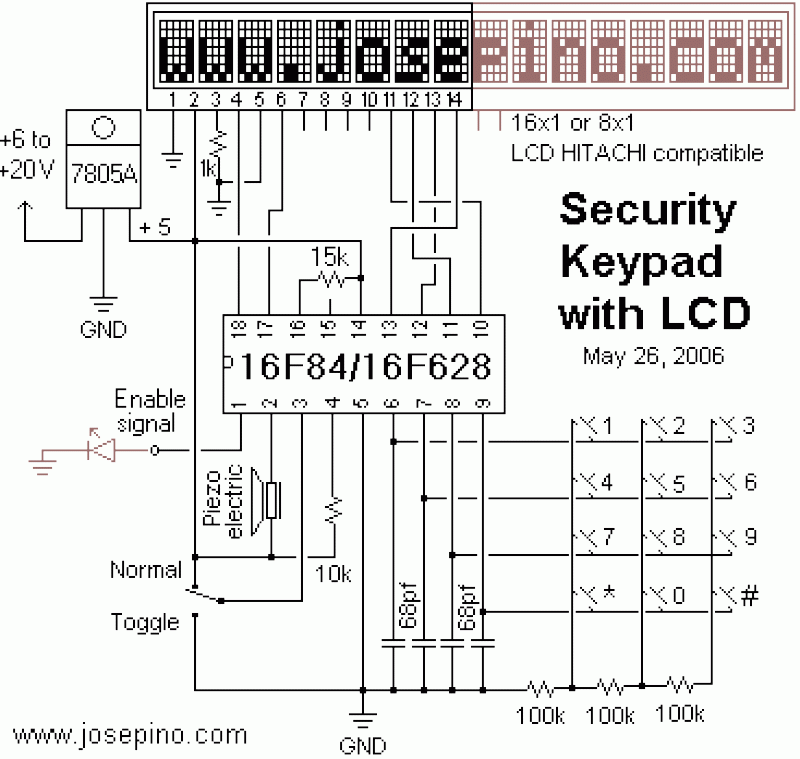
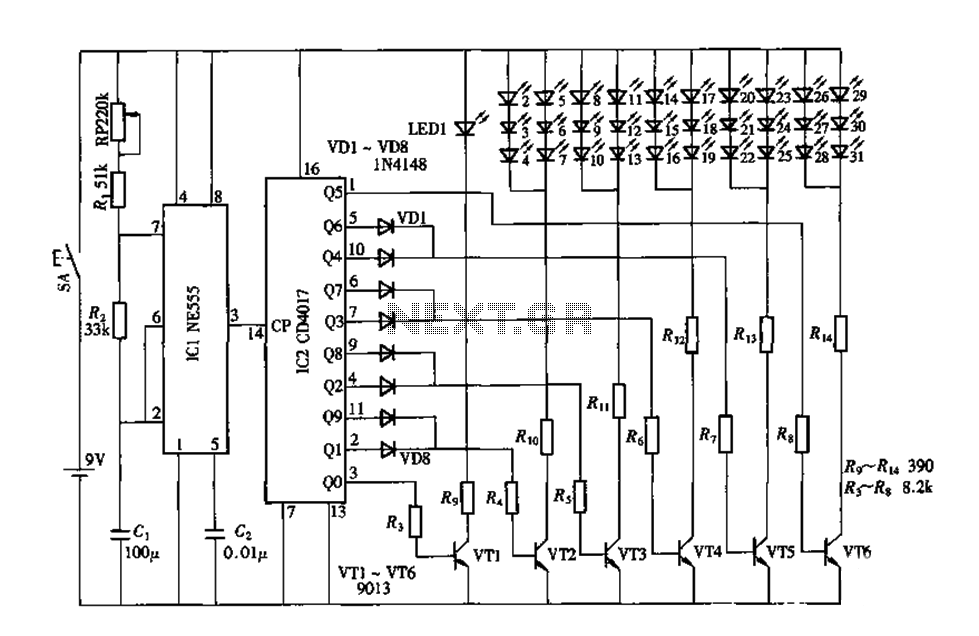
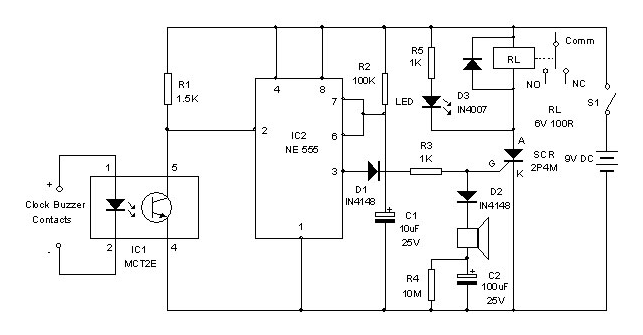
digital electronic lock

The digital lock utilizes four common logic integrated circuits (ICs) to manage a relay activation by inputting a four-digit code via a keypad. The initial four outputs from the CD4017 decade counter (pins 3, 2, 4, and 7) are combined with the digits from the keypad. As the keys are pressed in the correct sequence, the counter progresses.
The digital lock circuit is designed to enhance security by requiring a specific four-digit code for relay activation. The main components include a keypad, a CD4017 decade counter, and a relay driver circuit. The keypad typically consists of a matrix arrangement of buttons, where each button corresponds to a specific digit. When a button is pressed, it sends a signal to the CD4017 counter.
The CD4017 counter is a decade counter that counts from 0 to 9. It has ten outputs, but only the first four outputs (pins 3, 2, 4, and 7) are utilized in this application. Each output corresponds to a specific digit in the code. The outputs are connected to a logic gate configuration that ensures only the correct sequence of inputs can advance the counter. This is achieved through the use of AND gates, which require multiple inputs to be high (logic level '1') simultaneously.
Once the correct sequence of digits is entered, the CD4017 counter advances to the final output, which activates the relay. The relay can then control a larger load, such as a door lock or alarm system, providing a physical mechanism for locking or unlocking based on the entered code.
To ensure reliability, debounce circuits may be implemented to filter out noise from the keypad inputs, preventing false triggering from mechanical bounce when buttons are pressed. Additionally, a reset mechanism can be integrated to reset the counter if an incorrect digit is entered, requiring the user to start over.
Overall, this digital lock circuit is a practical application of basic logic ICs and provides a straightforward yet effective method for securing access through electronic means.The digital lock shown below uses 4 common logic ICs to allow controlling a relay by entering a 4 digit number on a keypad. The first 4 outputs from the CD4017 decade counter (pins 3,2,4,7) are gated together with 4 digits from a keypad so that as the keys are depressed in the correct order, the counter will advance..
🔗 External reference
The digital lock circuit is designed to enhance security by requiring a specific four-digit code for relay activation. The main components include a keypad, a CD4017 decade counter, and a relay driver circuit. The keypad typically consists of a matrix arrangement of buttons, where each button corresponds to a specific digit. When a button is pressed, it sends a signal to the CD4017 counter.
The CD4017 counter is a decade counter that counts from 0 to 9. It has ten outputs, but only the first four outputs (pins 3, 2, 4, and 7) are utilized in this application. Each output corresponds to a specific digit in the code. The outputs are connected to a logic gate configuration that ensures only the correct sequence of inputs can advance the counter. This is achieved through the use of AND gates, which require multiple inputs to be high (logic level '1') simultaneously.
Once the correct sequence of digits is entered, the CD4017 counter advances to the final output, which activates the relay. The relay can then control a larger load, such as a door lock or alarm system, providing a physical mechanism for locking or unlocking based on the entered code.
To ensure reliability, debounce circuits may be implemented to filter out noise from the keypad inputs, preventing false triggering from mechanical bounce when buttons are pressed. Additionally, a reset mechanism can be integrated to reset the counter if an incorrect digit is entered, requiring the user to start over.
Overall, this digital lock circuit is a practical application of basic logic ICs and provides a straightforward yet effective method for securing access through electronic means.The digital lock shown below uses 4 common logic ICs to allow controlling a relay by entering a 4 digit number on a keypad. The first 4 outputs from the CD4017 decade counter (pins 3,2,4,7) are gated together with 4 digits from a keypad so that as the keys are depressed in the correct order, the counter will advance..
🔗 External reference