digital clock in recycled retro-modern case
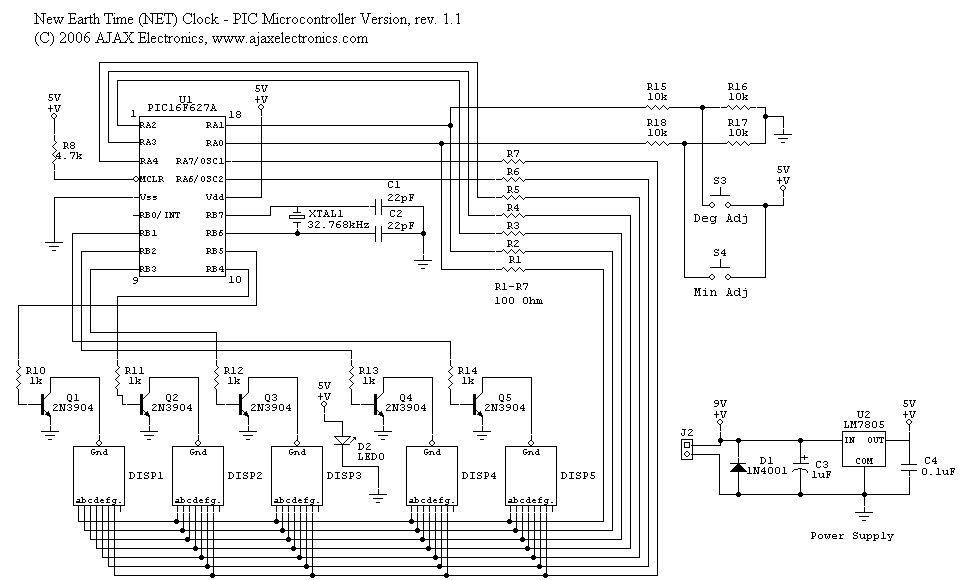
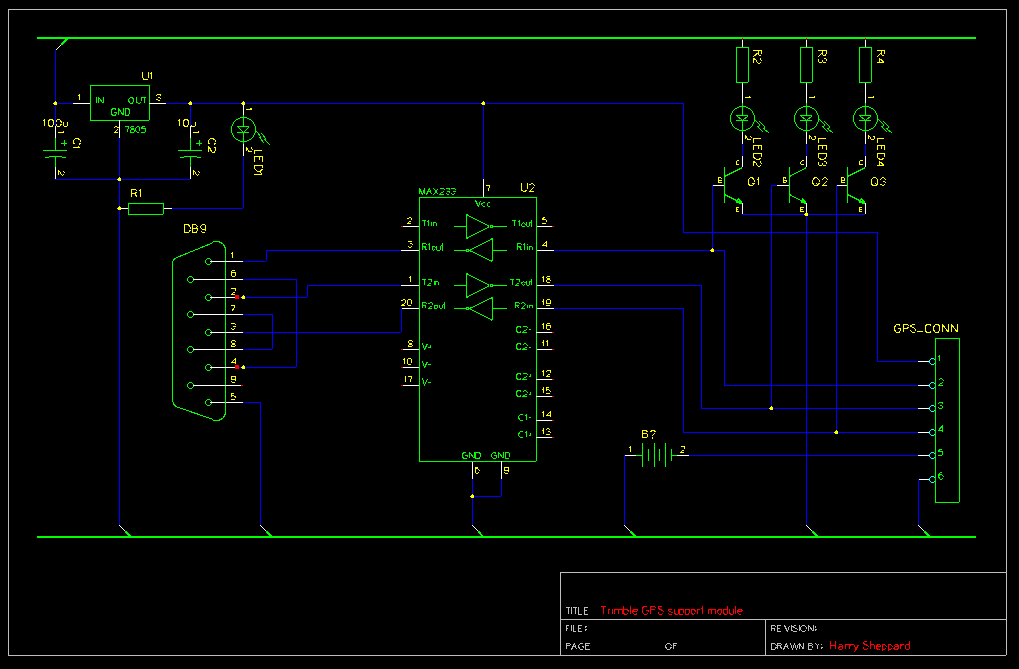
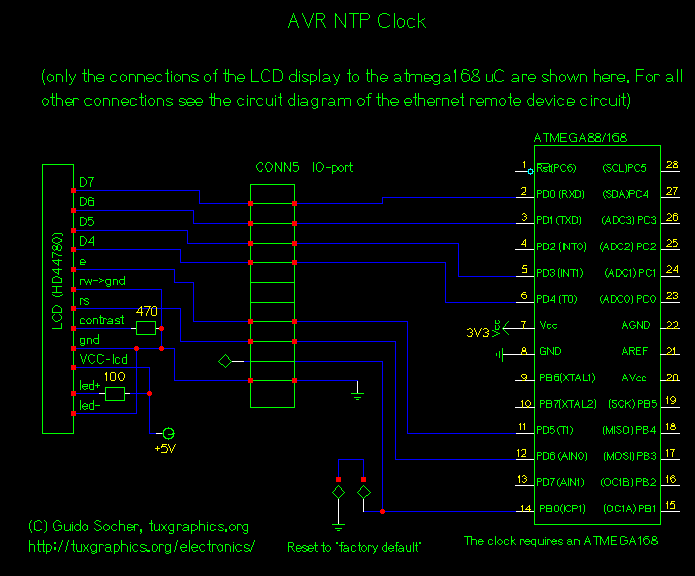
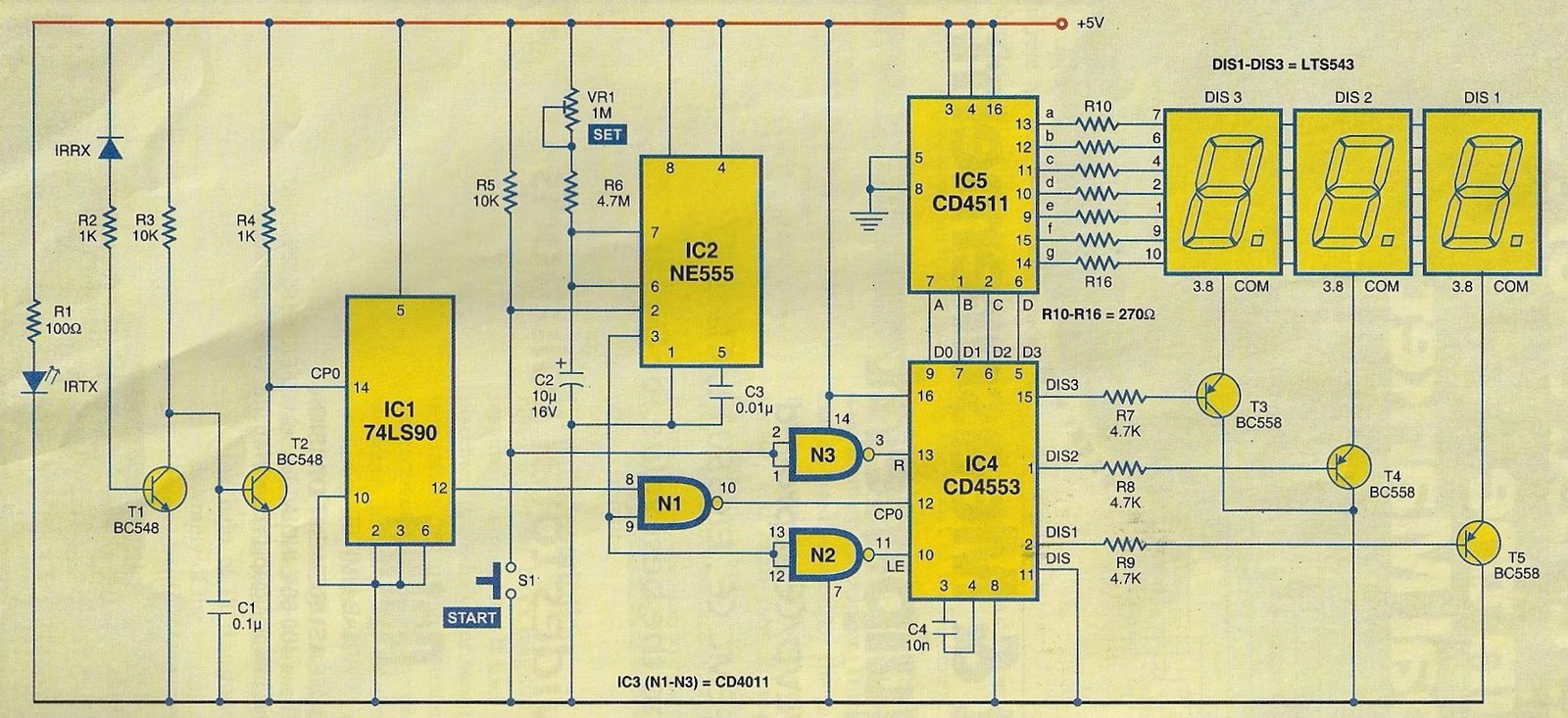
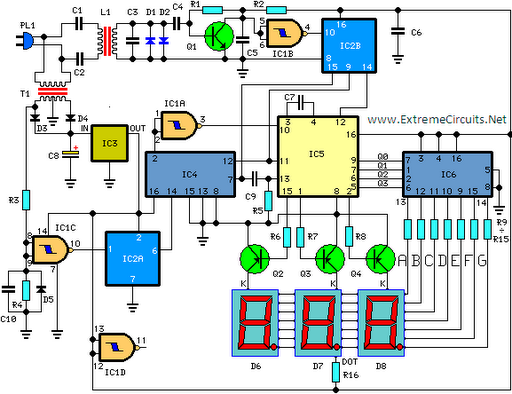
The schematic diagram and electronic assembly are relatively simple, as most of the functionality is managed by the microcontroller code.
The schematic diagram serves as a visual representation of the electronic circuit, outlining the connections between various components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and the microcontroller itself. Microcontrollers are integral to modern electronic systems, acting as the brain of the circuit. They process input signals, execute programmed instructions, and control output devices.
In this design, the microcontroller likely interfaces with various sensors and actuators, which are essential for the system's operation. Input devices such as temperature sensors or switches can provide real-time data to the microcontroller, while output devices like LEDs or motors perform tasks based on the processed information.
Power supply considerations are also crucial in the schematic. The circuit must include a stable power source to ensure reliable operation of the microcontroller and other components. Bypass capacitors may be employed to filter out noise from the power supply, providing a clean voltage to the microcontroller.
Additionally, the layout of the schematic should prioritize signal integrity and minimize interference. Proper routing of traces and the placement of components can significantly impact the performance of the circuit. Ground planes may be used to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve overall circuit stability.
In summary, while the schematic diagram and electronic assembly may appear straightforward, the complexity and functionality of the system are largely dictated by the microcontroller's programming and the careful design of the circuit.The schematic diagram (see picture) and electronic assembly are fairly straightforward since most of the magic happens in the microcontroller code.. 🔗 External reference
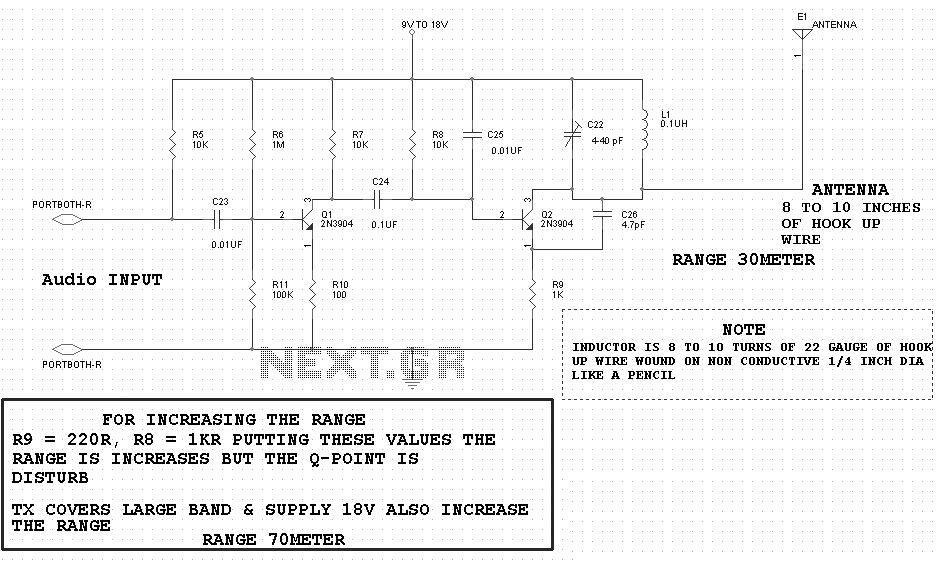
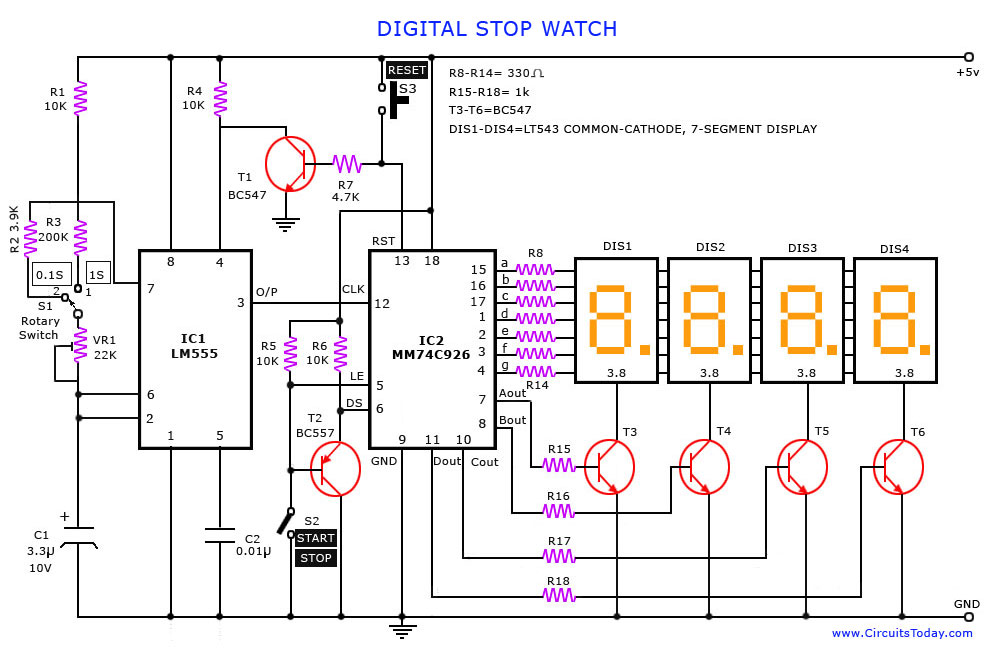
The schematic diagram serves as a visual representation of the electronic circuit, outlining the connections between various components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and the microcontroller itself. Microcontrollers are integral to modern electronic systems, acting as the brain of the circuit. They process input signals, execute programmed instructions, and control output devices.
In this design, the microcontroller likely interfaces with various sensors and actuators, which are essential for the system's operation. Input devices such as temperature sensors or switches can provide real-time data to the microcontroller, while output devices like LEDs or motors perform tasks based on the processed information.
Power supply considerations are also crucial in the schematic. The circuit must include a stable power source to ensure reliable operation of the microcontroller and other components. Bypass capacitors may be employed to filter out noise from the power supply, providing a clean voltage to the microcontroller.
Additionally, the layout of the schematic should prioritize signal integrity and minimize interference. Proper routing of traces and the placement of components can significantly impact the performance of the circuit. Ground planes may be used to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve overall circuit stability.
In summary, while the schematic diagram and electronic assembly may appear straightforward, the complexity and functionality of the system are largely dictated by the microcontroller's programming and the careful design of the circuit.The schematic diagram (see picture) and electronic assembly are fairly straightforward since most of the magic happens in the microcontroller code.. 🔗 External reference