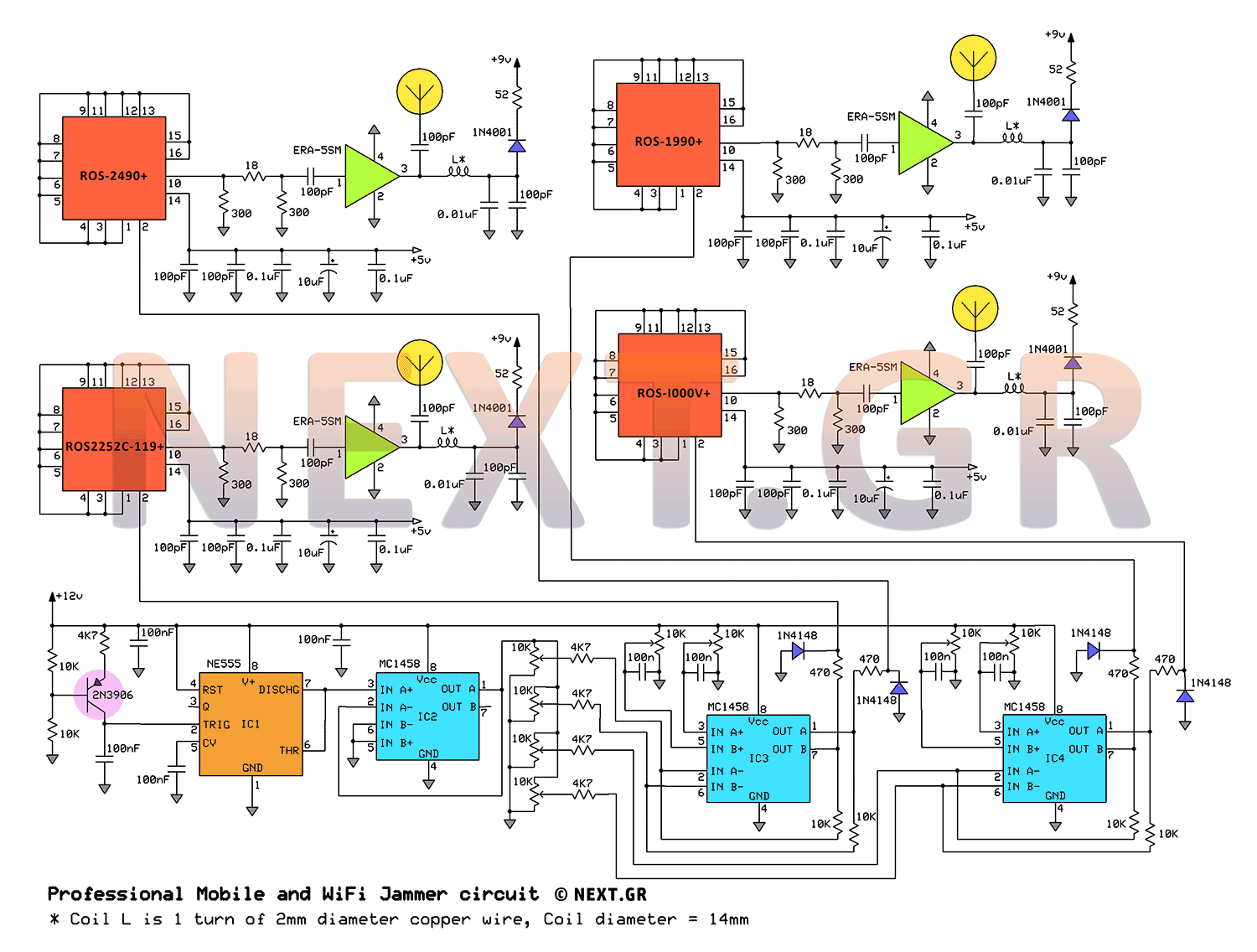
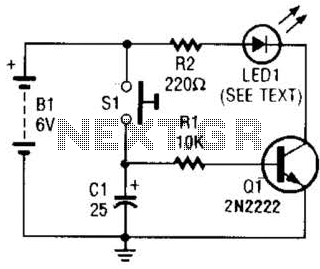
bias current compensation circuit

This is the design of a bias current compensation circuit. This circuit can operate with medium wattage source resistances while maintaining a minimal increase in the equivalent offset voltage. It is based on the LM11 operational amplifier. The circuit exhibits impressive performance considering the low initial offset voltage. The situation can be significantly improved if the design is configured to ensure that the operational amplifier experiences equal resistance at both inputs. However, this configuration is not feasible for all circuit types, including integrators, sample-and-hold circuits, logarithmic converters, and signal-conditioning amplifiers. Although the LM11 has a low bias current, there are applications that require even lower bias current levels.
The bias current compensation circuit is designed to mitigate the effects of input bias currents in operational amplifiers, particularly in precision applications. The LM11 operational amplifier, known for its low offset voltage and bias current characteristics, serves as the core component of this design. The circuit aims to maintain a balanced input condition, which is crucial for minimizing offset errors that can affect the accuracy of signal processing.
In the context of this circuit, the operational amplifier's two inputs are subjected to source resistances that can introduce offset voltage variations. By employing a bias current compensation scheme, the circuit effectively reduces the impact of these resistances. The design ensures that the bias currents flowing into each input are equalized, thus preserving the integrity of the output signal.
For applications such as integrators and sample-and-hold circuits where maintaining precise voltage levels is critical, the challenge lies in achieving equal resistance at both inputs without compromising the circuit's functionality. In these instances, alternative methods may be required to further reduce bias current effects, such as utilizing additional components or selecting operational amplifiers with even lower bias current specifications.
Overall, this bias current compensation circuit represents a valuable approach for enhancing the performance of analog signal processing systems, particularly in scenarios where offset voltage precision is essential. The careful selection of components and design configurations can lead to significant improvements in circuit accuracy, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.This is design circuit of bias current compensation circuit. This circuit can operate from MW source resistances with little increase in the equivalent offset voltage. This circuit is based on LM11. This is the figure of the circuit. This is impressive considering the low initial offset voltage. The situation is much improved if the design can be configured so that the op amp sees equal resistance on the two inputs. However, this cannot be done with all circuits. Examples are integrators, sample and holds, logarithmic converters and signal-conditioning amplifiers. And even though the LM11 bias current is low, there will be those applications where it needs to be lower.
🔗 External reference
The bias current compensation circuit is designed to mitigate the effects of input bias currents in operational amplifiers, particularly in precision applications. The LM11 operational amplifier, known for its low offset voltage and bias current characteristics, serves as the core component of this design. The circuit aims to maintain a balanced input condition, which is crucial for minimizing offset errors that can affect the accuracy of signal processing.
In the context of this circuit, the operational amplifier's two inputs are subjected to source resistances that can introduce offset voltage variations. By employing a bias current compensation scheme, the circuit effectively reduces the impact of these resistances. The design ensures that the bias currents flowing into each input are equalized, thus preserving the integrity of the output signal.
For applications such as integrators and sample-and-hold circuits where maintaining precise voltage levels is critical, the challenge lies in achieving equal resistance at both inputs without compromising the circuit's functionality. In these instances, alternative methods may be required to further reduce bias current effects, such as utilizing additional components or selecting operational amplifiers with even lower bias current specifications.
Overall, this bias current compensation circuit represents a valuable approach for enhancing the performance of analog signal processing systems, particularly in scenarios where offset voltage precision is essential. The careful selection of components and design configurations can lead to significant improvements in circuit accuracy, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.This is design circuit of bias current compensation circuit. This circuit can operate from MW source resistances with little increase in the equivalent offset voltage. This circuit is based on LM11. This is the figure of the circuit. This is impressive considering the low initial offset voltage. The situation is much improved if the design can be configured so that the op amp sees equal resistance on the two inputs. However, this cannot be done with all circuits. Examples are integrators, sample and holds, logarithmic converters and signal-conditioning amplifiers. And even though the LM11 bias current is low, there will be those applications where it needs to be lower.
🔗 External reference