clock Crystal circuit works in breadboard but not in perfboard
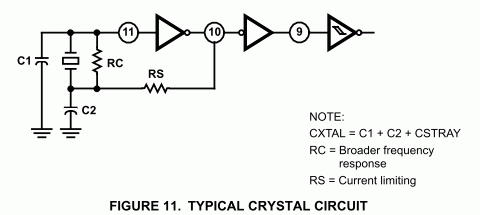
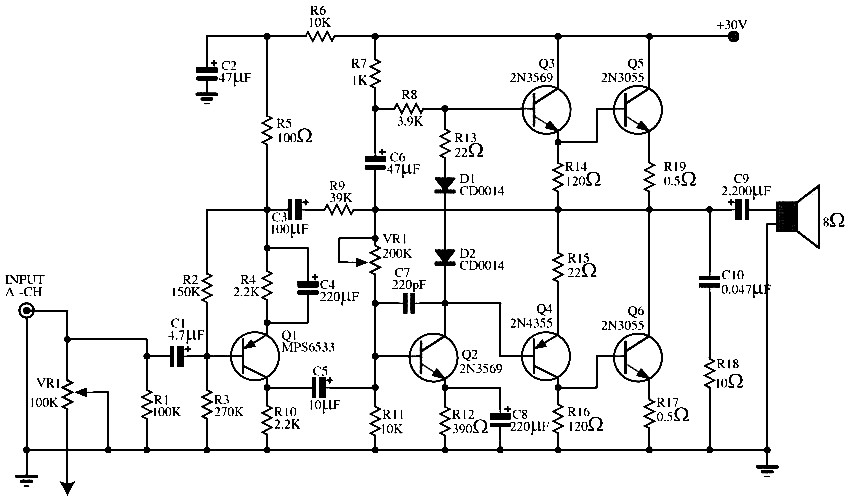
The circuit operates correctly on a breadboard, with the LED blinking at a frequency of 2 Hz. However, when soldered onto a perfboard, the LED blinks at a significantly higher frequency, approximately 10 Hz, although this is an estimation as there is no measuring device available. The circuit has been assembled multiple times on both the breadboard and perfboard, yielding consistent results. All connections have been thoroughly checked and appear to be in order. Despite attempts to replace the two 15 pF capacitors with two 22 pF capacitors, the issue persists. The soldering quality is suboptimal due to the individual's beginner status, resulting in a somewhat messy appearance, but all connections have been verified as correct.
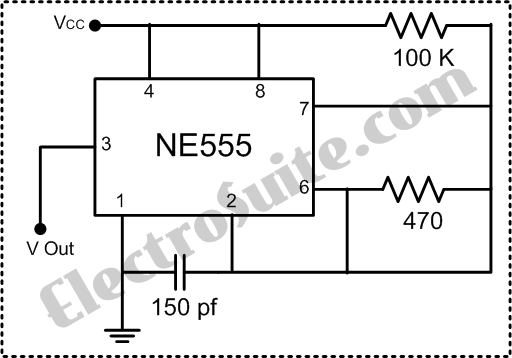
The circuit in question appears to be a simple LED blinking circuit, likely utilizing a 555 timer or a similar astable multivibrator configuration. The discrepancy in blinking frequency between the breadboard and perfboard could be attributed to several factors, including variations in capacitance due to the use of different components, soldering issues leading to unintended connections, or differences in the layout affecting the circuit's performance.
In a typical 555 timer circuit, the blinking frequency is determined by the resistors and capacitors used. The formula for the frequency (f) of the blinking LED is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \times C} \]
where R1 and R2 are the resistances in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads. If the capacitors have been changed from 15 pF to 22 pF, it is essential to recalculate the expected frequency to confirm that it aligns with the observed behavior.
Furthermore, soldering on a perfboard introduces potential issues such as cold solder joints, bridging, or unintentional shorts, which can alter the circuit's characteristics. It is advisable to inspect the solder joints closely and ensure that there are no unintended connections between adjacent pads. Additionally, the layout of the perfboard may introduce parasitic capacitance or inductance, which could affect the timing characteristics of the circuit.
To troubleshoot the issue, it is recommended to:
1. Reassess the component values and ensure they are correctly rated and functioning.
2. Double-check all solder joints for quality and integrity, ensuring no shorts or cold joints exist.
3. If possible, utilize a multimeter to measure the resistances and capacitances in the circuit to confirm they match the expected values.
4. Consider using a different perfboard or layout to minimize potential interference from parasitic elements.
These steps may help diagnose the cause of the unexpected blinking frequency when transitioning from breadboard to perfboard.It works perfectly on the breadboard, where I can see the LED blinking at 2 Hz. However, when I try to solder it on the perfboard, it blinks much faster. I don`t have a way to measure, but I`d say something like 10 Hz. I tried to mount three times on the breadboard and three times on the perfboard, and always get the same result. I checked and rechecked the connections, and everything seems to be fine. I have no idea where the problem might be. What could be wrong I tried replacing the two 15pF capacitor for two 22pF, but it didn`t help. Unfortunately, I don`t have access to a oscilloscope to see what`s happening inside. The second one is the soldering side. Please excuse my bad soldering, I`m a beginner, and it`s a little messy from all soldering/desoldering. However, I tested all connections and the connections are correct. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question appears to be a simple LED blinking circuit, likely utilizing a 555 timer or a similar astable multivibrator configuration. The discrepancy in blinking frequency between the breadboard and perfboard could be attributed to several factors, including variations in capacitance due to the use of different components, soldering issues leading to unintended connections, or differences in the layout affecting the circuit's performance.
In a typical 555 timer circuit, the blinking frequency is determined by the resistors and capacitors used. The formula for the frequency (f) of the blinking LED is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \times C} \]
where R1 and R2 are the resistances in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads. If the capacitors have been changed from 15 pF to 22 pF, it is essential to recalculate the expected frequency to confirm that it aligns with the observed behavior.
Furthermore, soldering on a perfboard introduces potential issues such as cold solder joints, bridging, or unintentional shorts, which can alter the circuit's characteristics. It is advisable to inspect the solder joints closely and ensure that there are no unintended connections between adjacent pads. Additionally, the layout of the perfboard may introduce parasitic capacitance or inductance, which could affect the timing characteristics of the circuit.
To troubleshoot the issue, it is recommended to:
1. Reassess the component values and ensure they are correctly rated and functioning.
2. Double-check all solder joints for quality and integrity, ensuring no shorts or cold joints exist.
3. If possible, utilize a multimeter to measure the resistances and capacitances in the circuit to confirm they match the expected values.
4. Consider using a different perfboard or layout to minimize potential interference from parasitic elements.
These steps may help diagnose the cause of the unexpected blinking frequency when transitioning from breadboard to perfboard.It works perfectly on the breadboard, where I can see the LED blinking at 2 Hz. However, when I try to solder it on the perfboard, it blinks much faster. I don`t have a way to measure, but I`d say something like 10 Hz. I tried to mount three times on the breadboard and three times on the perfboard, and always get the same result. I checked and rechecked the connections, and everything seems to be fine. I have no idea where the problem might be. What could be wrong I tried replacing the two 15pF capacitor for two 22pF, but it didn`t help. Unfortunately, I don`t have access to a oscilloscope to see what`s happening inside. The second one is the soldering side. Please excuse my bad soldering, I`m a beginner, and it`s a little messy from all soldering/desoldering. However, I tested all connections and the connections are correct. 🔗 External reference