided your voltages are all within the range the transistor can handle. I think the attached circuit would work. I`ve used something like this in a recent design and now the main and backup voltages can be equal. The transistor in the diagram is a PNP. Diodes have a voltage drop that needs to be accounted for. Another way to do it is with complementary FETs. A nice example is in the power source switching used here (the part of the schematic labeled "Power" which switches between +5v and +3v sources): Of course, the two weaknesses here are 1) these are low-power parts (intended for extremely low current device), and 2) it relies on the battery backup power source having a lower voltage than the external power source. Diodes have a voltage drop that needs to be accounted for. Another way to do it is with complementary FETs. A nice example is in the power source switching used here (the part of the schematic labeled "Power" which switches between +5v and +3v sources): Of course, the two weaknesses here are 1) these are low-power parts (intended for extremely low current device), and 2) it relies on the battery backup power source having a lower voltage than the external power source.
Left out a diode. Here is a circuit I`m using for switching between a battery and adapter (power pack to you aussies) for input to a lcd backlight driver. It employs a PNP mosfet to prevent current from being drawn from the battery when there is a voltage (provided by the adapter) present on the Gate.
🔗 External reference
The two-diode selector circuit is an efficient solution for applications requiring automatic switching between power sources while ensuring optimal performance and reliability. The use of Schottky diodes is advantageous due to their low forward voltage drop and rapid switching capabilities, which minimize power loss and enhance circuit responsiveness.
In this configuration, when the primary voltage source is present and exceeds the turn-on voltage of the diodes, the circuit allows current to flow through the selected diode, powering the load. If the primary source fails or drops below the necessary voltage, the second diode can take over, ensuring continuous power supply.
The inclusion of a PNP transistor in the circuit serves to manage the flow of current effectively, preventing reverse current from the load back into the power sources. The design also accounts for the voltage drop across the diodes, which is critical in low-voltage applications where even minor losses can impact performance.
For applications that require flexibility in power source selection, the complementary FETs can be employed as an alternative to diodes. This approach can provide improved efficiency and is particularly suitable for higher power applications, although it necessitates careful consideration of the voltage levels between the power sources.
The schematic's power source switching section demonstrates a practical implementation of this concept, allowing the circuit to switch seamlessly between different voltage levels (e.g., +5V and +3V) based on availability. This feature is essential for devices like LCD backlight drivers, where consistent power supply is crucial for operation.
Overall, this two-diode selector circuit design is well-suited for applications requiring reliable power management with minimal losses, making it a valuable addition to low-power electronic systems.A 2 diode selector circuit if your primary voltage source is greater than the diodes turn on voltage and the input voltage of the second diode. Schottky diodes are recommended for both their low lower turn on voltage (typically 0. 4v) and high switching speed. You can use a 2 diode selector circuit if your primary voltage source is grea ter than the diodes turn on voltage and the input voltage of the second diode. Schottky diodes are recommended for both their low lower turn on voltage (typically 0. 4v) and high switching speed. Yes provided your voltages are all within the range the transistor can handle. I think the attached circuit would work. I`ve used something like this in a recent design and now the main and backup voltages can be equal. The transistor in the diagram is a PNP. Diodes have a voltage drop that needs to be accounted for. Another way to do it is with complementary FETs. A nice example is in the power source switching used here (the part of the schematic labeled "Power" which switches between +5v and +3v sources): Of course, the two weaknesses here are 1) these are low-power parts (intended for extremely low current device), and 2) it relies on the battery backup power source having a lower voltage than the external power source. Diodes have a voltage drop that needs to be accounted for. Another way to do it is with complementary FETs. A nice example is in the power source switching used here (the part of the schematic labeled "Power" which switches between +5v and +3v sources): Of course, the two weaknesses here are 1) these are low-power parts (intended for extremely low current device), and 2) it relies on the battery backup power source having a lower voltage than the external power source.
Left out a diode. Here is a circuit I`m using for switching between a battery and adapter (power pack to you aussies) for input to a lcd backlight driver. It employs a PNP mosfet to prevent current from being drawn from the battery when there is a voltage (provided by the adapter) present on the Gate.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713