connect a lcd to a picaxe
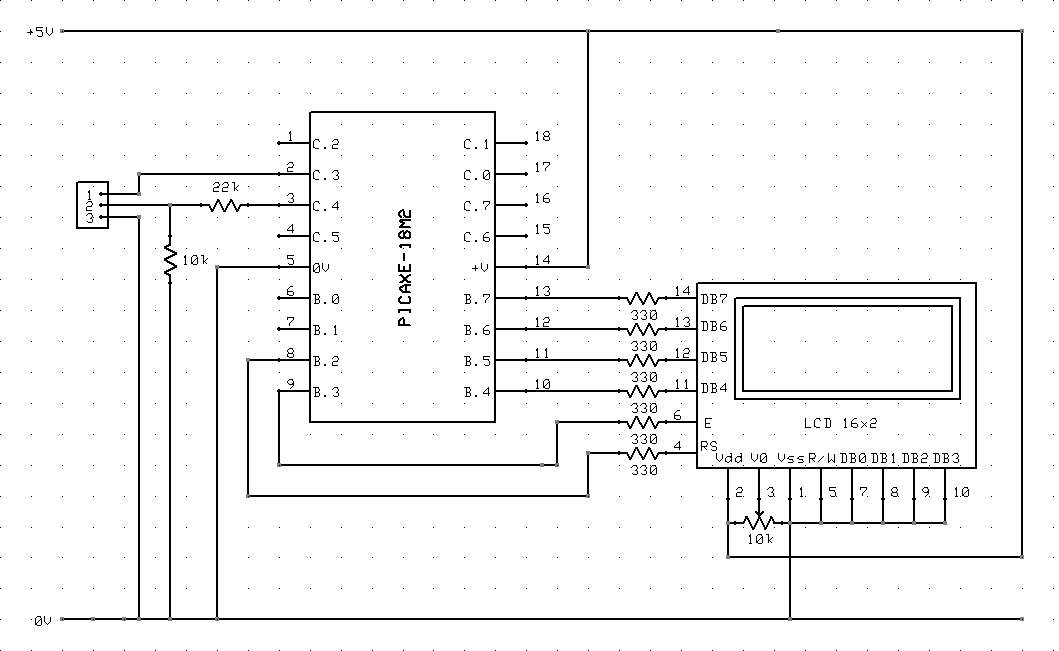
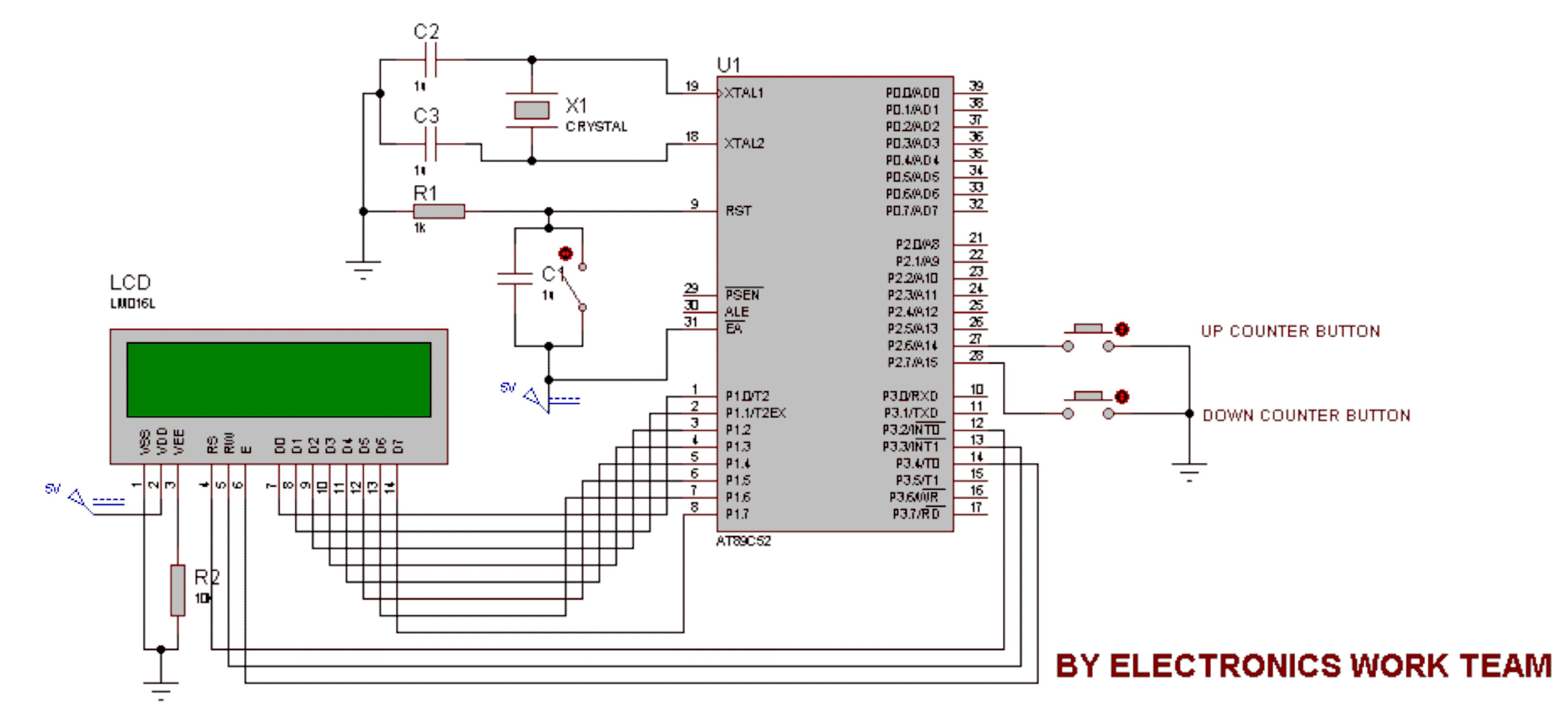
The circuit diagram and code on how to connect a 16x2 LCD to a PICAXE-18M2 microcontroller.
The circuit involves interfacing a 16x2 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) with a PICAXE-18M2 microcontroller. The 16x2 LCD is a popular display module that can show two lines of 16 characters each. The PICAXE-18M2 is a versatile microcontroller that allows for easy programming and control of various electronic components.
To connect the LCD to the PICAXE-18M2, the following connections should be made:
1. **Power Connections**:
- Connect the VSS pin of the LCD to the ground (GND) of the PICAXE.
- Connect the VDD pin of the LCD to the +5V power supply.
2. **Control Pins**:
- The RS (Register Select) pin should be connected to one of the digital output pins of the PICAXE (e.g., pin C.0).
- The RW (Read/Write) pin should be connected to ground to set the LCD in write mode.
- The E (Enable) pin should be connected to another digital output pin (e.g., pin C.1).
3. **Data Pins**:
- The data pins D0 to D7 of the LCD can be connected to the digital output pins of the PICAXE (e.g., D.0 to D.7). However, for simplicity, it is common to use only the upper four data pins (D4 to D7) for 4-bit mode operation.
- Connect D4 to pin C.2, D5 to pin C.3, D6 to pin C.4, and D7 to pin C.5 of the PICAXE.
4. **Additional Components**:
- A potentiometer (typically 10kΩ) can be connected between the VDD and GND, with the wiper connected to the V0 pin of the LCD. This is used for adjusting the contrast of the display.
The programming code for the PICAXE-18M2 should include initialization commands for the LCD, setting it to 4-bit mode, and providing functions to write characters and strings to the display. The typical sequence of commands includes initializing the display, setting the cursor position, and sending data to be displayed.
This setup allows for the effective use of the LCD with the PICAXE-18M2, enabling the display of text-based information in various applications. Proper power management and signal integrity should be maintained to ensure reliable operation of the LCD module.The circuit diagram and code on how to connect an 16x2 LCD to a PICAXE-18M2 microcontroller.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit involves interfacing a 16x2 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) with a PICAXE-18M2 microcontroller. The 16x2 LCD is a popular display module that can show two lines of 16 characters each. The PICAXE-18M2 is a versatile microcontroller that allows for easy programming and control of various electronic components.
To connect the LCD to the PICAXE-18M2, the following connections should be made:
1. **Power Connections**:
- Connect the VSS pin of the LCD to the ground (GND) of the PICAXE.
- Connect the VDD pin of the LCD to the +5V power supply.
2. **Control Pins**:
- The RS (Register Select) pin should be connected to one of the digital output pins of the PICAXE (e.g., pin C.0).
- The RW (Read/Write) pin should be connected to ground to set the LCD in write mode.
- The E (Enable) pin should be connected to another digital output pin (e.g., pin C.1).
3. **Data Pins**:
- The data pins D0 to D7 of the LCD can be connected to the digital output pins of the PICAXE (e.g., D.0 to D.7). However, for simplicity, it is common to use only the upper four data pins (D4 to D7) for 4-bit mode operation.
- Connect D4 to pin C.2, D5 to pin C.3, D6 to pin C.4, and D7 to pin C.5 of the PICAXE.
4. **Additional Components**:
- A potentiometer (typically 10kΩ) can be connected between the VDD and GND, with the wiper connected to the V0 pin of the LCD. This is used for adjusting the contrast of the display.
The programming code for the PICAXE-18M2 should include initialization commands for the LCD, setting it to 4-bit mode, and providing functions to write characters and strings to the display. The typical sequence of commands includes initializing the display, setting the cursor position, and sending data to be displayed.
This setup allows for the effective use of the LCD with the PICAXE-18M2, enabling the display of text-based information in various applications. Proper power management and signal integrity should be maintained to ensure reliable operation of the LCD module.The circuit diagram and code on how to connect an 16x2 LCD to a PICAXE-18M2 microcontroller.. 🔗 External reference