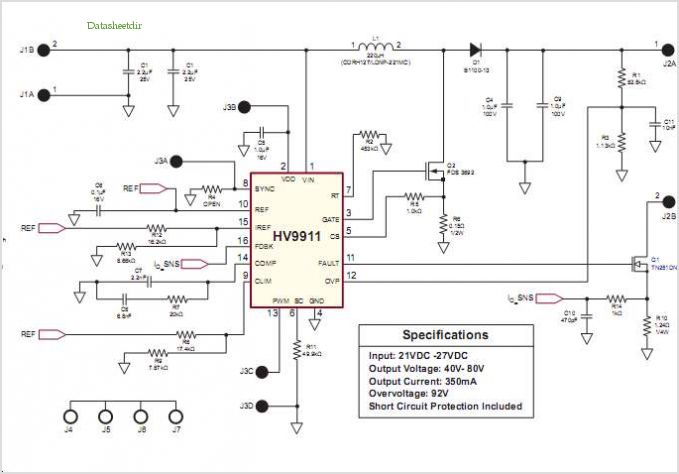
Bipolar Transistor HBridge Motor Driver
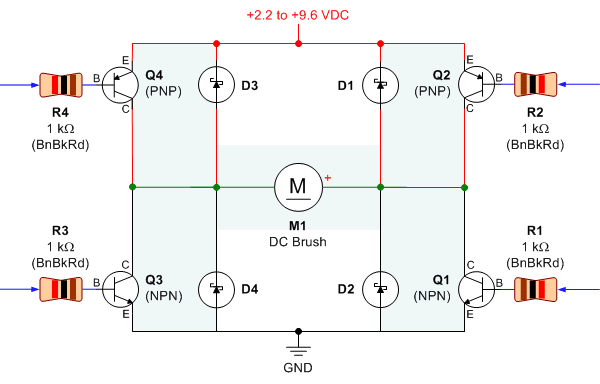
Schematic, breadboard photo, parts list, and results of several transistor variations on the classic bipolar H-bridge motor driver circuit.
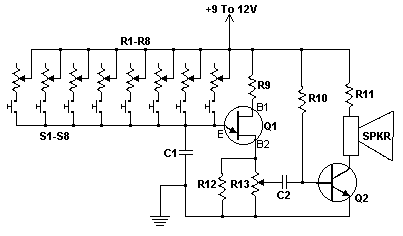
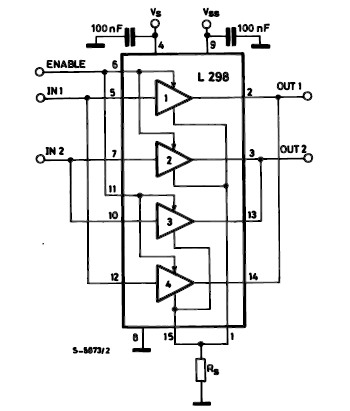
The classic bipolar H-bridge motor driver circuit is a widely used configuration that allows for the control of DC motors in both forward and reverse directions. This circuit utilizes four transistors arranged in a bridge configuration, which enables the reversal of current flow through the motor. The schematic representation of this circuit typically includes the four transistors, which can be either bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or MOSFETs, depending on the desired characteristics and performance requirements.
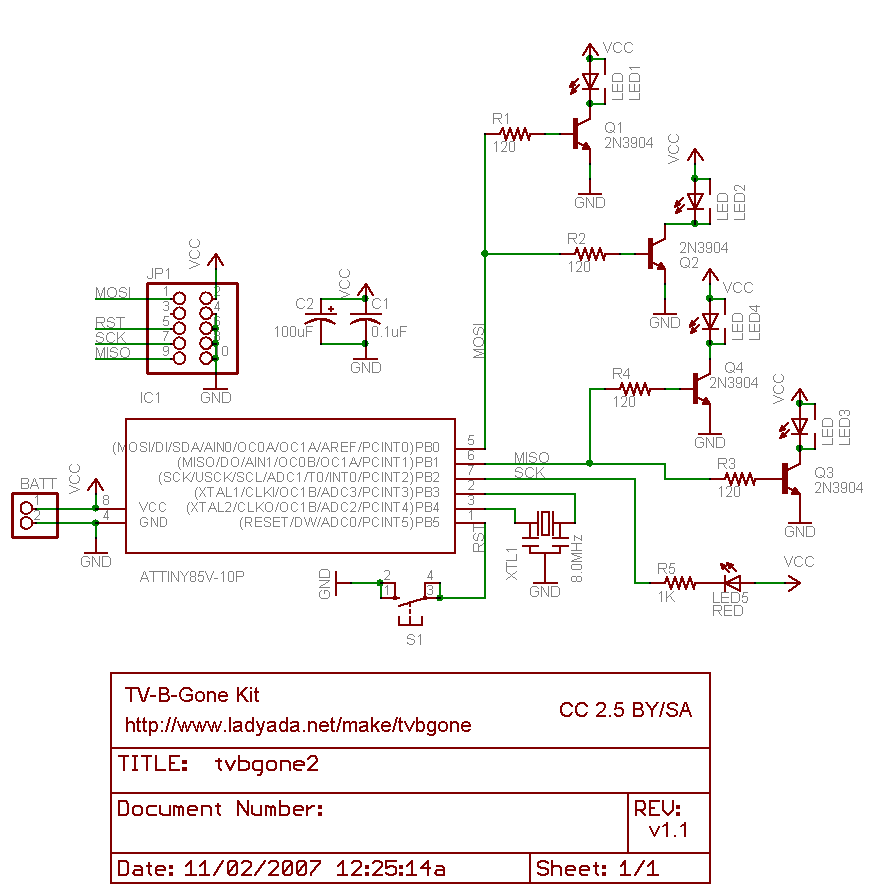
In the breadboard photo, the physical layout of the circuit can be observed, showcasing the arrangement of components, including the transistors, resistors, diodes, and the motor. The breadboard setup is essential for prototyping and testing the circuit before finalizing the design on a printed circuit board (PCB).
The parts list includes all necessary components for constructing the H-bridge motor driver circuit. This typically encompasses the transistors, resistors for base or gate control, flyback diodes to protect against voltage spikes generated by the motor, and any additional components necessary for proper operation, such as capacitors for filtering.
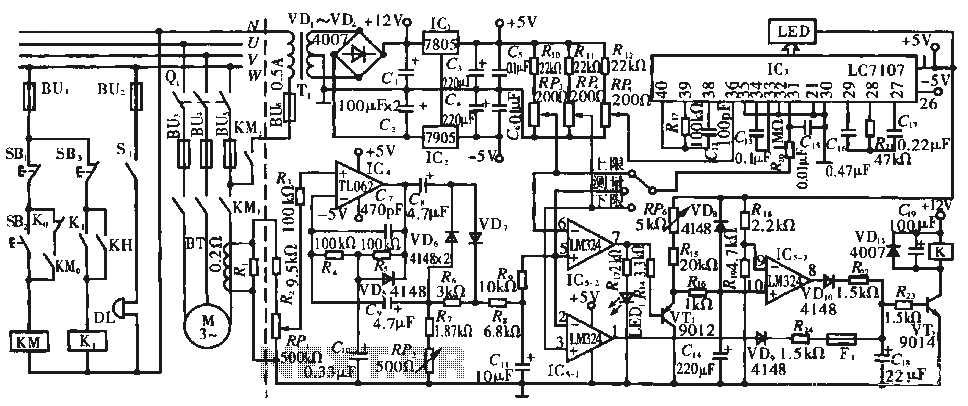
The results of several transistor variations indicate the performance differences when using different types of transistors. For instance, BJTs may provide different switching characteristics compared to MOSFETs, affecting efficiency, heat dissipation, and response time. Testing various configurations allows for optimization of the circuit for specific applications, ensuring reliable operation under varying load conditions.
Overall, the combination of the schematic, breadboard photo, parts list, and experimental results provides a comprehensive overview of the classic bipolar H-bridge motor driver circuit, facilitating understanding and implementation in various electronic projects.Schematic, breadboard photo, parts list, and results of several transistor variations on the classic bipolar hbridge motor driver circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The classic bipolar H-bridge motor driver circuit is a widely used configuration that allows for the control of DC motors in both forward and reverse directions. This circuit utilizes four transistors arranged in a bridge configuration, which enables the reversal of current flow through the motor. The schematic representation of this circuit typically includes the four transistors, which can be either bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or MOSFETs, depending on the desired characteristics and performance requirements.
In the breadboard photo, the physical layout of the circuit can be observed, showcasing the arrangement of components, including the transistors, resistors, diodes, and the motor. The breadboard setup is essential for prototyping and testing the circuit before finalizing the design on a printed circuit board (PCB).
The parts list includes all necessary components for constructing the H-bridge motor driver circuit. This typically encompasses the transistors, resistors for base or gate control, flyback diodes to protect against voltage spikes generated by the motor, and any additional components necessary for proper operation, such as capacitors for filtering.
The results of several transistor variations indicate the performance differences when using different types of transistors. For instance, BJTs may provide different switching characteristics compared to MOSFETs, affecting efficiency, heat dissipation, and response time. Testing various configurations allows for optimization of the circuit for specific applications, ensuring reliable operation under varying load conditions.
Overall, the combination of the schematic, breadboard photo, parts list, and experimental results provides a comprehensive overview of the classic bipolar H-bridge motor driver circuit, facilitating understanding and implementation in various electronic projects.Schematic, breadboard photo, parts list, and results of several transistor variations on the classic bipolar hbridge motor driver circuit.. 🔗 External reference