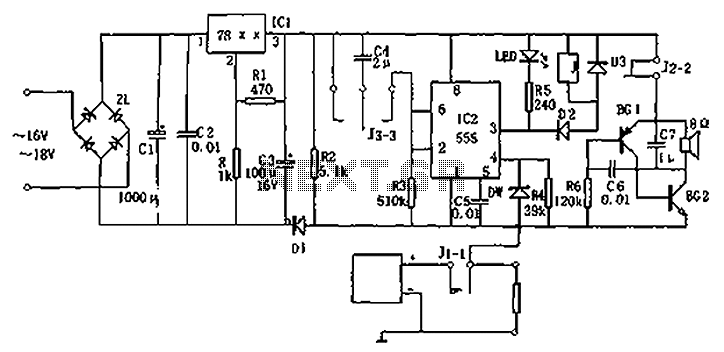
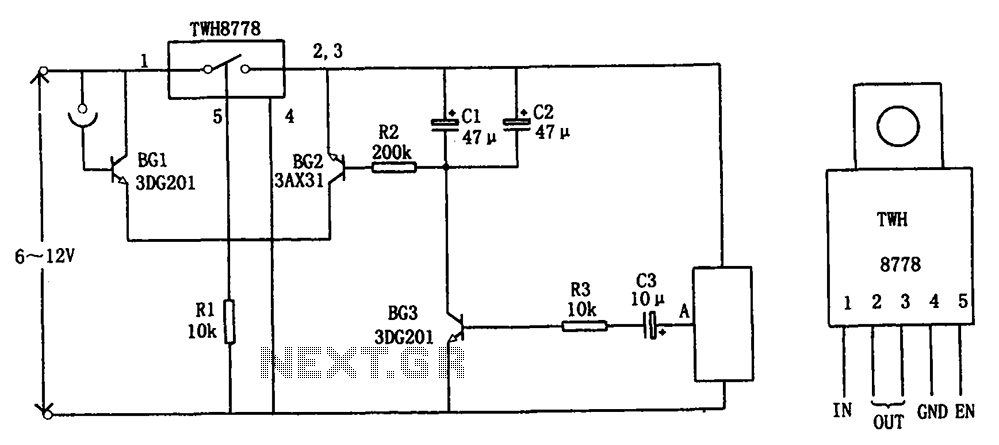
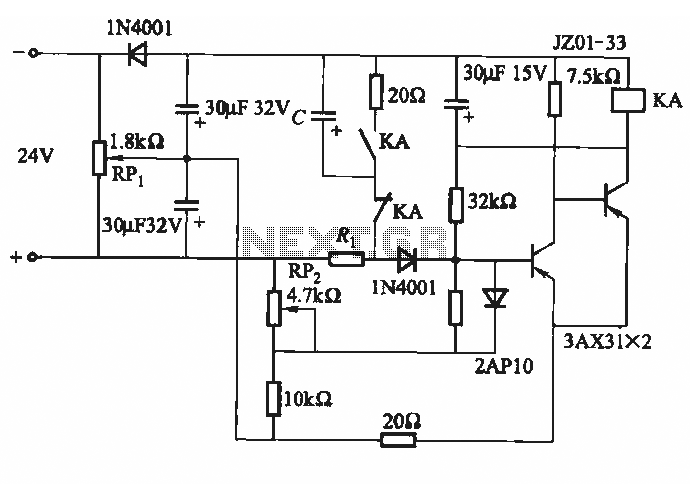
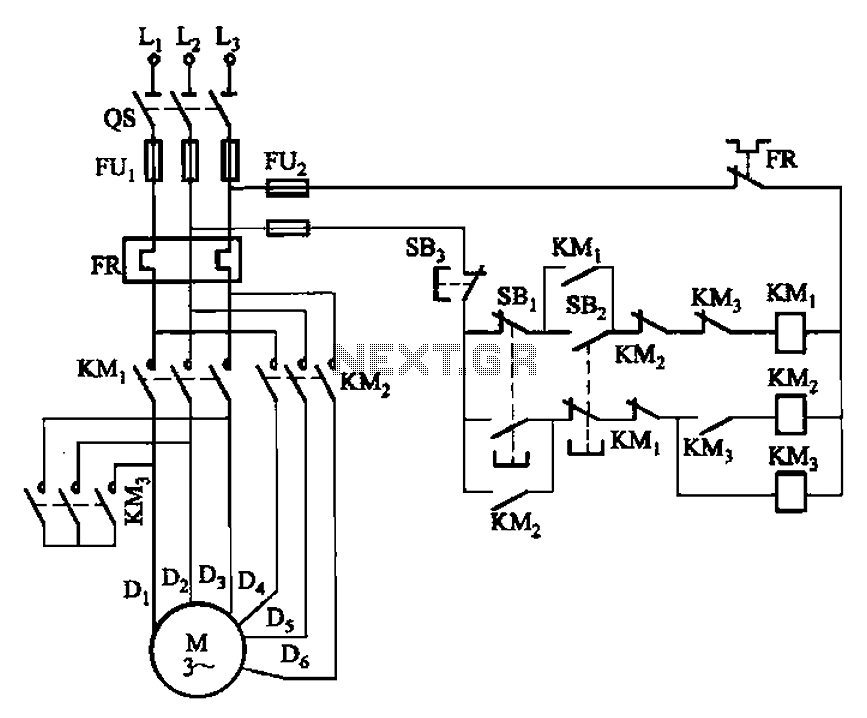
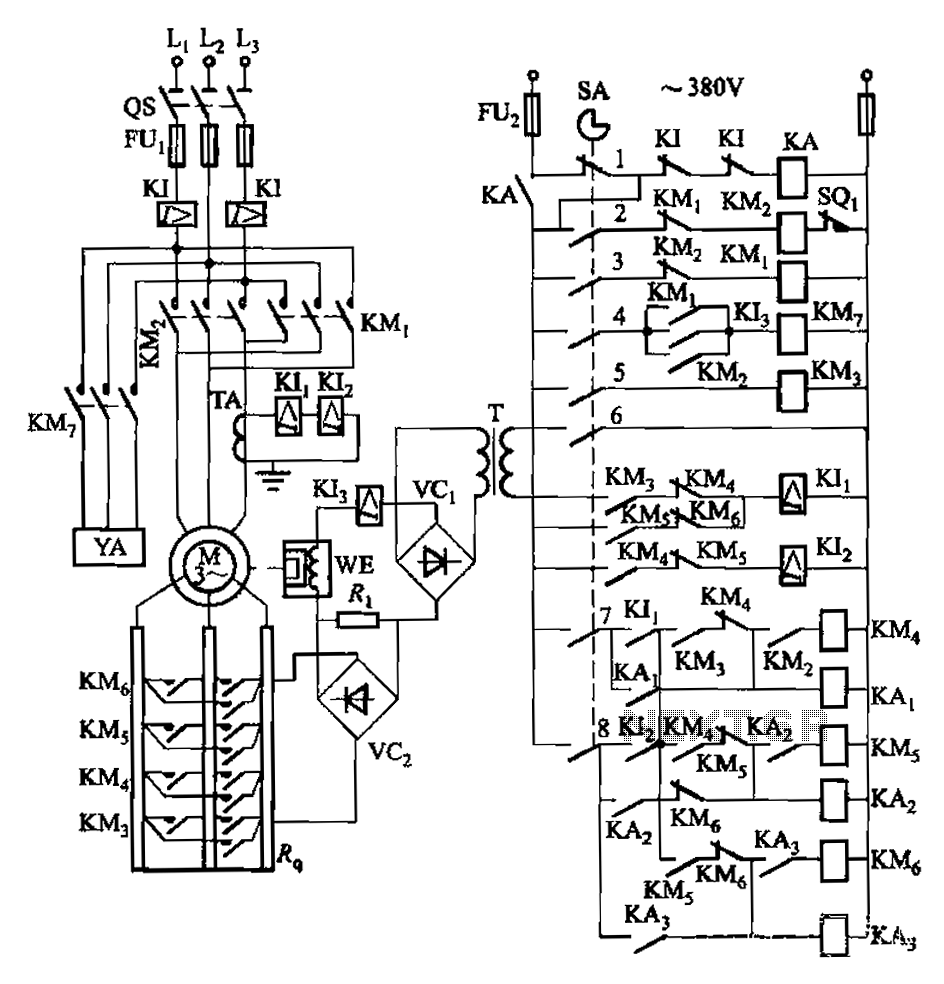
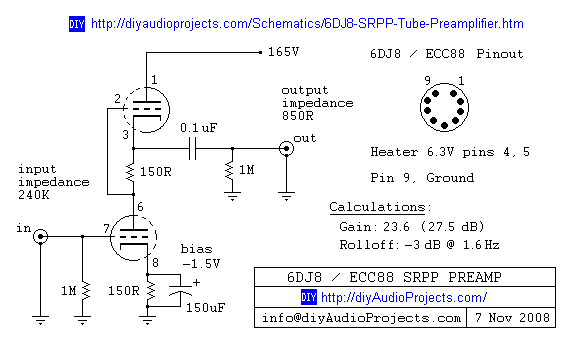
BLW96 RF Amplifier Circuit
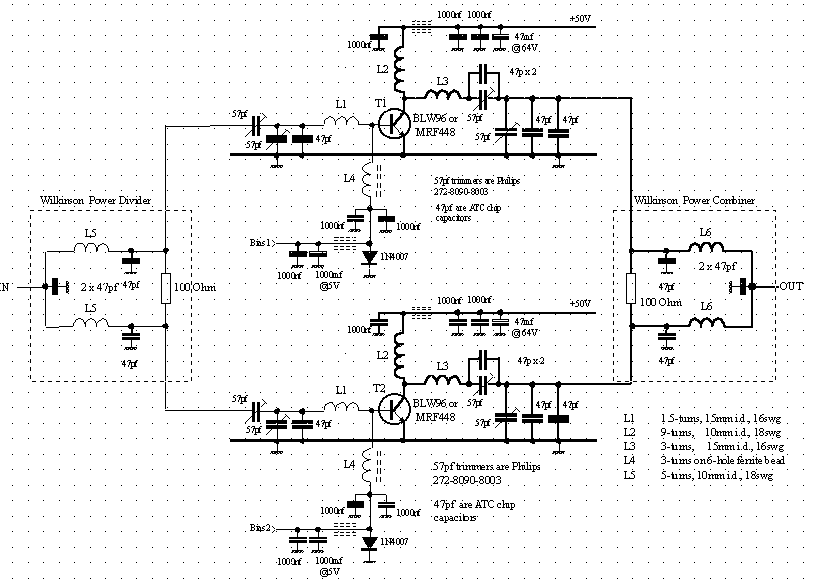
The BLW96 is a high-frequency (HF) and very high-frequency (VHF) power transistor designed for use in class A, AB, and B operated high-power industrial and military transmitting equipment.
The BLW96 transistor is a crucial component in RF (radio frequency) applications, particularly in transmitting equipment that operates within the HF and VHF bands. This transistor is designed to handle high power levels, making it suitable for industrial and military applications where robust performance is required.
In terms of specifications, the BLW96 typically features a maximum collector current rating, allowing for efficient power amplification while maintaining thermal stability. Its construction often includes a metal case, which aids in heat dissipation, thereby enhancing reliability during prolonged operation.
The transistor operates in various classes, including Class A, which is known for its linearity and low distortion, Class AB, which balances efficiency and linearity, and Class B, which is optimized for high efficiency. The selection of the operating class is critical and depends on the specific requirements of the transmitting application, such as power output, efficiency, and linearity.
When designing circuits with the BLW96, it is essential to consider the biasing arrangement, load impedance, and cooling requirements to ensure optimal performance. Proper heat sinking and thermal management strategies must be implemented to prevent thermal runaway and ensure long-term reliability.
Overall, the BLW96 serves as a versatile and powerful solution for high-frequency and high-power applications, making it a valuable component in the design of advanced transmitting systems.BLW96 is a HF/VHF power transistor intended for use in class-A, AB and B operated high power industrial and military transmitting equipment in the h.f. and.. 🔗 External reference
The BLW96 transistor is a crucial component in RF (radio frequency) applications, particularly in transmitting equipment that operates within the HF and VHF bands. This transistor is designed to handle high power levels, making it suitable for industrial and military applications where robust performance is required.
In terms of specifications, the BLW96 typically features a maximum collector current rating, allowing for efficient power amplification while maintaining thermal stability. Its construction often includes a metal case, which aids in heat dissipation, thereby enhancing reliability during prolonged operation.
The transistor operates in various classes, including Class A, which is known for its linearity and low distortion, Class AB, which balances efficiency and linearity, and Class B, which is optimized for high efficiency. The selection of the operating class is critical and depends on the specific requirements of the transmitting application, such as power output, efficiency, and linearity.
When designing circuits with the BLW96, it is essential to consider the biasing arrangement, load impedance, and cooling requirements to ensure optimal performance. Proper heat sinking and thermal management strategies must be implemented to prevent thermal runaway and ensure long-term reliability.
Overall, the BLW96 serves as a versatile and powerful solution for high-frequency and high-power applications, making it a valuable component in the design of advanced transmitting systems.BLW96 is a HF/VHF power transistor intended for use in class-A, AB and B operated high power industrial and military transmitting equipment in the h.f. and.. 🔗 External reference