Temperature Sensor Project
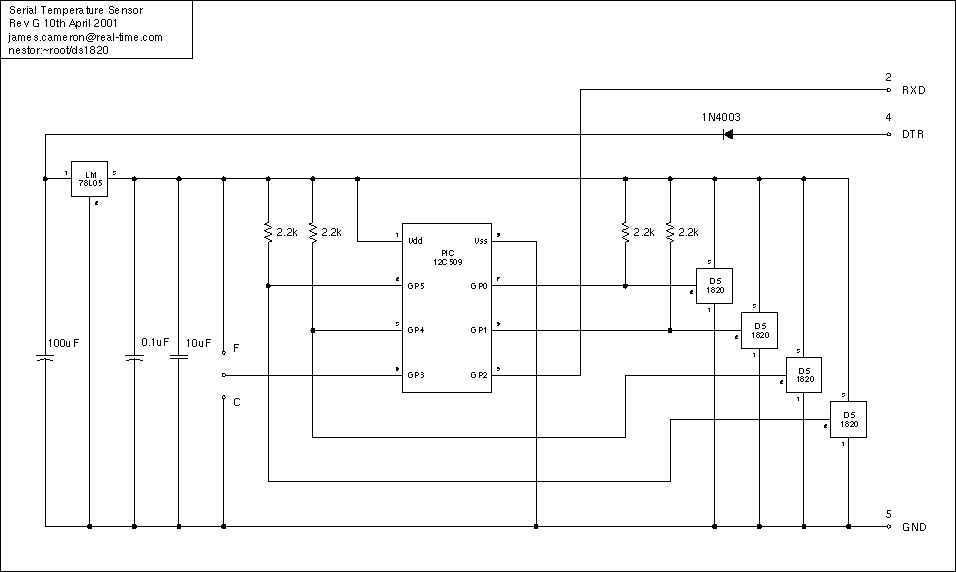
Just a handful of components builds an 8-pin microcontroller based circuit for temperature logging via a serial port; small, fast, and acceptably accurate. More: provides real-time data to your computer via serial port, interfaces up to four DS1820 temperature sensors, absolute accuracy near 0.5 degrees Celsius (as per DS1820 specifications), relative accuracy near 0.01 degrees Celsius.
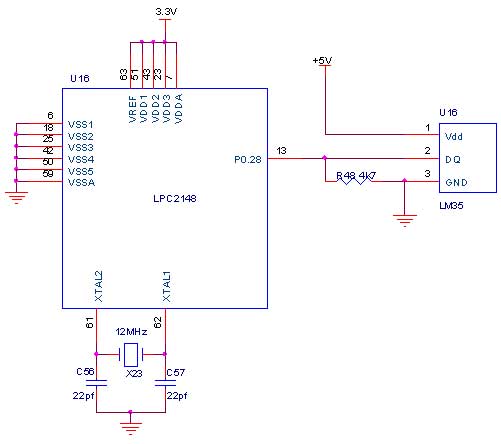
The circuit utilizes an 8-pin microcontroller, which serves as the central processing unit for collecting and transmitting temperature data. The microcontroller is programmed to interface with up to four DS1820 digital temperature sensors. These sensors communicate over a 1-Wire bus, allowing multiple devices to be connected in parallel while utilizing only a single data line, thereby simplifying wiring and reducing the number of required pins on the microcontroller.
The DS1820 sensors are capable of measuring temperatures in the range of -55°C to +125°C with an absolute accuracy of approximately ±0.5°C, as specified by the manufacturer. The relative accuracy is significantly higher, at about ±0.01°C, which makes this setup suitable for applications requiring precise temperature monitoring.
Data collected from the sensors is transmitted in real-time to a computer via a serial port. This communication can be implemented using standard UART protocols, allowing for easy integration with various computing platforms. The microcontroller handles the timing and control of data transmission, ensuring that temperature readings from each sensor are accurately captured and sent sequentially.
The circuit's design emphasizes compactness and efficiency, making it suitable for applications where space is limited. Power requirements are minimal, allowing the system to operate effectively in battery-powered scenarios. Additionally, the fast processing capability of the microcontroller ensures timely data logging, which is critical for monitoring temperature fluctuations in dynamic environments.
Overall, this microcontroller-based temperature logging circuit offers a reliable solution for real-time temperature monitoring, combining simplicity in design with high performance and accuracy.Just a handful of components builds an 8-pin microcontroller based circuit for temperature logging via a serial port; small, fast, and acceptably accurate. * provides real-time data to your computer via serial port, * interfaces up to four DS1820 temperature sensors, * absolute accuracy near 0.5 degrees celcius (as per DS1820 specifications), * relative accuracy near 0.01 degrees celcius, 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an 8-pin microcontroller, which serves as the central processing unit for collecting and transmitting temperature data. The microcontroller is programmed to interface with up to four DS1820 digital temperature sensors. These sensors communicate over a 1-Wire bus, allowing multiple devices to be connected in parallel while utilizing only a single data line, thereby simplifying wiring and reducing the number of required pins on the microcontroller.
The DS1820 sensors are capable of measuring temperatures in the range of -55°C to +125°C with an absolute accuracy of approximately ±0.5°C, as specified by the manufacturer. The relative accuracy is significantly higher, at about ±0.01°C, which makes this setup suitable for applications requiring precise temperature monitoring.
Data collected from the sensors is transmitted in real-time to a computer via a serial port. This communication can be implemented using standard UART protocols, allowing for easy integration with various computing platforms. The microcontroller handles the timing and control of data transmission, ensuring that temperature readings from each sensor are accurately captured and sent sequentially.
The circuit's design emphasizes compactness and efficiency, making it suitable for applications where space is limited. Power requirements are minimal, allowing the system to operate effectively in battery-powered scenarios. Additionally, the fast processing capability of the microcontroller ensures timely data logging, which is critical for monitoring temperature fluctuations in dynamic environments.
Overall, this microcontroller-based temperature logging circuit offers a reliable solution for real-time temperature monitoring, combining simplicity in design with high performance and accuracy.Just a handful of components builds an 8-pin microcontroller based circuit for temperature logging via a serial port; small, fast, and acceptably accurate. * provides real-time data to your computer via serial port, * interfaces up to four DS1820 temperature sensors, * absolute accuracy near 0.5 degrees celcius (as per DS1820 specifications), * relative accuracy near 0.01 degrees celcius, 🔗 External reference