Single-speed motor excitation power from a braking circuit
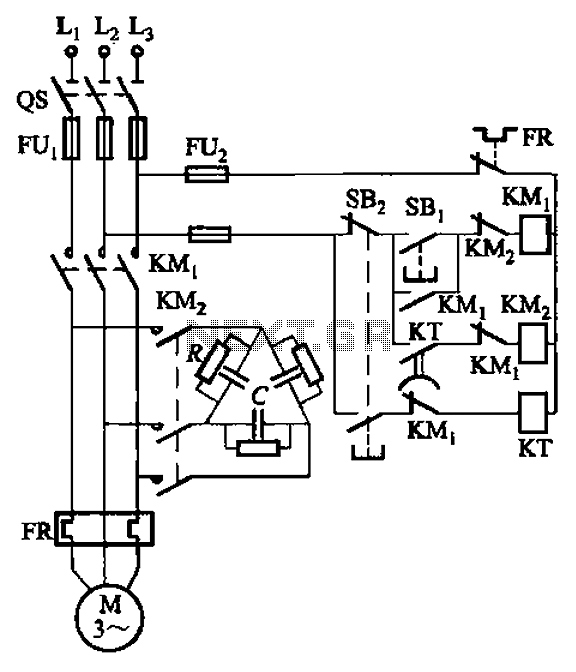
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-151 consists of capacitor banks arranged in a specific configuration. Figure 3-151 (a) depicts capacitor banks connected in a shaped manner, which is suitable for use with shaped or Y-connected motors. Figure 3-151 (b) shows Y-connected capacitor banks, which are applicable to Y-connected motors. The shaped capacitor connection requires a smaller electrical capacity but necessitates a higher voltage rating of 600V or above. For various power motors, refer to the C and R selection in Table 3-2.
The circuit design presented in Figure 3-151 is an essential configuration for enhancing the performance of Y-connected motors through the use of capacitor banks. The arrangement in Figure 3-151 (a) emphasizes a shaped connection, which optimizes the reactive power compensation for motors that operate under specific load conditions. This configuration is particularly beneficial for applications where the power factor needs to be improved without significantly increasing the physical footprint of the capacitor banks.
In contrast, Figure 3-151 (b) illustrates a more conventional Y-connected capacitor bank layout, which is straightforward and effective for standard Y-connected motor applications. This arrangement allows for balanced voltage distribution across the phases, ensuring that each phase receives adequate reactive power support.
It is important to note that the shaped capacitor connection is designed to operate at higher voltage levels, typically rated at 600V or more. This requirement arises due to the nature of the electrical stresses encountered in such configurations, making it imperative to select capacitors that can withstand these conditions without failure.
For the appropriate selection of capacitors and resistors based on motor power ratings, Table 3-2 serves as a reference guide. This table provides critical parameters that aid in determining the optimal values of capacitance (C) and resistance (R) necessary for achieving desired operational characteristics in various motor applications, ensuring efficiency and reliability in the overall system design. Circuit shown in Figure 3-151. Figure 3-151 (a) of the capacitor banks connected into shape, it applies to shaped or Y-connected motor; Fig. 3-151 (b) of the Y-connected capaci tor banks, it applies to Y-connected motor. Shaped capacitor using connection, the required electrical smaller capacity, but requires higher voltage value (600V or more). Different power motors, C and R selection Table 3-2.
The circuit design presented in Figure 3-151 is an essential configuration for enhancing the performance of Y-connected motors through the use of capacitor banks. The arrangement in Figure 3-151 (a) emphasizes a shaped connection, which optimizes the reactive power compensation for motors that operate under specific load conditions. This configuration is particularly beneficial for applications where the power factor needs to be improved without significantly increasing the physical footprint of the capacitor banks.
In contrast, Figure 3-151 (b) illustrates a more conventional Y-connected capacitor bank layout, which is straightforward and effective for standard Y-connected motor applications. This arrangement allows for balanced voltage distribution across the phases, ensuring that each phase receives adequate reactive power support.
It is important to note that the shaped capacitor connection is designed to operate at higher voltage levels, typically rated at 600V or more. This requirement arises due to the nature of the electrical stresses encountered in such configurations, making it imperative to select capacitors that can withstand these conditions without failure.
For the appropriate selection of capacitors and resistors based on motor power ratings, Table 3-2 serves as a reference guide. This table provides critical parameters that aid in determining the optimal values of capacitance (C) and resistance (R) necessary for achieving desired operational characteristics in various motor applications, ensuring efficiency and reliability in the overall system design. Circuit shown in Figure 3-151. Figure 3-151 (a) of the capacitor banks connected into shape, it applies to shaped or Y-connected motor; Fig. 3-151 (b) of the Y-connected capaci tor banks, it applies to Y-connected motor. Shaped capacitor using connection, the required electrical smaller capacity, but requires higher voltage value (600V or more). Different power motors, C and R selection Table 3-2.