cmos based single zone alarm

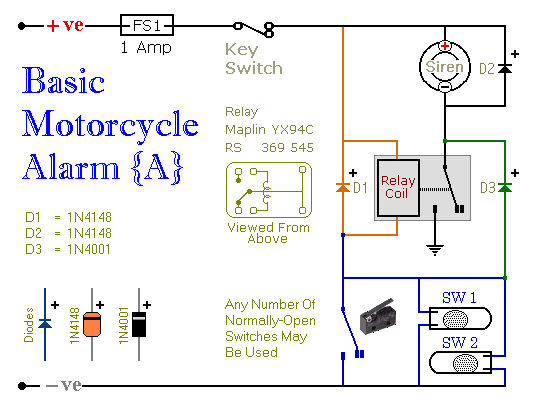
This circuit includes automatic exit and entry delays, a timed bell cut-off, and a system reset feature. It is designed to support both normally-open and normally-closed switches and can accommodate standard input devices such as pressure mats, magnetic reed contacts, foil tape, passive infrared sensors (PIRs), and inertia sensors.
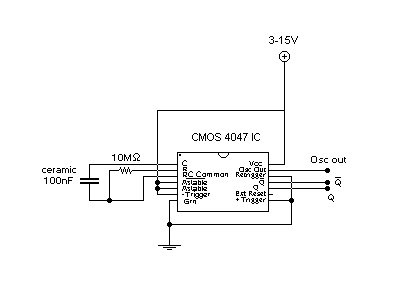
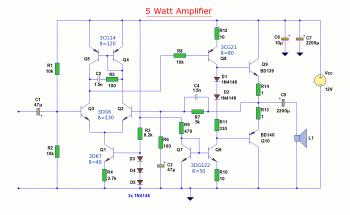
The circuit operates by managing the timing of entry and exit delays, which allows users to have a grace period when entering or exiting a secured area. The timed bell cut-off feature ensures that any alarm or notification sound will automatically stop after a predetermined duration, preventing unnecessary disturbances. Additionally, the system reset function allows the circuit to return to its initial state after an alarm condition is cleared or after a manual reset is performed.
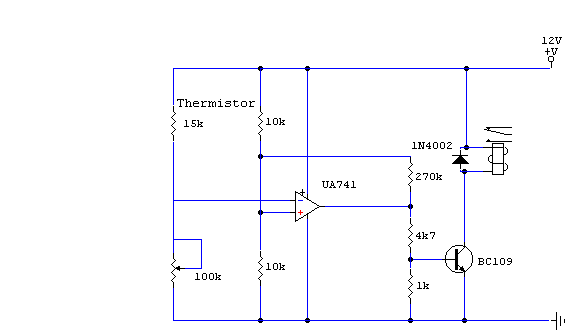
Input devices are critical for the operation of this circuit, as they provide the necessary signals to trigger the system. Pressure mats can detect the presence of an individual by sensing weight, while magnetic reed contacts can be used on doors or windows to signal when they are opened or closed. Foil tape can serve as a perimeter sensor, detecting any breaches along its length. PIRs are effective in sensing movement based on changes in infrared radiation, making them suitable for detecting human presence. Inertia sensors can detect motion or changes in position, adding another layer of security.
The circuit's design incorporates flexibility to allow integration with various types of switches and sensors, making it adaptable to different security environments. The inclusion of both normally-open and normally-closed switch configurations enhances its versatility, enabling it to interface with a wide range of security devices. Overall, this circuit is engineered to provide reliable security management with user-friendly features that enhance its functionality in real-world applications.This circuit features automatic Exit/Entry delays, timed Bell Cut-off and System Reset. It has provision for normally-open and normally-closed switches and will accommodate the usual input devices (Pressure Mats, Magnetic Reed contacts, Foil Tape, PIRs and Inertia Sensors).. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by managing the timing of entry and exit delays, which allows users to have a grace period when entering or exiting a secured area. The timed bell cut-off feature ensures that any alarm or notification sound will automatically stop after a predetermined duration, preventing unnecessary disturbances. Additionally, the system reset function allows the circuit to return to its initial state after an alarm condition is cleared or after a manual reset is performed.
Input devices are critical for the operation of this circuit, as they provide the necessary signals to trigger the system. Pressure mats can detect the presence of an individual by sensing weight, while magnetic reed contacts can be used on doors or windows to signal when they are opened or closed. Foil tape can serve as a perimeter sensor, detecting any breaches along its length. PIRs are effective in sensing movement based on changes in infrared radiation, making them suitable for detecting human presence. Inertia sensors can detect motion or changes in position, adding another layer of security.
The circuit's design incorporates flexibility to allow integration with various types of switches and sensors, making it adaptable to different security environments. The inclusion of both normally-open and normally-closed switch configurations enhances its versatility, enabling it to interface with a wide range of security devices. Overall, this circuit is engineered to provide reliable security management with user-friendly features that enhance its functionality in real-world applications.This circuit features automatic Exit/Entry delays, timed Bell Cut-off and System Reset. It has provision for normally-open and normally-closed switches and will accommodate the usual input devices (Pressure Mats, Magnetic Reed contacts, Foil Tape, PIRs and Inertia Sensors).. 🔗 External reference