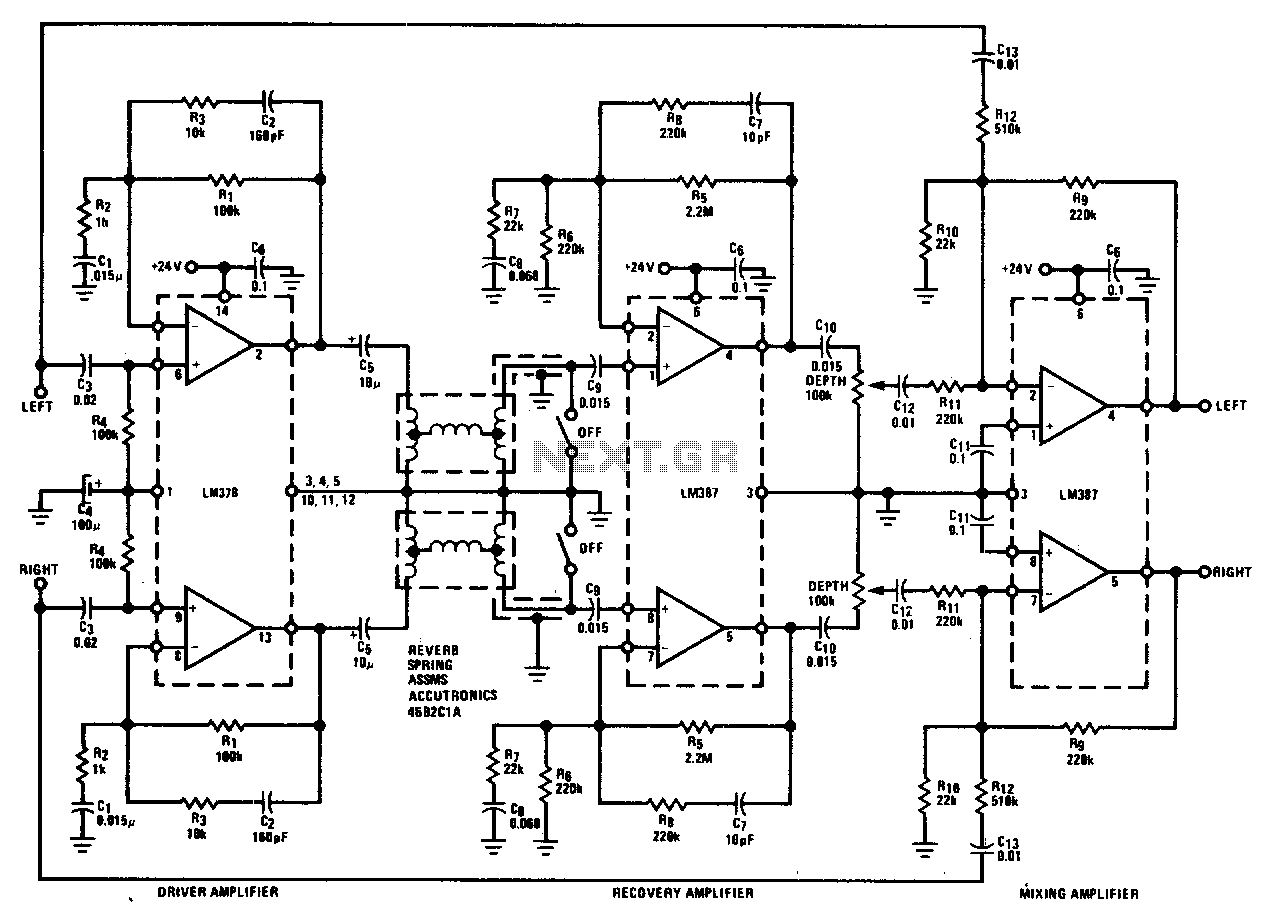
Data acquisition system
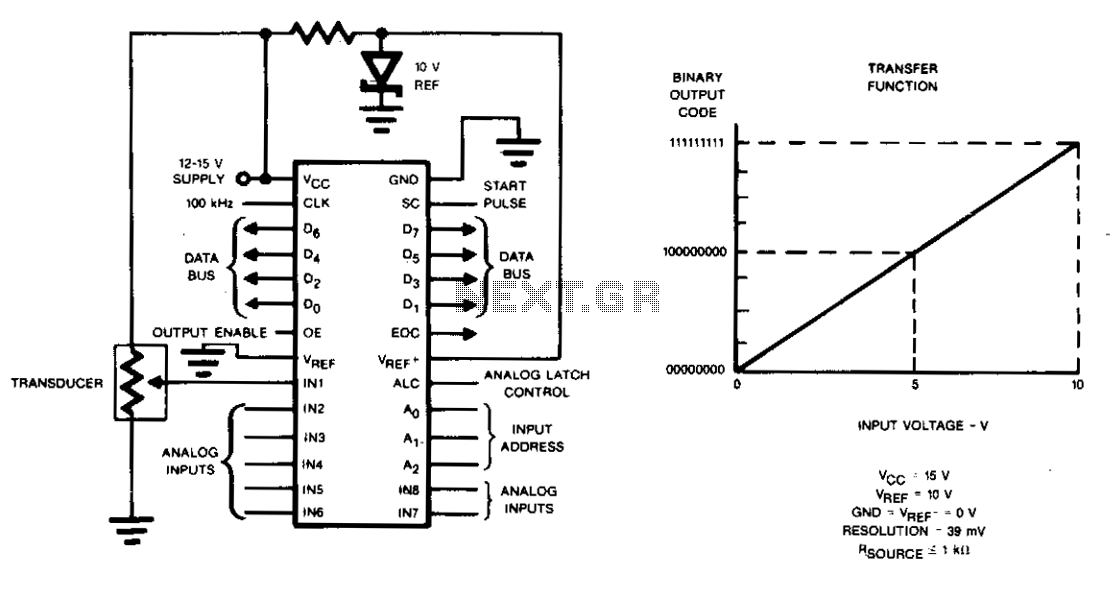
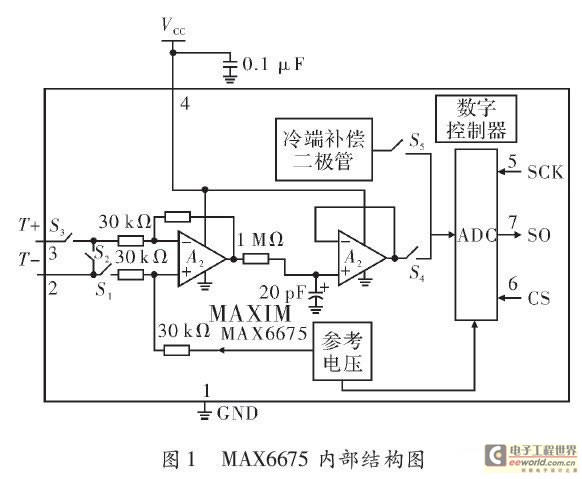
Charge redistribution is utilized to achieve analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. In standard applications, this operates as a ratiometric conversion system for a microprocessor, where V^p is connected to ground and VREF+ is connected to Vcc. The output will provide a straightforward proportional ratio between the analog input voltage and Vcc.
The described charge redistribution technique for A/D conversion is a critical component in interfacing analog signals with digital systems. In this ratiometric conversion setup, the connection of V^p to ground establishes a reference point for the conversion process, while VREF+, linked to Vcc, serves as the maximum reference voltage. This configuration ensures that the output voltage is scaled in direct proportion to the input analog voltage relative to the supply voltage (Vcc).
In practice, the A/D conversion process involves sampling the analog voltage and converting it into a digital representation. The charge redistribution method typically employs a capacitor network that charges and discharges based on the input voltage. By carefully managing the timing and control signals, the circuit can achieve high accuracy and resolution in the conversion process.
A microprocessor can then read the output, which is a digital value representing the analog input voltage as a fraction of Vcc. This ratiometric approach is particularly advantageous in applications where the supply voltage may vary, as it maintains consistent performance across different operating conditions. The resulting digital output can be processed further for various applications, including sensor interfacing, data acquisition systems, and control systems, where precise analog-to-digital conversion is essential.
Overall, the charge redistribution method for A/D conversion offers a reliable and efficient means to bridge the gap between analog and digital domains, ensuring accurate representation of analog signals in digital systems.Charge redistribution to achieve A/D conversion. In typical applications, as a ratiometric conversion system for a microprocessor, V^p, will be connected to ground and VREF+ will be connected to Vcc. The output will then be a simple proportional ratio between analog input voltage and Vcc.
The described charge redistribution technique for A/D conversion is a critical component in interfacing analog signals with digital systems. In this ratiometric conversion setup, the connection of V^p to ground establishes a reference point for the conversion process, while VREF+, linked to Vcc, serves as the maximum reference voltage. This configuration ensures that the output voltage is scaled in direct proportion to the input analog voltage relative to the supply voltage (Vcc).
In practice, the A/D conversion process involves sampling the analog voltage and converting it into a digital representation. The charge redistribution method typically employs a capacitor network that charges and discharges based on the input voltage. By carefully managing the timing and control signals, the circuit can achieve high accuracy and resolution in the conversion process.
A microprocessor can then read the output, which is a digital value representing the analog input voltage as a fraction of Vcc. This ratiometric approach is particularly advantageous in applications where the supply voltage may vary, as it maintains consistent performance across different operating conditions. The resulting digital output can be processed further for various applications, including sensor interfacing, data acquisition systems, and control systems, where precise analog-to-digital conversion is essential.
Overall, the charge redistribution method for A/D conversion offers a reliable and efficient means to bridge the gap between analog and digital domains, ensuring accurate representation of analog signals in digital systems.Charge redistribution to achieve A/D conversion. In typical applications, as a ratiometric conversion system for a microprocessor, V^p, will be connected to ground and VREF+ will be connected to Vcc. The output will then be a simple proportional ratio between analog input voltage and Vcc.