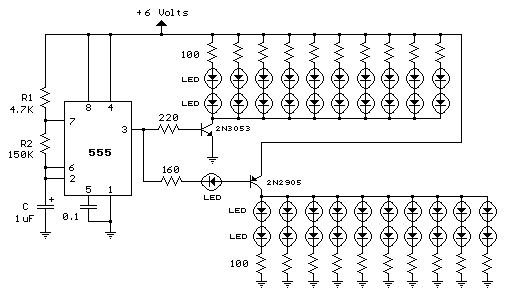
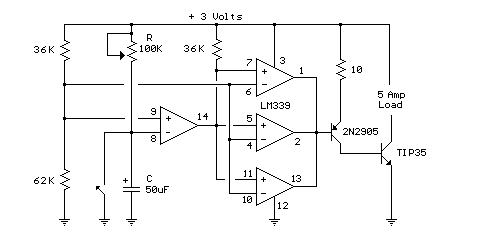
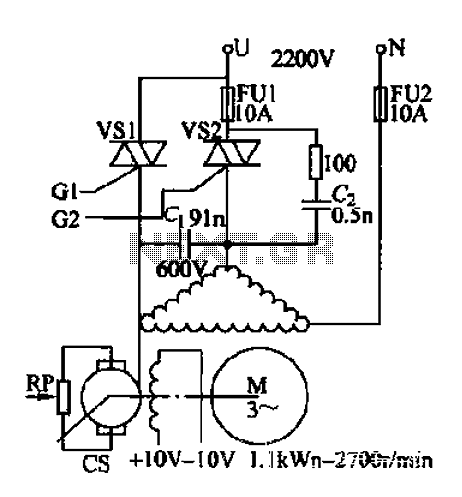
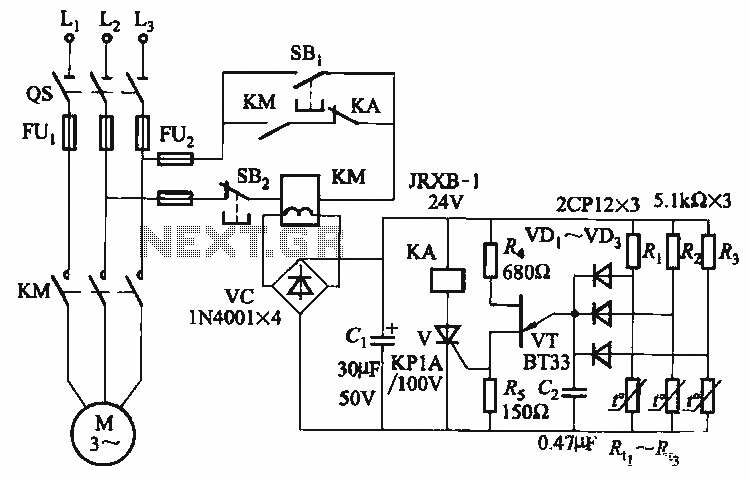
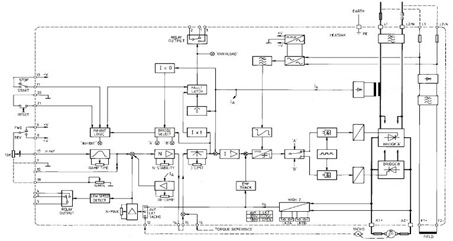
Heath SB-200 keying circuit
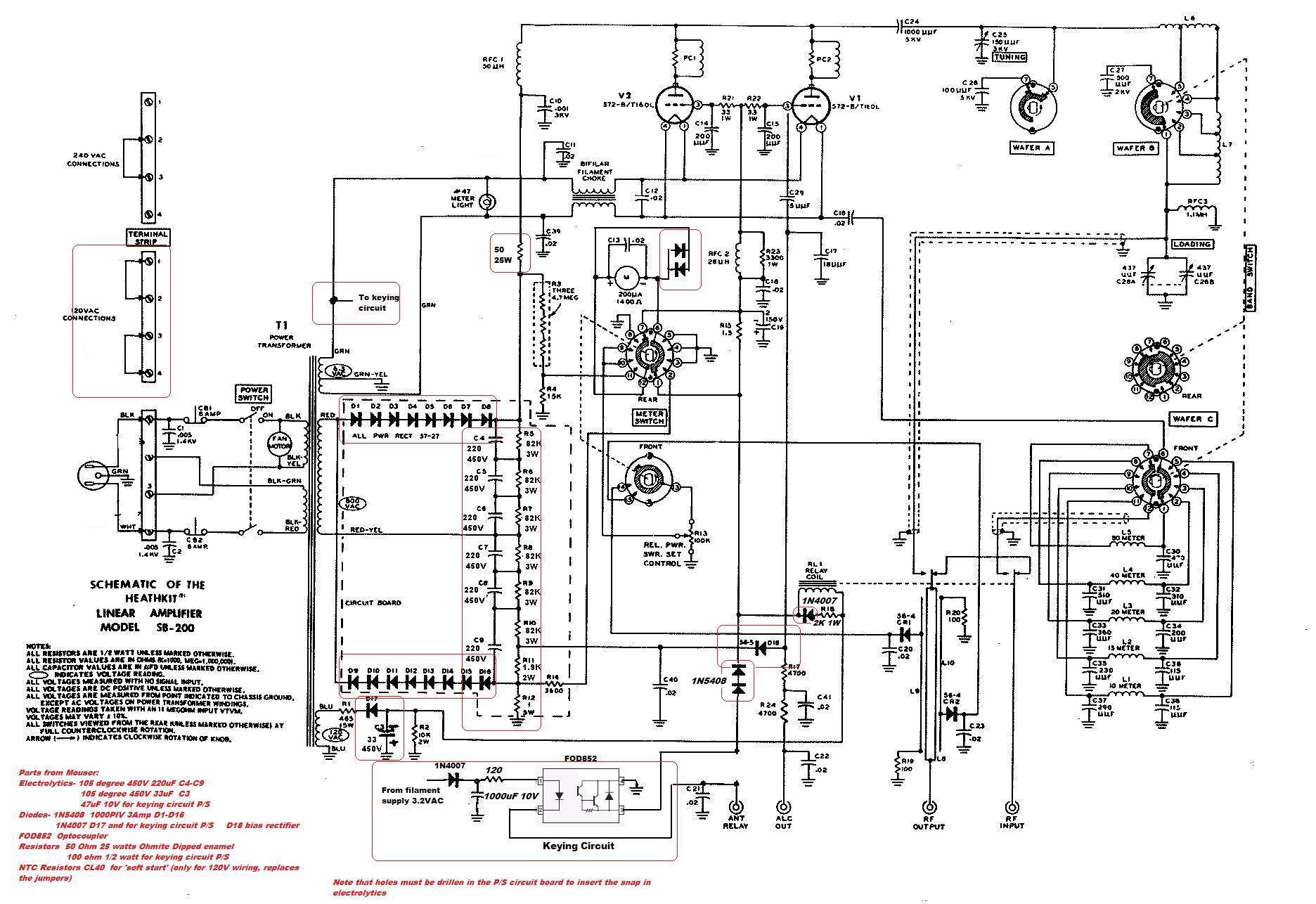
This circuit serves as a cost-effective alternative to commercially available keying circuits. It has been successfully implemented in the SB-200 amplifier. A schematic of the modified SB-200 is provided.
The described circuit is designed to function as a keying mechanism for RF amplifiers, specifically tailored for the SB-200 model. The keying circuit allows for the controlled operation of the amplifier, ensuring that it engages and disengages efficiently during transmission and reception modes.
The schematic typically includes essential components such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, and diodes, which work together to create a reliable switching mechanism. The transistors are often used as switches to control the flow of power to the amplifier, while resistors and capacitors help to manage the timing and stability of the circuit.
In a standard configuration, a small signal from a transmitter or keying device is fed into the base of a transistor, which then allows a larger current to flow from the power supply to the amplifier, effectively turning it on. Conversely, when the signal is removed, the transistor cuts off the current, turning off the amplifier. This method not only provides an economical solution but also ensures that the amplifier operates safely and effectively without the need for expensive commercial keying circuits.
In summary, this modified keying circuit is a practical and efficient solution for users seeking to enhance their SB-200 amplifier's performance while minimizing costs. The schematic serves as a valuable reference for those looking to implement similar modifications in their equipment.For those who may want to try a cheaper alternative to the commercially available keying circuits. Works well in my SB-200. Here is a schematic of my modified SB-200.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to function as a keying mechanism for RF amplifiers, specifically tailored for the SB-200 model. The keying circuit allows for the controlled operation of the amplifier, ensuring that it engages and disengages efficiently during transmission and reception modes.
The schematic typically includes essential components such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, and diodes, which work together to create a reliable switching mechanism. The transistors are often used as switches to control the flow of power to the amplifier, while resistors and capacitors help to manage the timing and stability of the circuit.
In a standard configuration, a small signal from a transmitter or keying device is fed into the base of a transistor, which then allows a larger current to flow from the power supply to the amplifier, effectively turning it on. Conversely, when the signal is removed, the transistor cuts off the current, turning off the amplifier. This method not only provides an economical solution but also ensures that the amplifier operates safely and effectively without the need for expensive commercial keying circuits.
In summary, this modified keying circuit is a practical and efficient solution for users seeking to enhance their SB-200 amplifier's performance while minimizing costs. The schematic serves as a valuable reference for those looking to implement similar modifications in their equipment.For those who may want to try a cheaper alternative to the commercially available keying circuits. Works well in my SB-200. Here is a schematic of my modified SB-200.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713