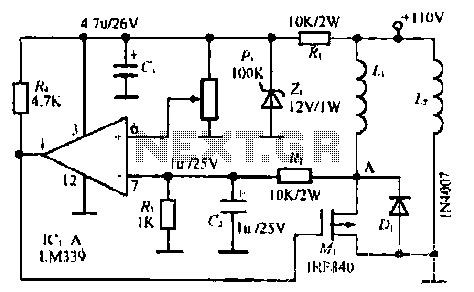
Current negative feedback voltage divider biasing circuit diagram
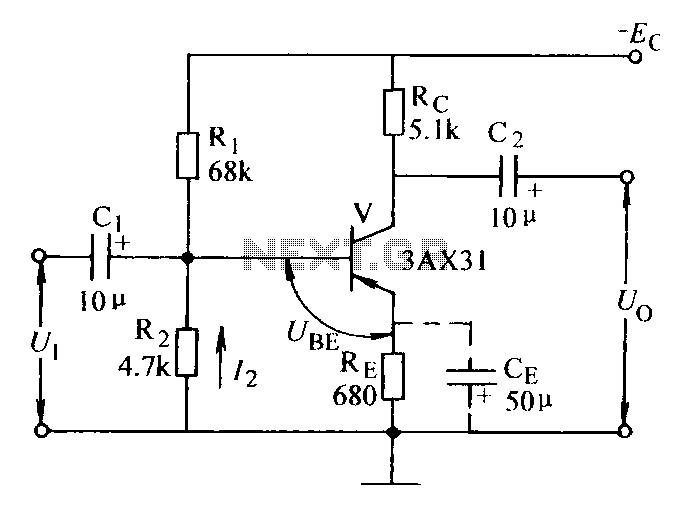
Current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit diagram.
The current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit is a configuration commonly used in electronic amplifiers to stabilize the operating point and improve linearity. This circuit typically consists of an amplifier, a voltage divider network, and feedback components that work together to maintain consistent performance despite variations in temperature or supply voltage.
In this setup, the voltage divider is formed by two resistors connected in series across the power supply. The junction of these resistors provides a stable reference voltage that is fed back to the input of the amplifier. This feedback mechanism reduces the gain of the amplifier, allowing for better control over the output signal and minimizing distortion.
The feedback loop is critical in ensuring that the amplifier operates within its linear region. The negative feedback effectively reduces the overall gain but improves bandwidth and stability, making the circuit less susceptible to fluctuations. Additionally, the choice of resistor values in the voltage divider directly impacts the feedback level and, consequently, the amplifier's performance.
In summary, the current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit is an essential design in analog electronics, providing enhanced stability and linearity for various applications, including audio amplifiers and signal processing units. Proper selection of components and configuration is vital to achieving the desired performance characteristics.Current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit diagram:
The current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit is a configuration commonly used in electronic amplifiers to stabilize the operating point and improve linearity. This circuit typically consists of an amplifier, a voltage divider network, and feedback components that work together to maintain consistent performance despite variations in temperature or supply voltage.
In this setup, the voltage divider is formed by two resistors connected in series across the power supply. The junction of these resistors provides a stable reference voltage that is fed back to the input of the amplifier. This feedback mechanism reduces the gain of the amplifier, allowing for better control over the output signal and minimizing distortion.
The feedback loop is critical in ensuring that the amplifier operates within its linear region. The negative feedback effectively reduces the overall gain but improves bandwidth and stability, making the circuit less susceptible to fluctuations. Additionally, the choice of resistor values in the voltage divider directly impacts the feedback level and, consequently, the amplifier's performance.
In summary, the current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit is an essential design in analog electronics, providing enhanced stability and linearity for various applications, including audio amplifiers and signal processing units. Proper selection of components and configuration is vital to achieving the desired performance characteristics.Current negative feedback voltage divider biased circuit diagram: