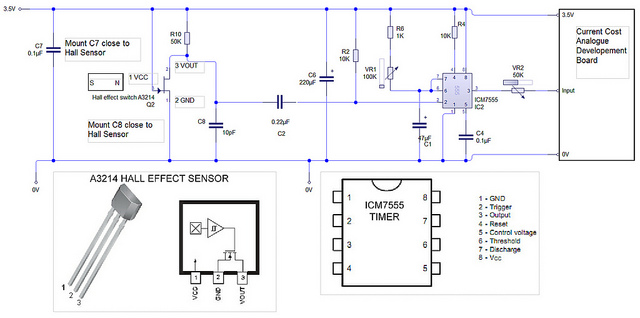
Cable Tester Circuit
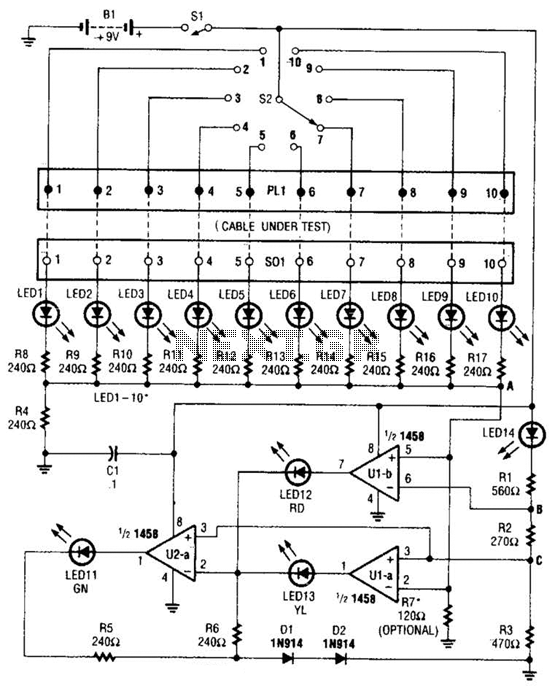
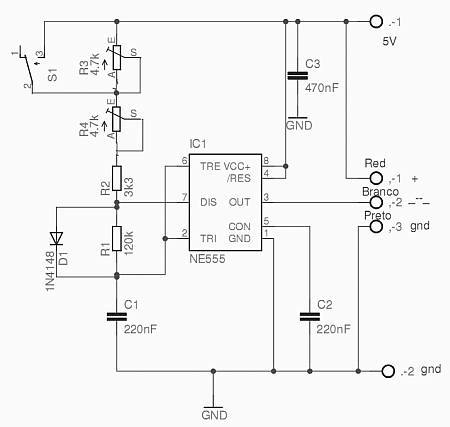
The cable tester utilizes two operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured as window comparators to detect short or open circuit conditions. A third op-amp comparator is employed to indicate a properly functioning circuit, meaning it is neither open nor shorted. Colored light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are used to represent the status of individual conductors within the cable being tested: a red LED indicates a short between conductors, a yellow LED signifies an open conductor, and a green LED shows that the conductor is functioning correctly. Additionally, a bar-graph display with individual LEDs is implemented to indicate which specific conductor in the cable is currently being tested.
The cable tester circuit is designed for efficient and reliable testing of cable integrity. The two op-amps configured as window comparators are set up to monitor the voltage levels across the cable conductors. When a short circuit occurs, the voltage level drops below a predefined threshold, triggering the red LED to illuminate, signaling the presence of a fault. Conversely, if an open circuit is detected, the voltage remains above the threshold, and the yellow LED is activated to indicate an open conductor.
The third op-amp comparator plays a crucial role in verifying the integrity of the circuit. It ensures that when all conductors are intact, the green LED lights up, providing a clear visual indication that the cable is functioning as intended.
The inclusion of a bar-graph display enhances the usability of the tester by allowing for real-time monitoring of each conductor's status. Each LED in the bar-graph corresponds to a specific conductor, illuminating sequentially as the tester cycles through the conductors. This feature not only facilitates quick identification of faults but also provides a comprehensive overview of the cable's condition.
Overall, the design of this cable tester emphasizes clarity and functionality, utilizing simple yet effective components to deliver accurate testing results. The use of color-coded LEDs and a bar-graph display ensures that users can easily interpret the status of the cable under test, making it an invaluable tool for technicians and engineers in the field of electronics. At the heart of the cable tester are two op amps, which are used as a window- comparator to indicate a short- or open-circuit condition. A third op-amp comparator is used to indicate a good circuit (i.e., neither open nor shorted). Colored LEDs are used to show the condition of individual conductors within the cable under test; a red one to indicate a short between conductors, a yellow one to identify an open conductor, and a green one to signify that the conductor is okay.
Individual LEDs of a bar-graph display are used to show which conductor in the cable is being tested.
The cable tester circuit is designed for efficient and reliable testing of cable integrity. The two op-amps configured as window comparators are set up to monitor the voltage levels across the cable conductors. When a short circuit occurs, the voltage level drops below a predefined threshold, triggering the red LED to illuminate, signaling the presence of a fault. Conversely, if an open circuit is detected, the voltage remains above the threshold, and the yellow LED is activated to indicate an open conductor.
The third op-amp comparator plays a crucial role in verifying the integrity of the circuit. It ensures that when all conductors are intact, the green LED lights up, providing a clear visual indication that the cable is functioning as intended.
The inclusion of a bar-graph display enhances the usability of the tester by allowing for real-time monitoring of each conductor's status. Each LED in the bar-graph corresponds to a specific conductor, illuminating sequentially as the tester cycles through the conductors. This feature not only facilitates quick identification of faults but also provides a comprehensive overview of the cable's condition.
Overall, the design of this cable tester emphasizes clarity and functionality, utilizing simple yet effective components to deliver accurate testing results. The use of color-coded LEDs and a bar-graph display ensures that users can easily interpret the status of the cable under test, making it an invaluable tool for technicians and engineers in the field of electronics. At the heart of the cable tester are two op amps, which are used as a window- comparator to indicate a short- or open-circuit condition. A third op-amp comparator is used to indicate a good circuit (i.e., neither open nor shorted). Colored LEDs are used to show the condition of individual conductors within the cable under test; a red one to indicate a short between conductors, a yellow one to identify an open conductor, and a green one to signify that the conductor is okay.
Individual LEDs of a bar-graph display are used to show which conductor in the cable is being tested.