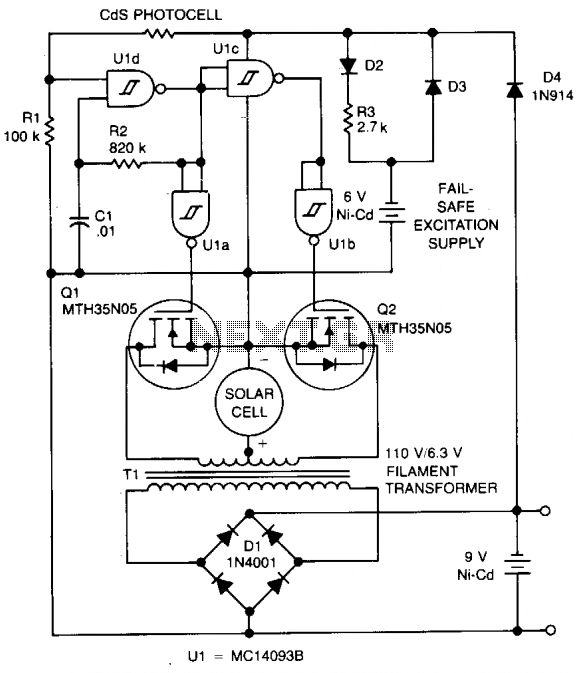
Cloth from idling stop saving circuit
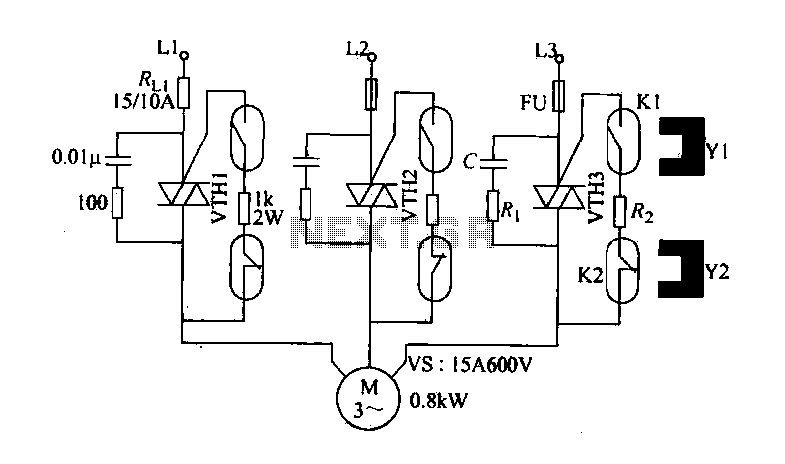
The circuit diagram illustrates a female textile machine power control circuit. VTH1-VTH3 represent TRIACs, while R and C form the absorption line. Rz serves as the triggering current limiting resistor. K1 is designated for starting the reed, and K2 is the first stop reed. Y1 and Y2 are magnets. The three-phase power supply, consisting of L1, L2, and L3, is applied to the motor M through VTH1-VTH3. When the clutch lever is moved, it pushes to the Y1 position, connecting the internal contacts of K1, which allows VTH1-VTH3 to conduct and energize motor M, enabling it to run. Upon shutdown, the clutch lever is moved to the stop near magnetic Y2 and K2, causing the normally closed contacts of K2 to open. This action deactivates VTH1-VTH3, resulting in the motor M stopping.
The female textile machine power control circuit is designed to manage the operation of a motor in a textile machine through a series of interconnected components. The primary elements include TRIACs (VTH1-VTH3) which act as electronic switches to control the flow of current to the motor. The absorption line, composed of resistors (R) and capacitors (C), is utilized to mitigate voltage spikes and ensure stable operation of the TRIACs.
The triggering current limiting resistor (Rz) is crucial for protecting the circuit from excessive current that could potentially damage the TRIACs or other components. K1 and K2 are reed switches that facilitate the control of the motor's operation. K1 initiates the motor's operation when the clutch lever is engaged, while K2 serves as a safety mechanism to stop the motor when the lever is disengaged.
The circuit is powered by a three-phase supply (L1, L2, L3), which is essential for providing sufficient power to the motor (M). The operation begins when the clutch lever is pushed into the Y1 position, which activates K1. This action allows VTH1-VTH3 to conduct, thereby energizing the motor and enabling it to run.
For stopping the motor, the clutch lever is moved to a position near the magnetic reed switch K2, which opens its normally closed contacts. This action interrupts the triggering signals to the TRIACs, leading to their deactivation and subsequently halting the motor.
This circuit design is critical for ensuring efficient operation and safety in textile machinery, providing both control and protection for the motor and associated components.Female textile machine power control circuit shown in a diagram, VTH1-VTH3 is TRIAC, R, and C is the absorption line, Rz is triggering the current limiting resistor, Kl is to s tart reed. K2 is the first stop Reed, Yl, Y2 is a magnet. Three-phase power Ll, L2, L3 through V th1 - VTH3 applied to the motor M on. Moving the clutch lever, the push to boot Yl position, Kl internal contacts connected, VTH1-VTH3 touch made conducting, energizing the motor M is running; shutdown, mounted on the clutch lever from the stop near the magnetic J Y2 K2, K2 inside the normally closed contacts break l open. Trigger off go the same way, VTH1 ~ VTH3 have been turned off, the motor M is stopped,
The female textile machine power control circuit is designed to manage the operation of a motor in a textile machine through a series of interconnected components. The primary elements include TRIACs (VTH1-VTH3) which act as electronic switches to control the flow of current to the motor. The absorption line, composed of resistors (R) and capacitors (C), is utilized to mitigate voltage spikes and ensure stable operation of the TRIACs.
The triggering current limiting resistor (Rz) is crucial for protecting the circuit from excessive current that could potentially damage the TRIACs or other components. K1 and K2 are reed switches that facilitate the control of the motor's operation. K1 initiates the motor's operation when the clutch lever is engaged, while K2 serves as a safety mechanism to stop the motor when the lever is disengaged.
The circuit is powered by a three-phase supply (L1, L2, L3), which is essential for providing sufficient power to the motor (M). The operation begins when the clutch lever is pushed into the Y1 position, which activates K1. This action allows VTH1-VTH3 to conduct, thereby energizing the motor and enabling it to run.
For stopping the motor, the clutch lever is moved to a position near the magnetic reed switch K2, which opens its normally closed contacts. This action interrupts the triggering signals to the TRIACs, leading to their deactivation and subsequently halting the motor.
This circuit design is critical for ensuring efficient operation and safety in textile machinery, providing both control and protection for the motor and associated components.Female textile machine power control circuit shown in a diagram, VTH1-VTH3 is TRIAC, R, and C is the absorption line, Rz is triggering the current limiting resistor, Kl is to s tart reed. K2 is the first stop Reed, Yl, Y2 is a magnet. Three-phase power Ll, L2, L3 through V th1 - VTH3 applied to the motor M on. Moving the clutch lever, the push to boot Yl position, Kl internal contacts connected, VTH1-VTH3 touch made conducting, energizing the motor M is running; shutdown, mounted on the clutch lever from the stop near the magnetic J Y2 K2, K2 inside the normally closed contacts break l open. Trigger off go the same way, VTH1 ~ VTH3 have been turned off, the motor M is stopped,