Broadband 0.1 to 10Hz filter amplifier
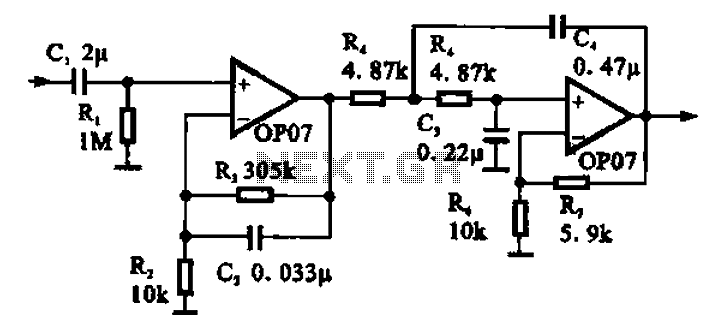
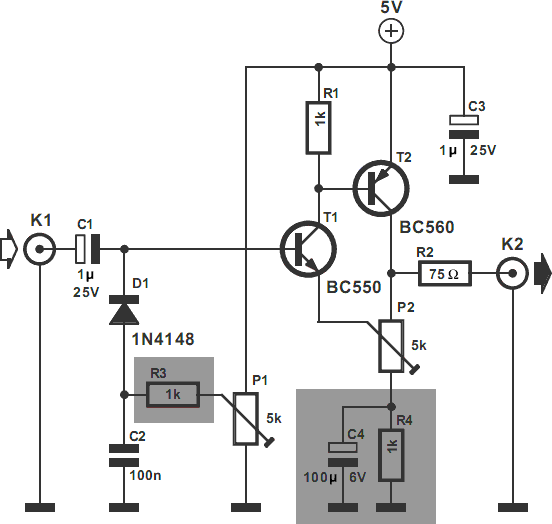
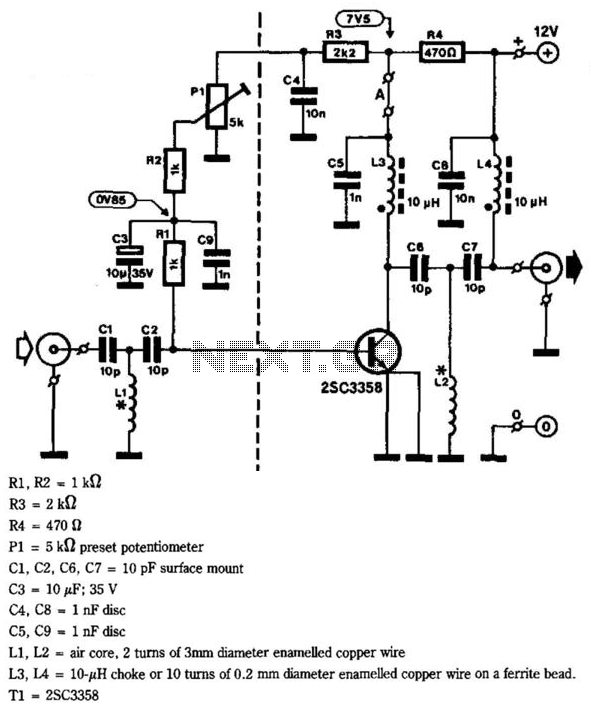
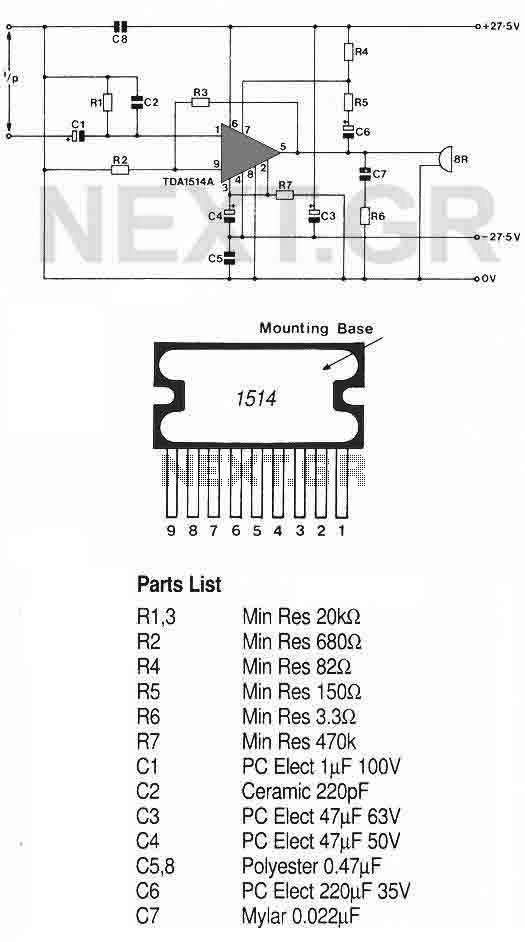
Broadband 0.1 to 10 Hz filter amplifier. The broadband circuit consists of two operational amplifiers configured as filter amplifiers operating in the frequency range of 0.1 to 10 Hz.
The broadband filter amplifier circuit utilizes two operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve signal amplification while filtering out unwanted frequencies outside the specified range of 0.1 to 10 Hz. The circuit is designed for applications that require precise signal processing of low-frequency signals, such as in biomedical instrumentation, seismic monitoring, or low-frequency audio applications.
The first stage of the circuit typically consists of a low-pass filter configuration, which is implemented using one of the operational amplifiers. This stage is designed to attenuate frequencies above 10 Hz, ensuring that only the desired low-frequency signals pass through. The cutoff frequency can be determined using a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, where the values of the resistor and capacitor are selected to achieve the desired -3 dB point at 10 Hz.
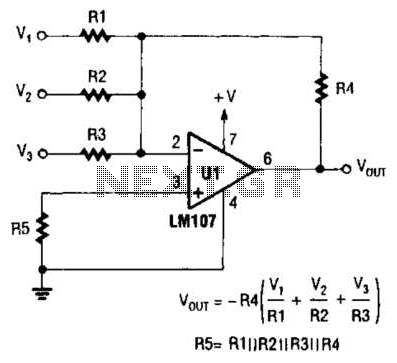
The second operational amplifier is configured as a non-inverting amplifier, providing gain to the filtered signal. The gain can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback and input resistor values, allowing for flexibility in the amplification level based on application requirements.
Power supply considerations for the op-amps must also be taken into account, ensuring that the supply voltage is sufficient to accommodate the expected output signal swing while maintaining linear operation of the amplifiers. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included at the power supply pins of the op-amps to reduce noise and improve stability.
Overall, this broadband filter amplifier circuit is essential for applications requiring precise low-frequency signal processing, ensuring that the output signal accurately reflects the input while minimizing noise and interference from higher frequency components. Broadband 0.1 to 10Hz filter amplifier Broadband circuit is composed of two operational amplifiers (0.1-10 Hz) filter amplifiers.
The broadband filter amplifier circuit utilizes two operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve signal amplification while filtering out unwanted frequencies outside the specified range of 0.1 to 10 Hz. The circuit is designed for applications that require precise signal processing of low-frequency signals, such as in biomedical instrumentation, seismic monitoring, or low-frequency audio applications.
The first stage of the circuit typically consists of a low-pass filter configuration, which is implemented using one of the operational amplifiers. This stage is designed to attenuate frequencies above 10 Hz, ensuring that only the desired low-frequency signals pass through. The cutoff frequency can be determined using a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, where the values of the resistor and capacitor are selected to achieve the desired -3 dB point at 10 Hz.
The second operational amplifier is configured as a non-inverting amplifier, providing gain to the filtered signal. The gain can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback and input resistor values, allowing for flexibility in the amplification level based on application requirements.
Power supply considerations for the op-amps must also be taken into account, ensuring that the supply voltage is sufficient to accommodate the expected output signal swing while maintaining linear operation of the amplifiers. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included at the power supply pins of the op-amps to reduce noise and improve stability.
Overall, this broadband filter amplifier circuit is essential for applications requiring precise low-frequency signal processing, ensuring that the output signal accurately reflects the input while minimizing noise and interference from higher frequency components. Broadband 0.1 to 10Hz filter amplifier Broadband circuit is composed of two operational amplifiers (0.1-10 Hz) filter amplifiers.