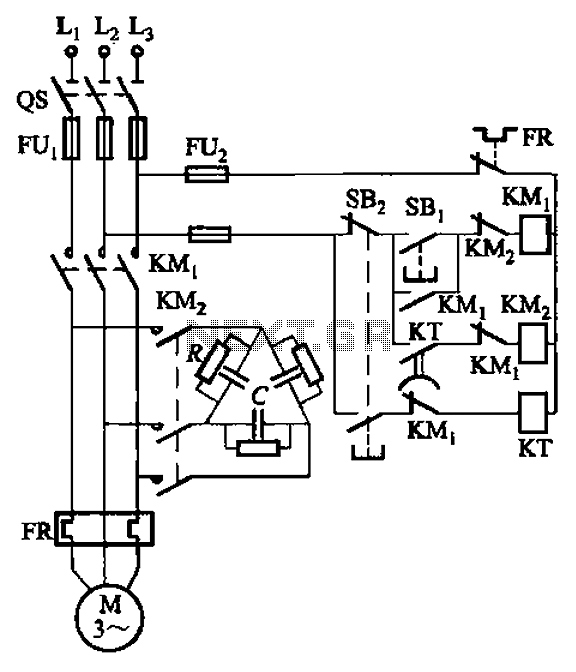
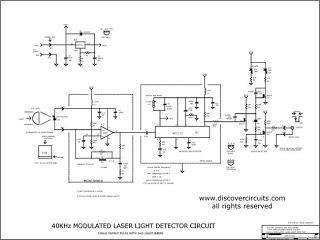
Building a device from a schematic
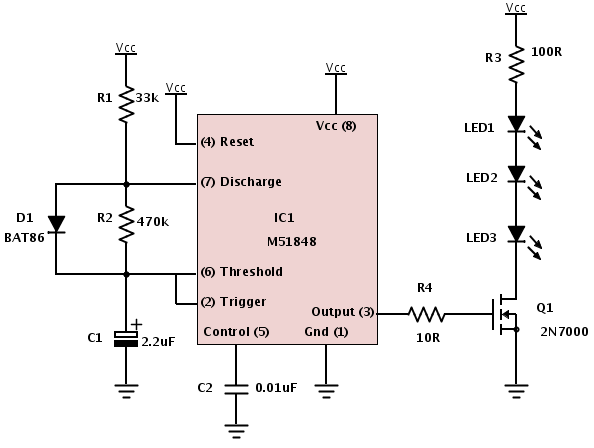
A common issue encountered is that individuals possess a schematic, also known as a circuit diagram, that they wish to construct. However, they discover that there are...
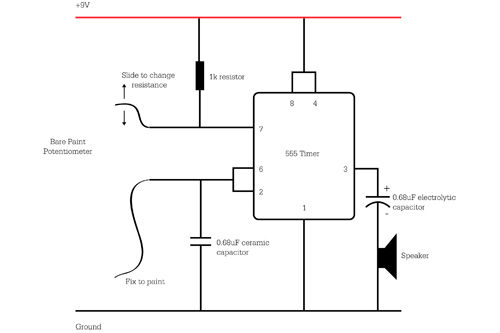
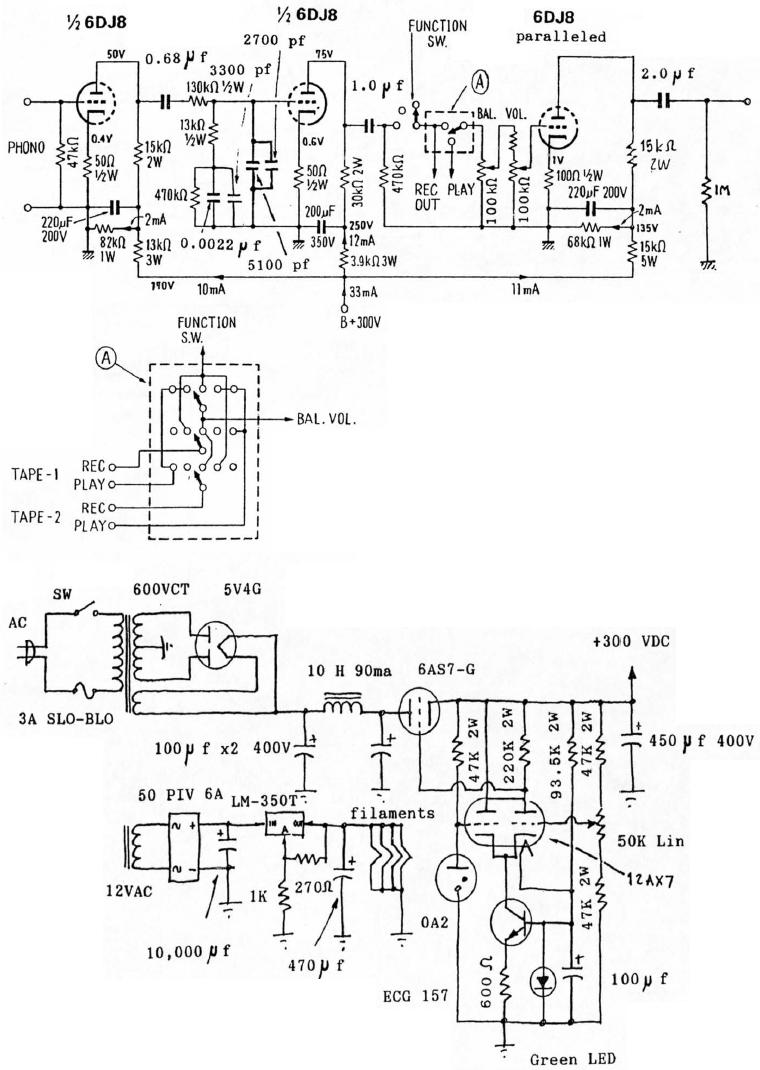
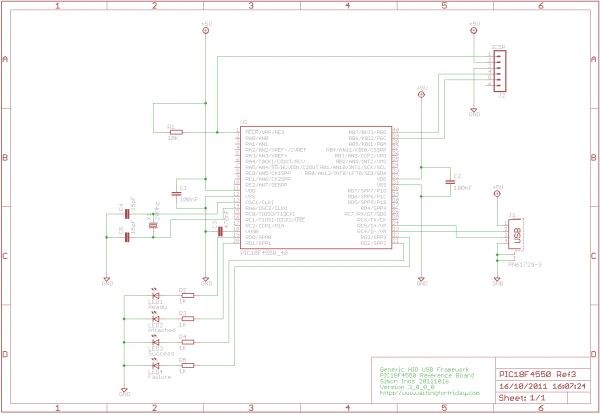
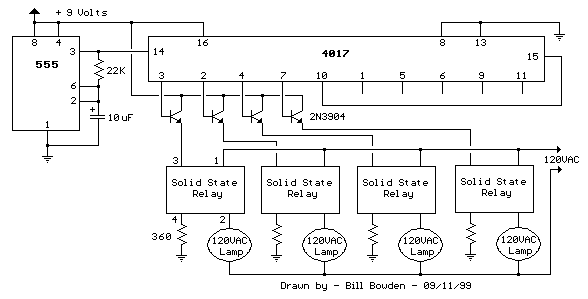
Building a circuit from a schematic requires a clear understanding of the components involved and their interconnections. A schematic diagram serves as a blueprint, providing essential information about the electrical connections and functionality of the circuit. Each symbol in the schematic represents a specific electronic component, such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and integrated circuits.
To successfully construct a circuit from a schematic, one must first identify all components listed in the diagram. This includes verifying the values of resistors, the capacitance of capacitors, and the specifications of any active components. It is also crucial to understand the power supply requirements, including voltage and current ratings, to ensure that the circuit operates correctly.
Next, the physical layout of the components on a breadboard or printed circuit board (PCB) should be planned. Proper placement can help minimize noise and interference, as well as facilitate easier troubleshooting later on. Following the schematic, connections between components should be made using appropriate wiring techniques to ensure reliable electrical contact.
Testing the circuit after assembly is a critical step. This involves using a multimeter to check for continuity in the connections and measuring voltages at various points to confirm that the circuit behaves as expected. If discrepancies arise, the schematic should be referenced to identify and rectify any errors in connections or component values.
In summary, constructing a circuit from a schematic requires careful attention to detail, a thorough understanding of electronic components, and systematic testing to ensure functionality.A problem we see a lot is that people have a schematic (otherwise knows as a circuit diagram) that they want to build. But they find there are.. 🔗 External reference
Building a circuit from a schematic requires a clear understanding of the components involved and their interconnections. A schematic diagram serves as a blueprint, providing essential information about the electrical connections and functionality of the circuit. Each symbol in the schematic represents a specific electronic component, such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and integrated circuits.
To successfully construct a circuit from a schematic, one must first identify all components listed in the diagram. This includes verifying the values of resistors, the capacitance of capacitors, and the specifications of any active components. It is also crucial to understand the power supply requirements, including voltage and current ratings, to ensure that the circuit operates correctly.
Next, the physical layout of the components on a breadboard or printed circuit board (PCB) should be planned. Proper placement can help minimize noise and interference, as well as facilitate easier troubleshooting later on. Following the schematic, connections between components should be made using appropriate wiring techniques to ensure reliable electrical contact.
Testing the circuit after assembly is a critical step. This involves using a multimeter to check for continuity in the connections and measuring voltages at various points to confirm that the circuit behaves as expected. If discrepancies arise, the schematic should be referenced to identify and rectify any errors in connections or component values.
In summary, constructing a circuit from a schematic requires careful attention to detail, a thorough understanding of electronic components, and systematic testing to ensure functionality.A problem we see a lot is that people have a schematic (otherwise knows as a circuit diagram) that they want to build. But they find there are.. 🔗 External reference