coin detector and counter
Coin detector and counter: How to detect different types of coins from their effect on an oscillating magnetic field.
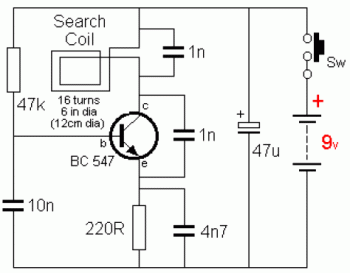
A coin detector and counter operates by utilizing the principles of electromagnetic induction to identify and differentiate between various types of coins. The system typically consists of an oscillating magnetic field generated by an inductor or coil. When a coin enters the field, it alters the magnetic flux due to its conductive properties. This change in the magnetic field induces a current in the coin, which in turn generates its own magnetic field.
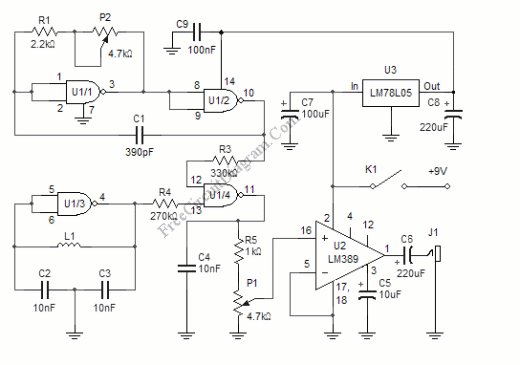
The circuit design usually includes a high-frequency oscillator to produce the oscillating magnetic field. The frequency of oscillation is chosen based on the expected properties of the coins to be detected, as different metals will interact with the magnetic field differently. The induced currents in the coins will produce varying impedance, which can be measured by a microcontroller or an analog circuit.
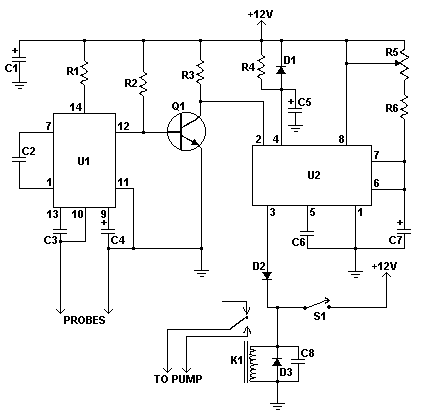
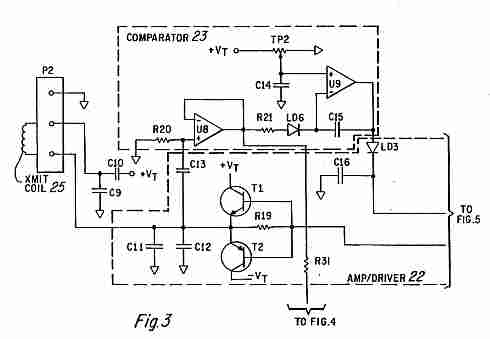
The detection mechanism may involve a comparator circuit that compares the impedance changes against preset thresholds corresponding to different coin types. This allows the system to distinguish between coins made of different materials, such as copper, nickel, and zinc, based on their unique electromagnetic signatures.
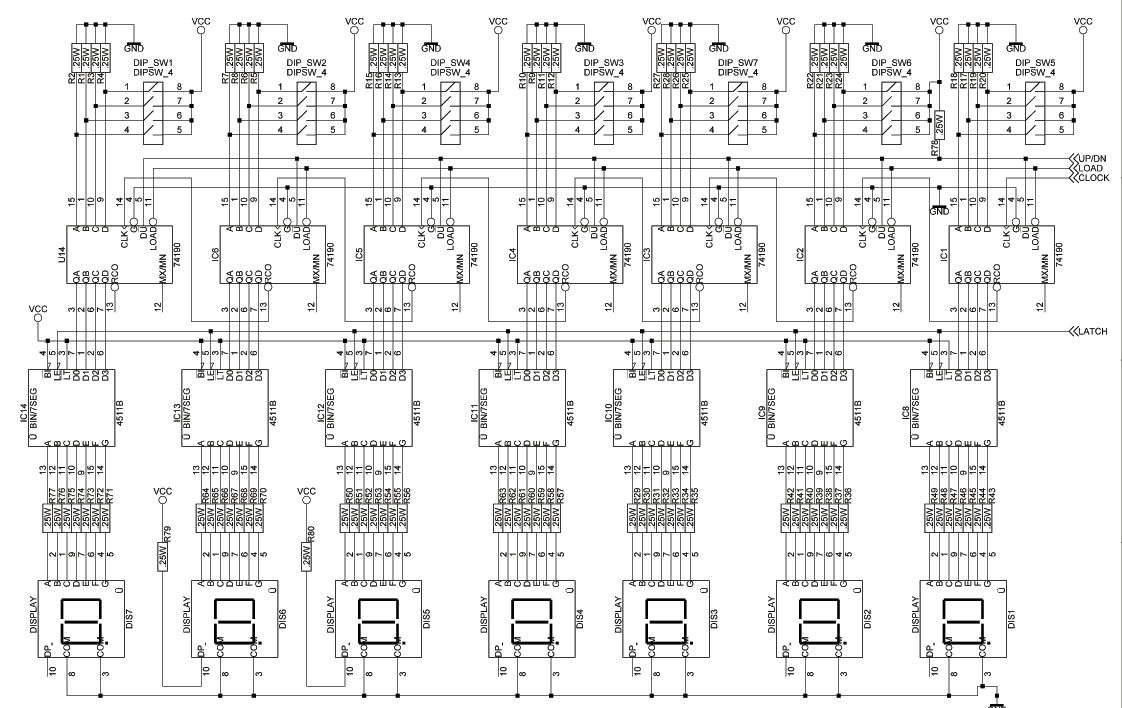
Furthermore, the output from the detection circuit can be interfaced with a digital counter to tally the number of coins detected. This counter can be designed to display the total value of the coins based on their types and quantities, providing a comprehensive solution for coin detection and counting in various applications, including vending machines and coin sorting systems.
In conclusion, a coin detector and counter leveraging an oscillating magnetic field is an effective electronic solution for identifying and quantifying different coin types through their electromagnetic interactions.Coin detector and counter : How to detect different types of coins from their effect on an oscillating magnetic field.. 🔗 External reference
A coin detector and counter operates by utilizing the principles of electromagnetic induction to identify and differentiate between various types of coins. The system typically consists of an oscillating magnetic field generated by an inductor or coil. When a coin enters the field, it alters the magnetic flux due to its conductive properties. This change in the magnetic field induces a current in the coin, which in turn generates its own magnetic field.
The circuit design usually includes a high-frequency oscillator to produce the oscillating magnetic field. The frequency of oscillation is chosen based on the expected properties of the coins to be detected, as different metals will interact with the magnetic field differently. The induced currents in the coins will produce varying impedance, which can be measured by a microcontroller or an analog circuit.
The detection mechanism may involve a comparator circuit that compares the impedance changes against preset thresholds corresponding to different coin types. This allows the system to distinguish between coins made of different materials, such as copper, nickel, and zinc, based on their unique electromagnetic signatures.
Furthermore, the output from the detection circuit can be interfaced with a digital counter to tally the number of coins detected. This counter can be designed to display the total value of the coins based on their types and quantities, providing a comprehensive solution for coin detection and counting in various applications, including vending machines and coin sorting systems.
In conclusion, a coin detector and counter leveraging an oscillating magnetic field is an effective electronic solution for identifying and quantifying different coin types through their electromagnetic interactions.Coin detector and counter : How to detect different types of coins from their effect on an oscillating magnetic field.. 🔗 External reference