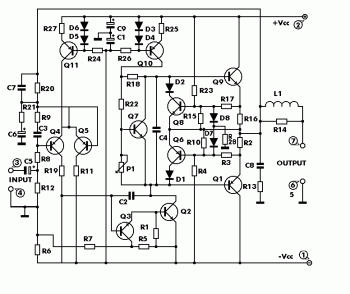
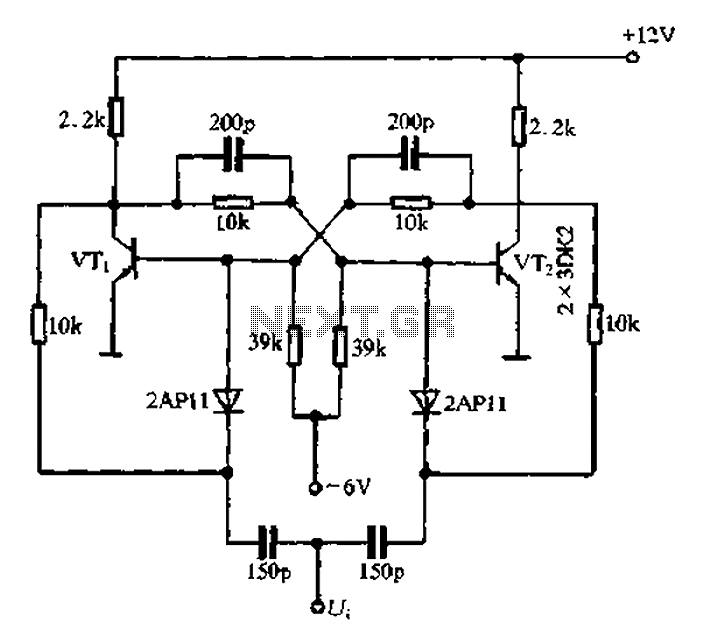
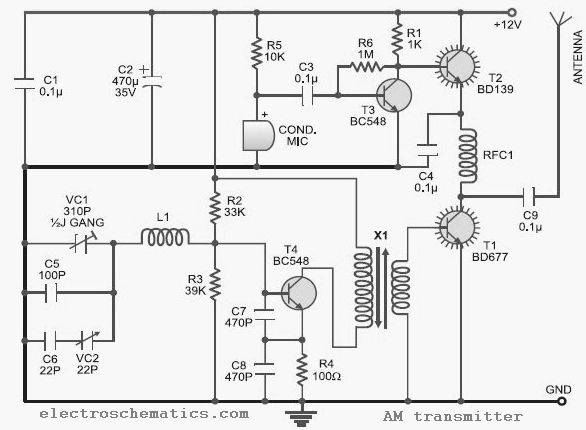
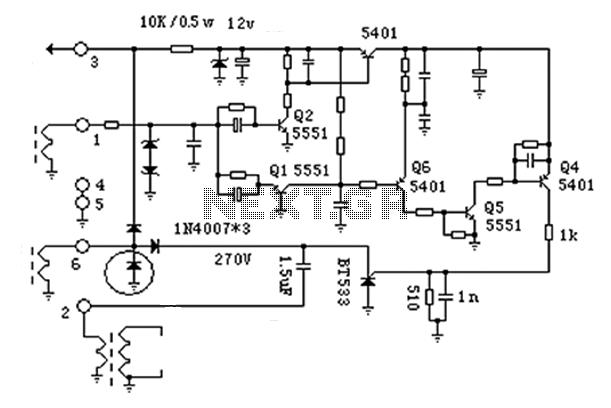
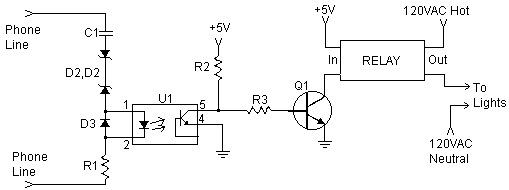
Inverting Summing Amplifier Circuit
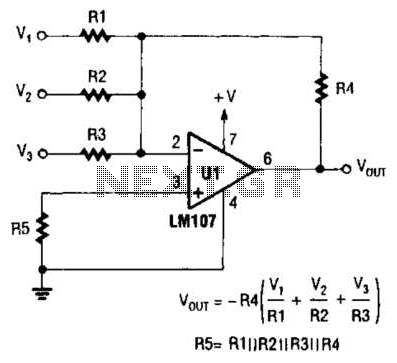
The output of Ul is the sum of Vv, multiplied by the ratio of Rx to Rv, RJRV, and respectively. Resistors R1, R2, and R3 are selected as required for individual gains. Additionally, R4 influences the gain of all these inputs.
The circuit under discussion involves an operational amplifier (Op-Amp) configuration where the output voltage (Ul) is determined by a combination of input voltages and resistive feedback. The input voltage, Vv, is processed through a gain structure that includes resistors Rx and Rv, which set the gain ratio for the operational amplifier. The expression "Rx/Rv" indicates that the gain is contingent on the values of these resistors, allowing for fine-tuning of the amplification factor.
Resistors R1, R2, and R3 serve as adjustable components for individual gains in the circuit. Each of these resistors can be selected or adjusted based on the desired amplification characteristics for each input, enabling tailored performance for specific applications. This selection process is crucial for ensuring that the output meets the required specifications.
Resistor R4 plays a significant role in the overall gain of the circuit, affecting all input signals collectively. By adjusting R4, the designer can control the total gain of the system, ensuring that the output remains within the desired operational range. The interaction between these resistors and the operational amplifier's feedback loop is vital for achieving stable and predictable performance in various electronic applications.
In summary, the described circuit utilizes a combination of resistors to manipulate gain levels for different inputs while maintaining control over the overall output voltage through careful selection and adjustment of component values. This allows for a versatile design suitable for a range of electronic signal processing tasks. The output of Ul is the sum of Vv and multiplied by Rx/Rv RJRV and respectively. Rlj R2, R3 are selected as required for individual gains. R4 affects gain of all these inputs.
The circuit under discussion involves an operational amplifier (Op-Amp) configuration where the output voltage (Ul) is determined by a combination of input voltages and resistive feedback. The input voltage, Vv, is processed through a gain structure that includes resistors Rx and Rv, which set the gain ratio for the operational amplifier. The expression "Rx/Rv" indicates that the gain is contingent on the values of these resistors, allowing for fine-tuning of the amplification factor.
Resistors R1, R2, and R3 serve as adjustable components for individual gains in the circuit. Each of these resistors can be selected or adjusted based on the desired amplification characteristics for each input, enabling tailored performance for specific applications. This selection process is crucial for ensuring that the output meets the required specifications.
Resistor R4 plays a significant role in the overall gain of the circuit, affecting all input signals collectively. By adjusting R4, the designer can control the total gain of the system, ensuring that the output remains within the desired operational range. The interaction between these resistors and the operational amplifier's feedback loop is vital for achieving stable and predictable performance in various electronic applications.
In summary, the described circuit utilizes a combination of resistors to manipulate gain levels for different inputs while maintaining control over the overall output voltage through careful selection and adjustment of component values. This allows for a versatile design suitable for a range of electronic signal processing tasks. The output of Ul is the sum of Vv and multiplied by Rx/Rv RJRV and respectively. Rlj R2, R3 are selected as required for individual gains. R4 affects gain of all these inputs.