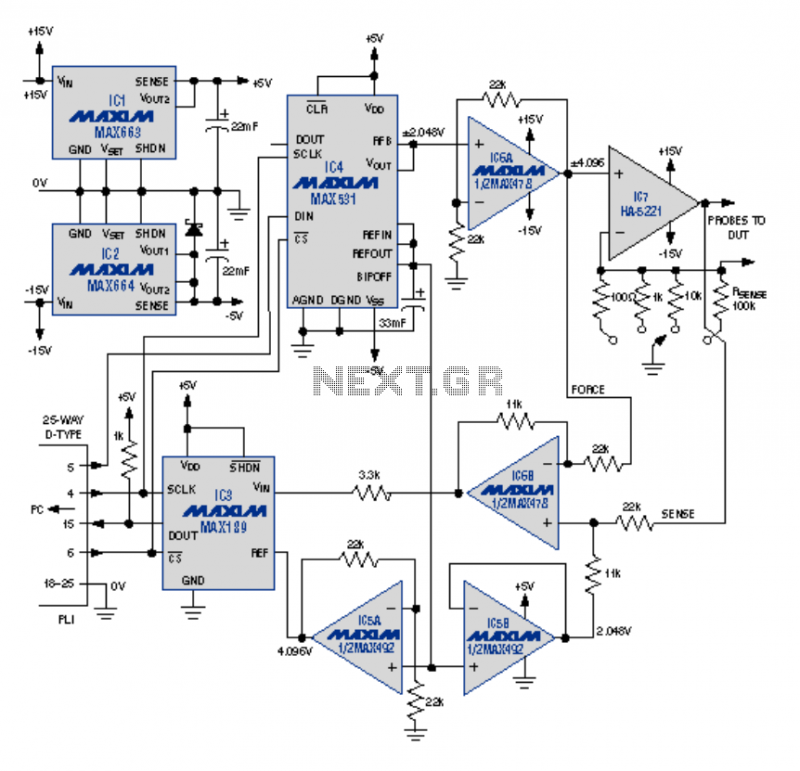
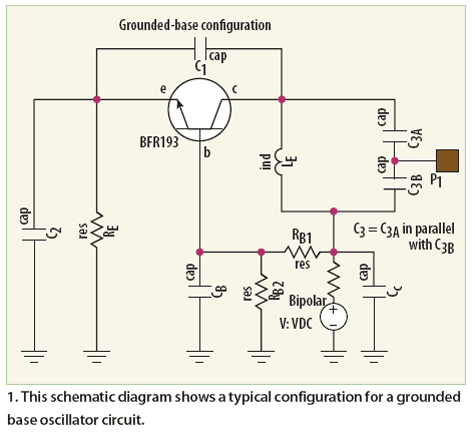
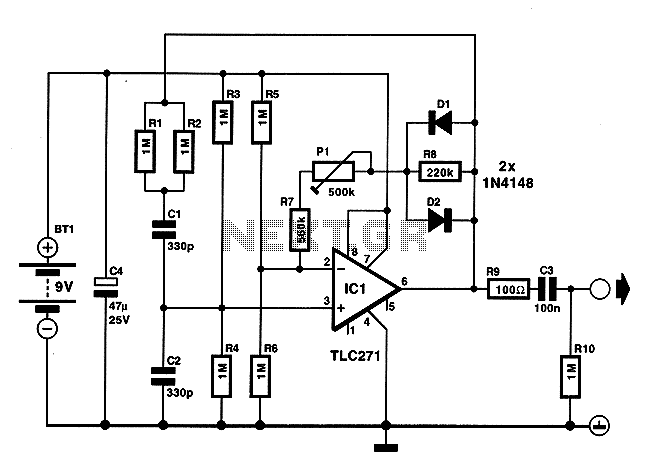
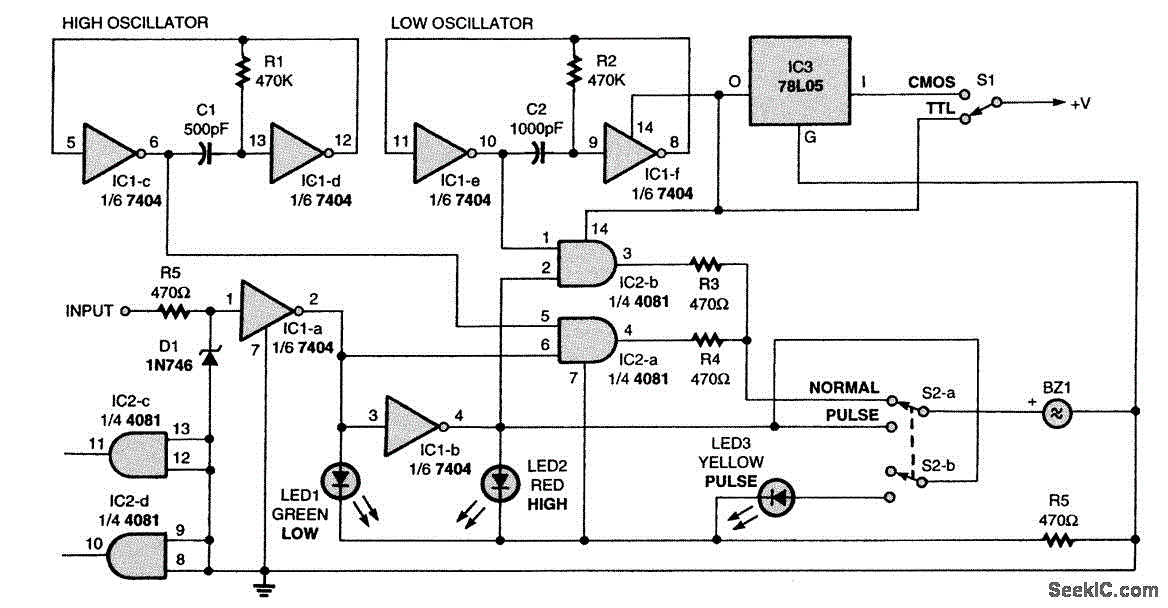
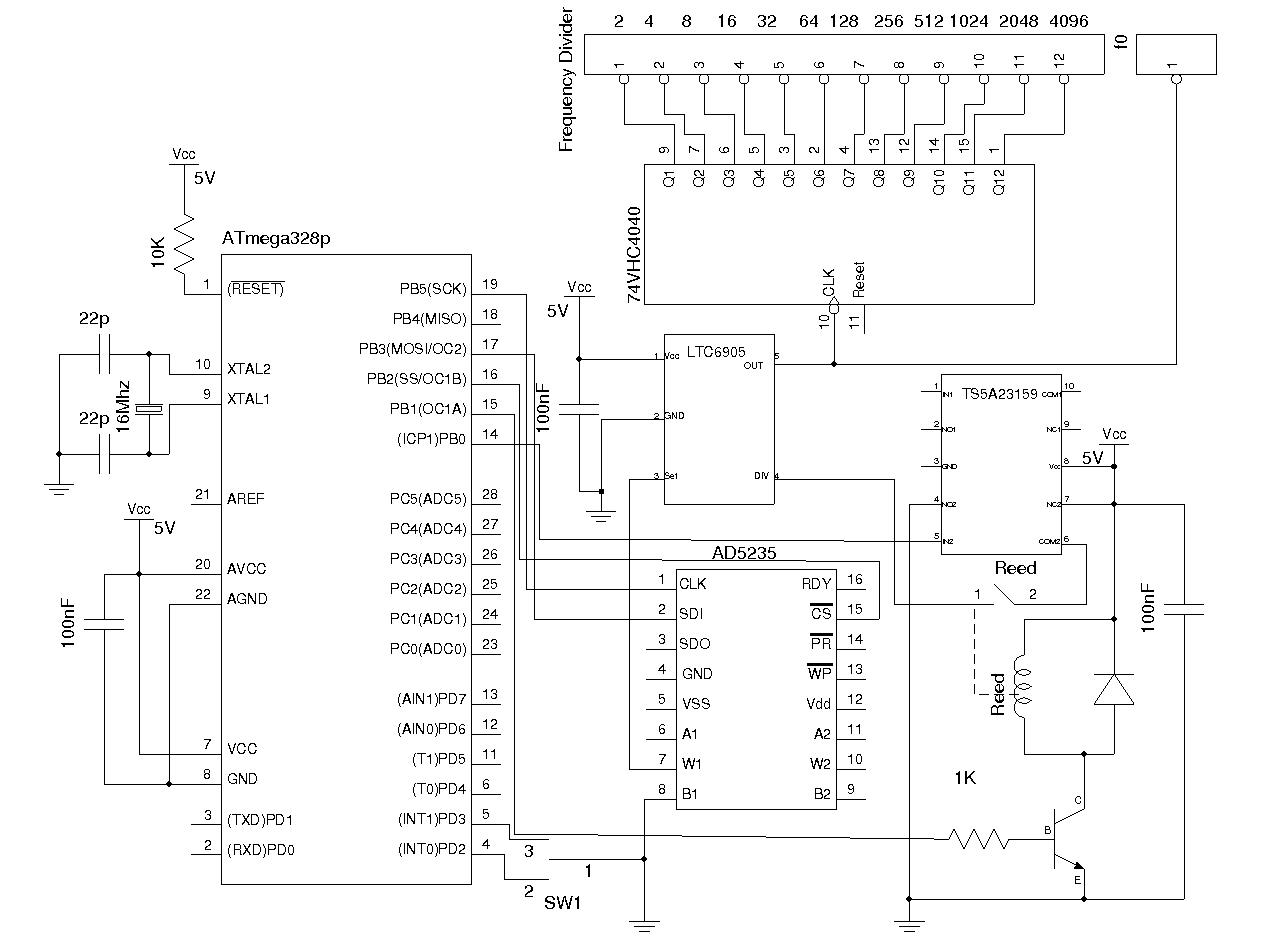
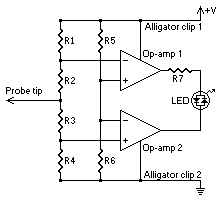Audio-rf signal tracer probe
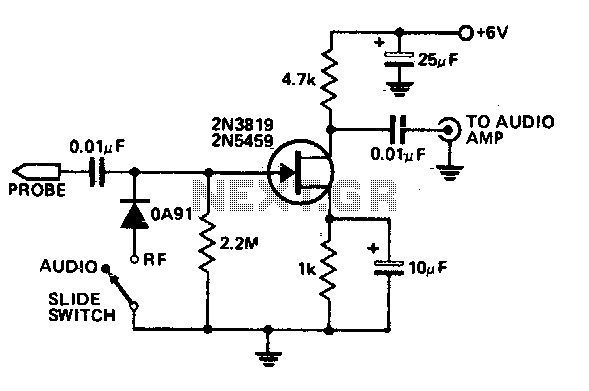
This economical signal tracer is useful for servicing and alignment work in receivers and low power transmitters. When switched to RF, the modulation on any signal is detected by the diode and amplified by the FET. A twin-core shielded lead can be used to connect the probe to an amplifier and to feed 6 volts to it.
The signal tracer is designed to facilitate the diagnosis and alignment of radio frequency (RF) circuits, particularly in receivers and low-power transmitters. The device operates by switching to RF mode, allowing it to detect modulation on incoming signals through a diode. The diode acts as a rectifier, converting the RF signal into a form that can be amplified. The subsequent amplification is performed by a Field Effect Transistor (FET), which enhances the signal strength for easier analysis.
The use of a twin-core shielded lead is critical in this setup. It serves a dual purpose: it connects the probe to an external amplifier, ensuring that the signal can be processed further, and it provides a power supply of 6 volts to the circuit. This power supply is essential for the operation of the FET and the overall functionality of the signal tracer.
The circuit design should include appropriate biasing for the FET to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, the diode should be selected based on its frequency response to ensure it can effectively detect the modulation present in the RF signals being tested. The shielding of the lead is also important to prevent interference from external electromagnetic fields, which could distort the signals being traced.
Overall, this economical signal tracer represents a valuable tool for technicians and engineers working in the field of electronics, enabling efficient troubleshooting and alignment of RF systems. Proper implementation of the circuit components and connections will enhance the reliability and accuracy of the device in various applications.This economical signal tracer is useful for servicing and alignment work in receivers and low power transmitters. When switched to RF, the modulation on any signal is detected by the diode and amplified by the FET A twin-core shielded lead can be used to connect the probe to an amplifier and to feed 6 volts to it.
The signal tracer is designed to facilitate the diagnosis and alignment of radio frequency (RF) circuits, particularly in receivers and low-power transmitters. The device operates by switching to RF mode, allowing it to detect modulation on incoming signals through a diode. The diode acts as a rectifier, converting the RF signal into a form that can be amplified. The subsequent amplification is performed by a Field Effect Transistor (FET), which enhances the signal strength for easier analysis.
The use of a twin-core shielded lead is critical in this setup. It serves a dual purpose: it connects the probe to an external amplifier, ensuring that the signal can be processed further, and it provides a power supply of 6 volts to the circuit. This power supply is essential for the operation of the FET and the overall functionality of the signal tracer.
The circuit design should include appropriate biasing for the FET to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, the diode should be selected based on its frequency response to ensure it can effectively detect the modulation present in the RF signals being tested. The shielding of the lead is also important to prevent interference from external electromagnetic fields, which could distort the signals being traced.
Overall, this economical signal tracer represents a valuable tool for technicians and engineers working in the field of electronics, enabling efficient troubleshooting and alignment of RF systems. Proper implementation of the circuit components and connections will enhance the reliability and accuracy of the device in various applications.This economical signal tracer is useful for servicing and alignment work in receivers and low power transmitters. When switched to RF, the modulation on any signal is detected by the diode and amplified by the FET A twin-core shielded lead can be used to connect the probe to an amplifier and to feed 6 volts to it.