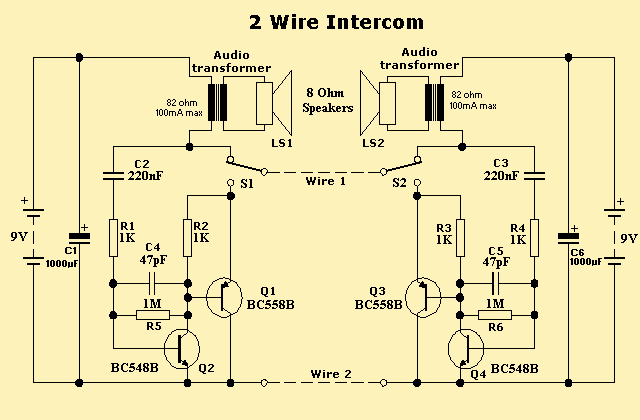
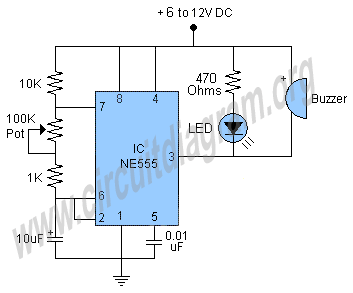
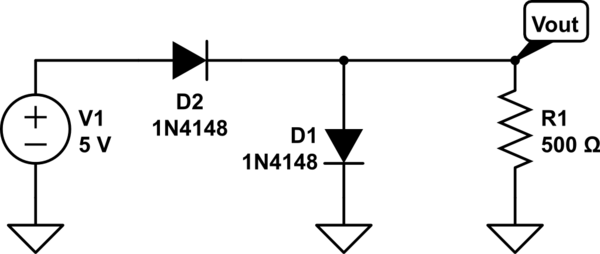
DC-RRS Application Circuit b
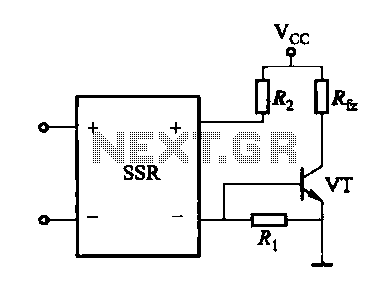
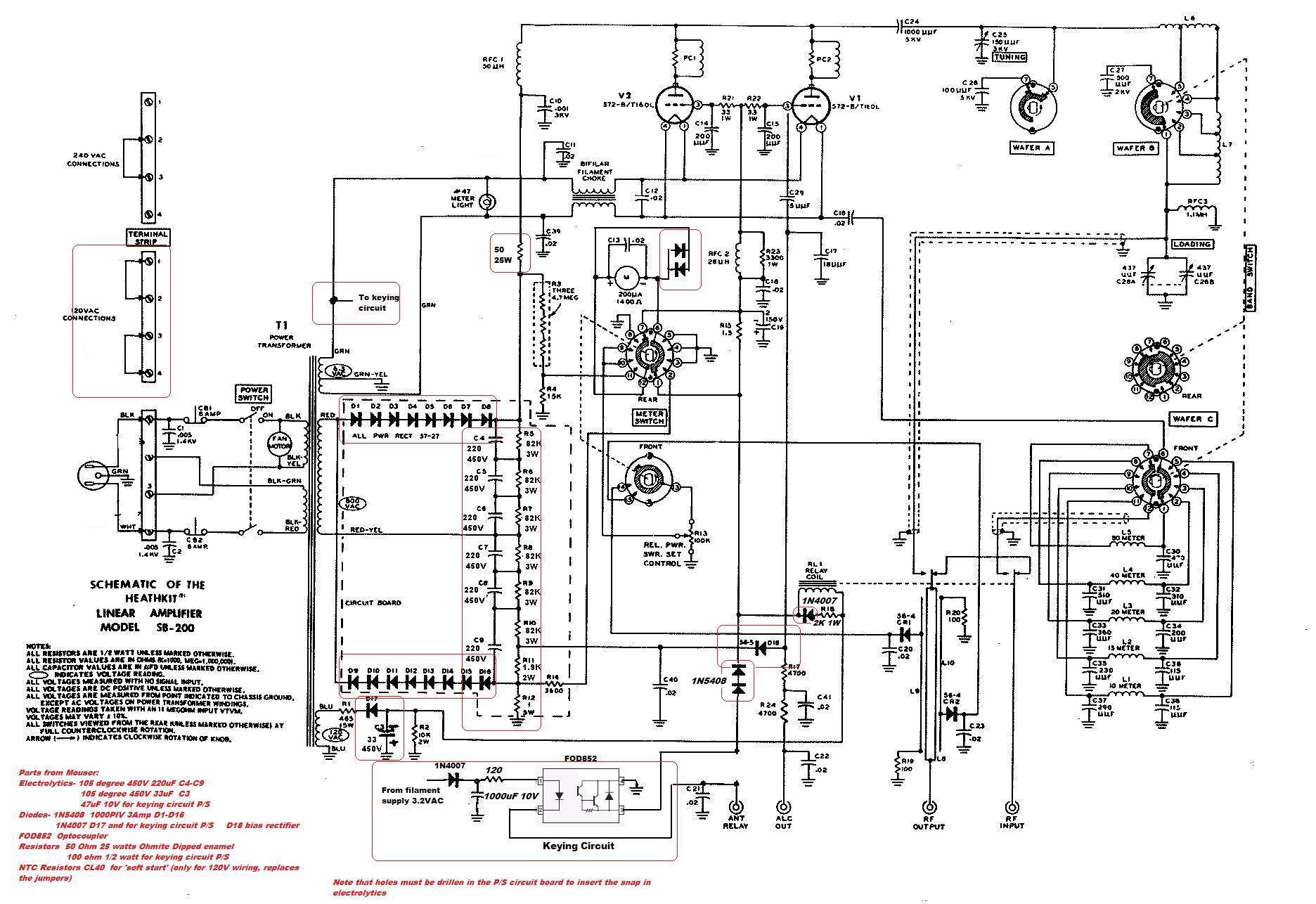
A DC solid-state relay (DC-SSR) driving a high-power load circuit is illustrated in diagram (a) below; the high-power load driving circuit is depicted in diagram (b) below.
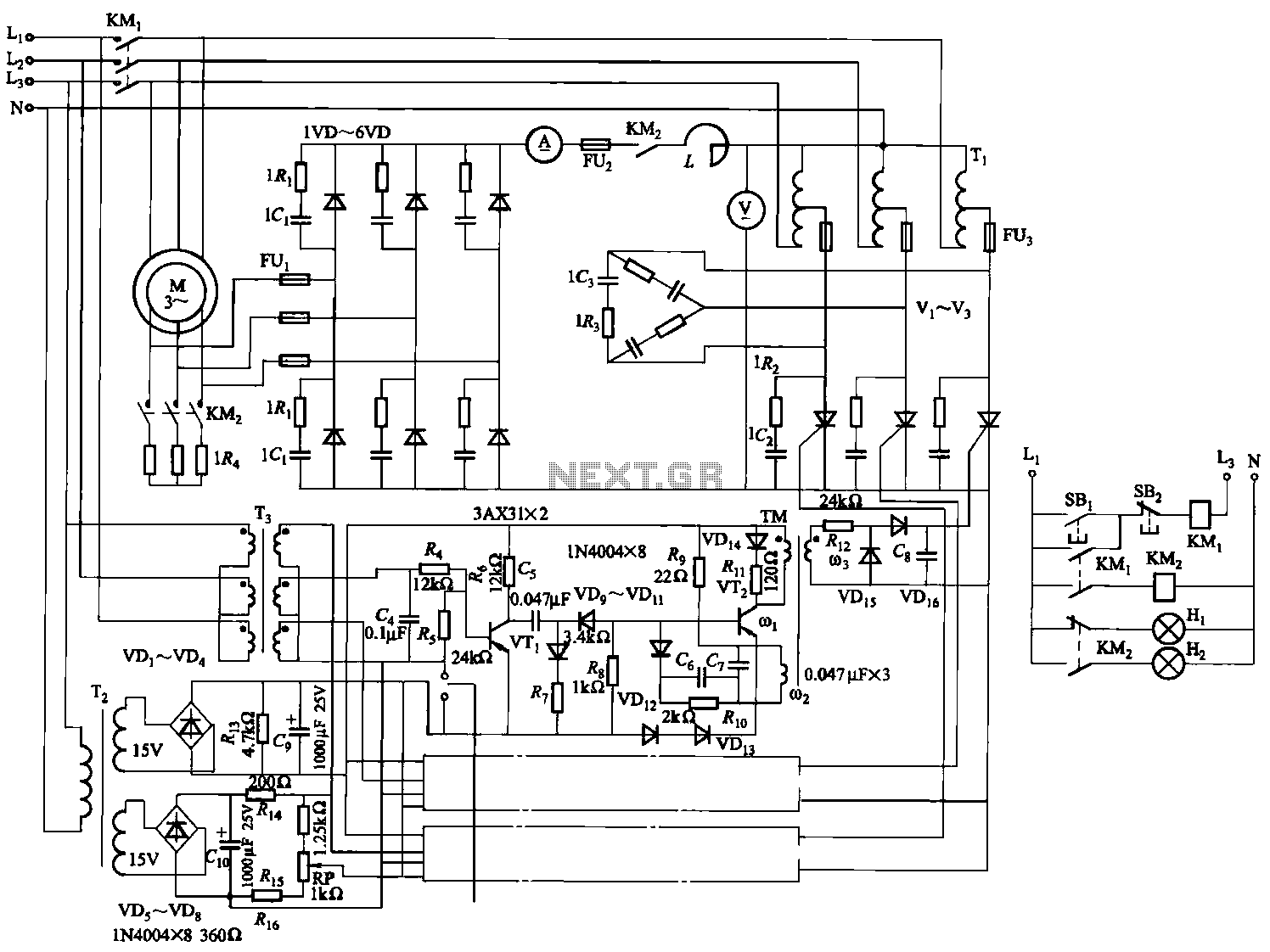
The DC solid-state relay (DC-SSR) serves as a crucial component in controlling high-power loads in various applications, such as industrial automation, heating systems, and motor control. The primary function of the DC-SSR is to switch high currents and voltages without mechanical contacts, thereby improving reliability and longevity.
In the schematic, the DC-SSR is connected in series with the high-power load, which may consist of resistive, inductive, or capacitive components. The input control circuit typically includes a low-power control signal, which can be generated by a microcontroller or a manual switch. This control signal activates the DC-SSR, allowing current to flow through the load circuit.
The DC-SSR features an opto-isolation mechanism that provides electrical isolation between the control side and the load side, ensuring that any high voltage or current fluctuations on the load do not affect the control circuitry. The relay's output characteristics depend on the specific model, with ratings typically ranging from a few amps to several hundred amps, suitable for various high-power applications.
Additionally, the high-power load driving circuit (shown in diagram b) may incorporate protective components such as fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against overcurrent conditions. It may also include snubber circuits to mitigate voltage spikes caused by inductive loads, enhancing overall circuit stability.
In summary, the combination of a DC-SSR and a well-designed high-power load driving circuit allows for efficient and safe control of high-power devices, making it an essential configuration in modern electronic systems.DC solid state relay (DC-SSR) driving high-power load circuit is shown in (a) below; high power load driving circuit shown in (b) below.
The DC solid-state relay (DC-SSR) serves as a crucial component in controlling high-power loads in various applications, such as industrial automation, heating systems, and motor control. The primary function of the DC-SSR is to switch high currents and voltages without mechanical contacts, thereby improving reliability and longevity.
In the schematic, the DC-SSR is connected in series with the high-power load, which may consist of resistive, inductive, or capacitive components. The input control circuit typically includes a low-power control signal, which can be generated by a microcontroller or a manual switch. This control signal activates the DC-SSR, allowing current to flow through the load circuit.
The DC-SSR features an opto-isolation mechanism that provides electrical isolation between the control side and the load side, ensuring that any high voltage or current fluctuations on the load do not affect the control circuitry. The relay's output characteristics depend on the specific model, with ratings typically ranging from a few amps to several hundred amps, suitable for various high-power applications.
Additionally, the high-power load driving circuit (shown in diagram b) may incorporate protective components such as fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against overcurrent conditions. It may also include snubber circuits to mitigate voltage spikes caused by inductive loads, enhancing overall circuit stability.
In summary, the combination of a DC-SSR and a well-designed high-power load driving circuit allows for efficient and safe control of high-power devices, making it an essential configuration in modern electronic systems.DC solid state relay (DC-SSR) driving high-power load circuit is shown in (a) below; high power load driving circuit shown in (b) below.