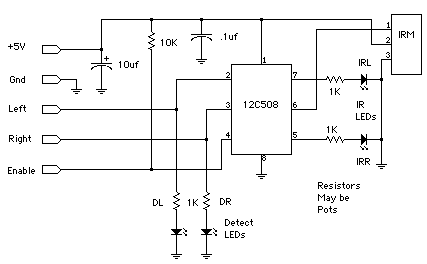
BUG DETECTOR
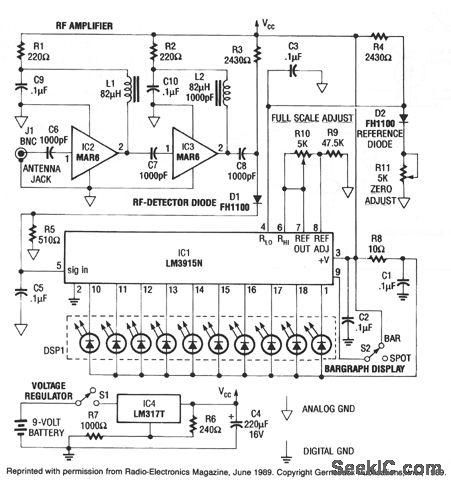
This RF detector can locate low-power transmitters (bugs) that are hidden from sight. It can sense the presence of a 1-mW transmitter at a distance of 20 feet, which is sensitive enough to detect the smallest bug. As the RF detector is brought closer to the bug, more segments of its LED bar-graph display illuminate, assisting in direction finding. The front end features a two-stage wideband RF amplifier and a forward-biased hot-carrier diode for detection. After detection, the signal is filtered and sent to IC1, an LM3915N bar-graph driver with a logarithmic output. Each successive LED segment represents a 3-dB step.
The RF detector circuit is designed to identify low-power RF signals, such as those emitted by covert transmitters. The circuit operates by amplifying the incoming RF signal through a two-stage wideband RF amplifier, which enhances the sensitivity of the device, allowing it to detect signals as weak as 1 mW from a distance of 20 feet. The use of a hot-carrier diode as the detection element is crucial, as it converts the RF signal into a baseband signal suitable for further processing.
Once the RF signal is detected, it undergoes filtering to remove unwanted frequencies and noise, ensuring that only the relevant signal is processed. The filtered signal is then fed into an LM3915N integrated circuit, which is specifically designed to drive an LED bar-graph display. The LM3915N interprets the amplitude of the incoming signal and provides a logarithmic output, allowing for a more intuitive visual representation of signal strength. Each segment of the LED bar-graph corresponds to a 3 dB increase in signal strength, enabling users to gauge the proximity of the RF source effectively.
The overall design of the RF detector emphasizes user-friendly operation, with the LED display providing immediate feedback on signal strength and direction. This makes the device particularly useful for applications in surveillance and monitoring, where locating hidden transmitters is critical. The combination of amplification, detection, and visual indication in this circuit creates a powerful tool for RF signal detection in various environments.This rf detector can locate low-power transmitters (bugs) that are hidden from sight. It can sense the presence of a 1-mW transmitter at 20 feet, which is sensitive enough to detect the tiniest bug. As you bring the rf detector closer to the bug, more and more segments of its LED bar-graph display light, which aids in direction finding.
The front end has a two-stage wideband rf amplifier, and a forward-biased hot-carrier diode for a detector. After detection, the signal is filtered and fed to IC1, an LM3915N bar-graph driver having a logarithmic output. Each successive LED segment represents a 3-dB step. 🔗 External reference
The RF detector circuit is designed to identify low-power RF signals, such as those emitted by covert transmitters. The circuit operates by amplifying the incoming RF signal through a two-stage wideband RF amplifier, which enhances the sensitivity of the device, allowing it to detect signals as weak as 1 mW from a distance of 20 feet. The use of a hot-carrier diode as the detection element is crucial, as it converts the RF signal into a baseband signal suitable for further processing.
Once the RF signal is detected, it undergoes filtering to remove unwanted frequencies and noise, ensuring that only the relevant signal is processed. The filtered signal is then fed into an LM3915N integrated circuit, which is specifically designed to drive an LED bar-graph display. The LM3915N interprets the amplitude of the incoming signal and provides a logarithmic output, allowing for a more intuitive visual representation of signal strength. Each segment of the LED bar-graph corresponds to a 3 dB increase in signal strength, enabling users to gauge the proximity of the RF source effectively.
The overall design of the RF detector emphasizes user-friendly operation, with the LED display providing immediate feedback on signal strength and direction. This makes the device particularly useful for applications in surveillance and monitoring, where locating hidden transmitters is critical. The combination of amplification, detection, and visual indication in this circuit creates a powerful tool for RF signal detection in various environments.This rf detector can locate low-power transmitters (bugs) that are hidden from sight. It can sense the presence of a 1-mW transmitter at 20 feet, which is sensitive enough to detect the tiniest bug. As you bring the rf detector closer to the bug, more and more segments of its LED bar-graph display light, which aids in direction finding.
The front end has a two-stage wideband rf amplifier, and a forward-biased hot-carrier diode for a detector. After detection, the signal is filtered and fed to IC1, an LM3915N bar-graph driver having a logarithmic output. Each successive LED segment represents a 3-dB step. 🔗 External reference