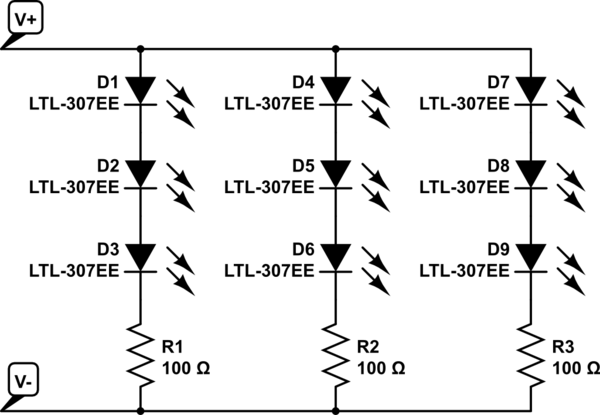
led brightness control circuit
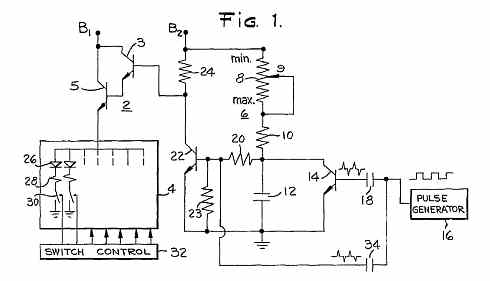
LED brightness control circuit: A simple circuit can be used to control the brightness level of an LED display.
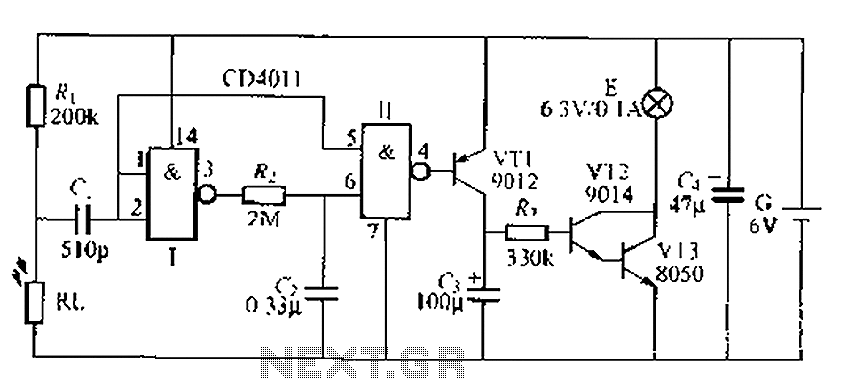
The LED brightness control circuit is designed to adjust the illumination level of an LED display according to user preferences or environmental conditions. This circuit typically employs a variable resistor or a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique to modulate the current flowing through the LED, effectively changing its brightness.
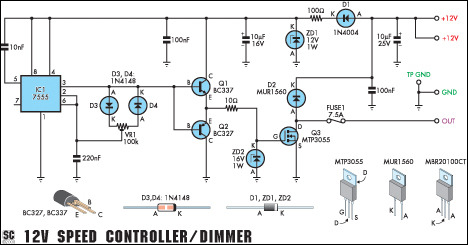
In a basic configuration, the circuit may consist of a microcontroller, a transistor, and a resistor in series with the LED. The microcontroller generates a PWM signal that controls the base of the transistor, allowing it to act as a switch. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average current supplied to the LED is altered, which in turn adjusts its brightness. A higher duty cycle results in a brighter LED, while a lower duty cycle dims the LED.
For applications requiring manual control, a potentiometer can be integrated into the circuit. The variable resistor allows the user to fine-tune the resistance, thereby changing the voltage at the input pin of the microcontroller. This input can be read as an analog signal, and the microcontroller can adjust the PWM output accordingly.
In addition to basic brightness control, this circuit can be enhanced with features such as automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light conditions. This can be achieved by incorporating a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or a phototransistor that detects surrounding light levels. The microcontroller can then adjust the PWM signal to maintain optimal visibility of the LED display.
Overall, the LED brightness control circuit is a versatile solution for managing LED illumination, suitable for various applications ranging from simple displays to more complex lighting systems.Led brightness control circuit : How to use a simple circuit to control the brightness level of an LED display.. 🔗 External reference
The LED brightness control circuit is designed to adjust the illumination level of an LED display according to user preferences or environmental conditions. This circuit typically employs a variable resistor or a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique to modulate the current flowing through the LED, effectively changing its brightness.
In a basic configuration, the circuit may consist of a microcontroller, a transistor, and a resistor in series with the LED. The microcontroller generates a PWM signal that controls the base of the transistor, allowing it to act as a switch. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average current supplied to the LED is altered, which in turn adjusts its brightness. A higher duty cycle results in a brighter LED, while a lower duty cycle dims the LED.
For applications requiring manual control, a potentiometer can be integrated into the circuit. The variable resistor allows the user to fine-tune the resistance, thereby changing the voltage at the input pin of the microcontroller. This input can be read as an analog signal, and the microcontroller can adjust the PWM output accordingly.
In addition to basic brightness control, this circuit can be enhanced with features such as automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light conditions. This can be achieved by incorporating a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or a phototransistor that detects surrounding light levels. The microcontroller can then adjust the PWM signal to maintain optimal visibility of the LED display.
Overall, the LED brightness control circuit is a versatile solution for managing LED illumination, suitable for various applications ranging from simple displays to more complex lighting systems.Led brightness control circuit : How to use a simple circuit to control the brightness level of an LED display.. 🔗 External reference