Blue Blinky Joule circuit

Daylight shutoff; the schematic has been updated but is not shown here.
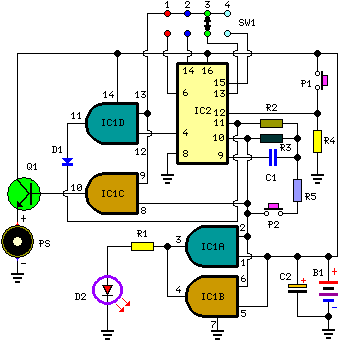
The daylight shutoff circuit is designed to automatically turn off lighting systems during daylight hours, thereby conserving energy and extending the lifespan of the lighting fixtures. Typically, this circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or a phototransistor to detect ambient light levels. When the light level exceeds a predetermined threshold, the circuit triggers a relay or a solid-state switch to disconnect the power from the lighting system.
In a typical implementation, the LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The voltage across the LDR changes based on the intensity of the ambient light. This voltage is then fed into a comparator or an operational amplifier configured to compare it against a reference voltage. When the ambient light is sufficient, the output of the comparator will change state, activating the control mechanism that turns off the lights.
The relay used in the circuit should be rated for the load it will control, ensuring it can handle the current and voltage requirements of the lighting system. In addition, a diode may be placed in parallel with the relay coil to prevent back EMF from damaging the circuit when the relay is de-energized.
For added functionality, the circuit can be equipped with a delay timer to prevent rapid on-off cycling due to transient changes in light levels, such as passing clouds. This timer can be implemented using a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) network or a more sophisticated microcontroller for programmable settings.
Overall, the daylight shutoff circuit is an effective solution for energy management in lighting systems, promoting sustainability while providing convenience.Daylight shutoff I updated the schematic not shown on this one 🔗 External reference
The daylight shutoff circuit is designed to automatically turn off lighting systems during daylight hours, thereby conserving energy and extending the lifespan of the lighting fixtures. Typically, this circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or a phototransistor to detect ambient light levels. When the light level exceeds a predetermined threshold, the circuit triggers a relay or a solid-state switch to disconnect the power from the lighting system.
In a typical implementation, the LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The voltage across the LDR changes based on the intensity of the ambient light. This voltage is then fed into a comparator or an operational amplifier configured to compare it against a reference voltage. When the ambient light is sufficient, the output of the comparator will change state, activating the control mechanism that turns off the lights.
The relay used in the circuit should be rated for the load it will control, ensuring it can handle the current and voltage requirements of the lighting system. In addition, a diode may be placed in parallel with the relay coil to prevent back EMF from damaging the circuit when the relay is de-energized.
For added functionality, the circuit can be equipped with a delay timer to prevent rapid on-off cycling due to transient changes in light levels, such as passing clouds. This timer can be implemented using a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) network or a more sophisticated microcontroller for programmable settings.
Overall, the daylight shutoff circuit is an effective solution for energy management in lighting systems, promoting sustainability while providing convenience.Daylight shutoff I updated the schematic not shown on this one 🔗 External reference