Delay circuit of a multi-level output
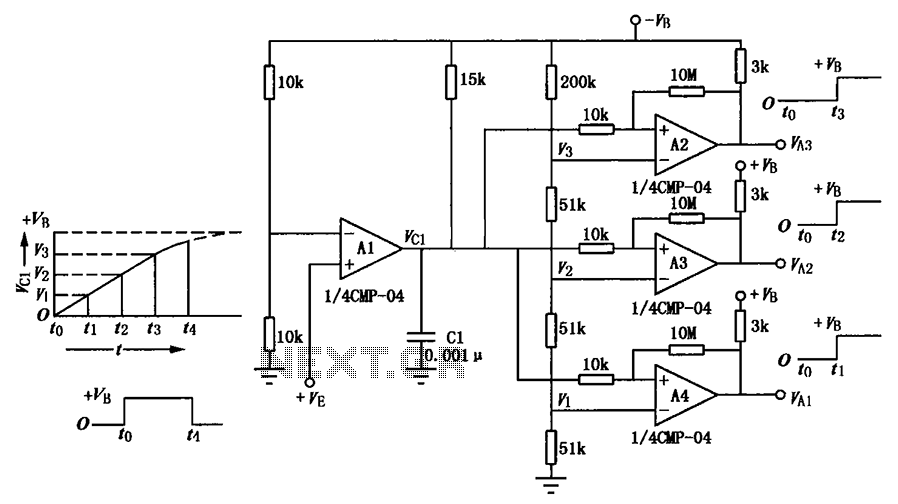
A multi-stage delay circuit is presented in this schematic. The operational amplifiers are configured as comparators. Operational amplifier A1 operates when the voltage at the inverting input exceeds + VE. As the voltage at the inverting input of operational amplifiers A2, A3, and A4 (denoted as VC1) rises, it follows an exponential curve. The inverting input voltage of the operational amplifiers is supplied by a voltage divider. Consequently, the input voltage VC1 transitions from zero to + VB (the power supply voltage) over time intervals t1, t2, and t3, resulting in inverted output signals that facilitate gradual delays for VA1, VA2, and VA3. It is important to note that this circuit requires dual power supplies: a positive supply of + VE and + VB, and a negative supply of -VB.
The multi-stage delay circuit utilizes a series of operational amplifiers configured as comparators to achieve precise timing control. Each operational amplifier in the sequence (A1, A2, A3, A4) is designed to respond to the voltage levels at its inverting input. The circuit's functionality is based on the principle that as the voltage at the inverting input (VC1) increases, the output of the operational amplifiers transitions from a high state to a low state, effectively creating a delay.
The voltage divider network connected to the inverting inputs of the operational amplifiers serves to scale down the input voltage, allowing for controlled switching thresholds. The exponential rise of VC1 is critical for defining the timing characteristics of the circuit. The time intervals t1, t2, and t3 correspond to the specific delay settings for each operational amplifier stage, ensuring that the output signals (VA1, VA2, VA3) are generated with the desired timing accuracy.
The dual power supply configuration is essential for the proper operation of the circuit. The positive supplies (+ VE and + VB) provide the necessary voltage levels for the operational amplifiers to function effectively, while the negative supply (-VB) ensures that the output can swing below ground level, which is often required in comparator applications. This arrangement enhances the versatility of the circuit, allowing it to be used in various timing and control applications in electronic systems. As shown having a multi-stage delay circuit is output. The operational amplifier circuit used as comparators, operational amplifier A1 when the applied voltage-inverting input + VE, the operational amplifier A2, A3, A4-inverting input terminal voltage VC1 on the rise along an exponential curve rule. Inverting input of the operational amplifier a voltage is provided by a voltage divider classification.
Therefore, each op amp input Vc1 from zero to + VB (power supply voltage) of t1, t2, t3 time, so that the output signals are inverted, enabling VA1, VA2, VA3 gradual delay purposes. Note that this circuit uses a dual power, namely the positive supply + VE, + VB and the negative supply -VB.
The multi-stage delay circuit utilizes a series of operational amplifiers configured as comparators to achieve precise timing control. Each operational amplifier in the sequence (A1, A2, A3, A4) is designed to respond to the voltage levels at its inverting input. The circuit's functionality is based on the principle that as the voltage at the inverting input (VC1) increases, the output of the operational amplifiers transitions from a high state to a low state, effectively creating a delay.
The voltage divider network connected to the inverting inputs of the operational amplifiers serves to scale down the input voltage, allowing for controlled switching thresholds. The exponential rise of VC1 is critical for defining the timing characteristics of the circuit. The time intervals t1, t2, and t3 correspond to the specific delay settings for each operational amplifier stage, ensuring that the output signals (VA1, VA2, VA3) are generated with the desired timing accuracy.
The dual power supply configuration is essential for the proper operation of the circuit. The positive supplies (+ VE and + VB) provide the necessary voltage levels for the operational amplifiers to function effectively, while the negative supply (-VB) ensures that the output can swing below ground level, which is often required in comparator applications. This arrangement enhances the versatility of the circuit, allowing it to be used in various timing and control applications in electronic systems. As shown having a multi-stage delay circuit is output. The operational amplifier circuit used as comparators, operational amplifier A1 when the applied voltage-inverting input + VE, the operational amplifier A2, A3, A4-inverting input terminal voltage VC1 on the rise along an exponential curve rule. Inverting input of the operational amplifier a voltage is provided by a voltage divider classification.
Therefore, each op amp input Vc1 from zero to + VB (power supply voltage) of t1, t2, t3 time, so that the output signals are inverted, enabling VA1, VA2, VA3 gradual delay purposes. Note that this circuit uses a dual power, namely the positive supply + VE, + VB and the negative supply -VB.

.png)