LOGIC PROBE
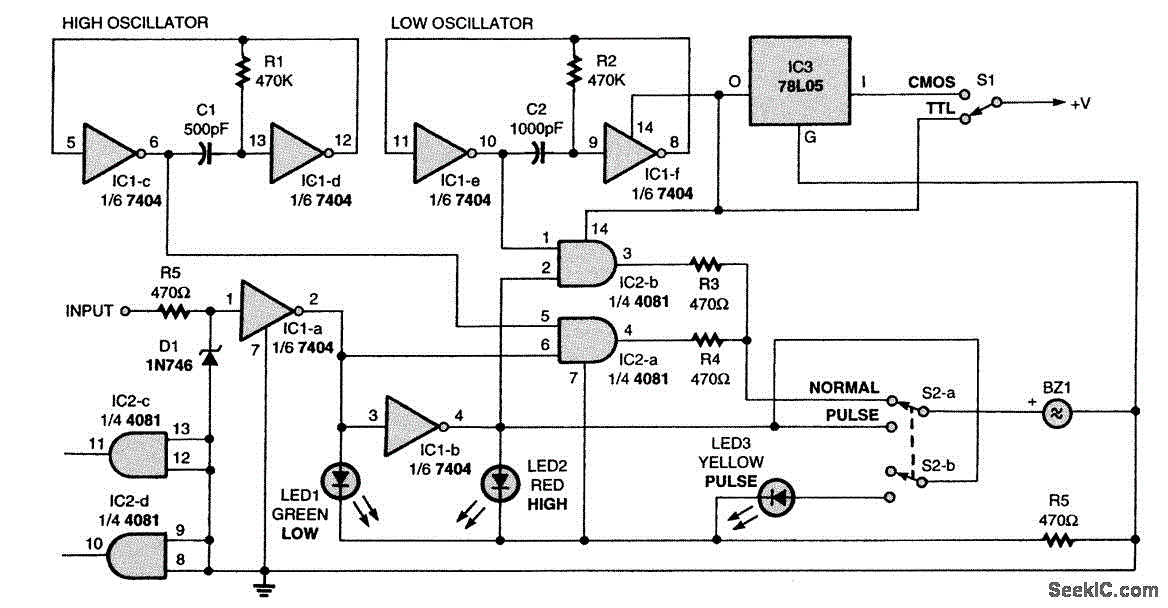
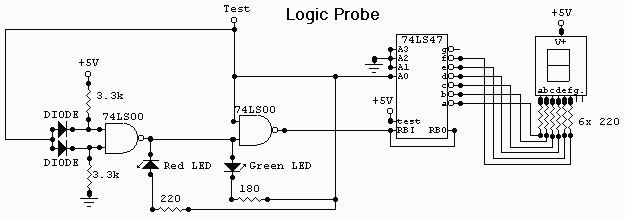
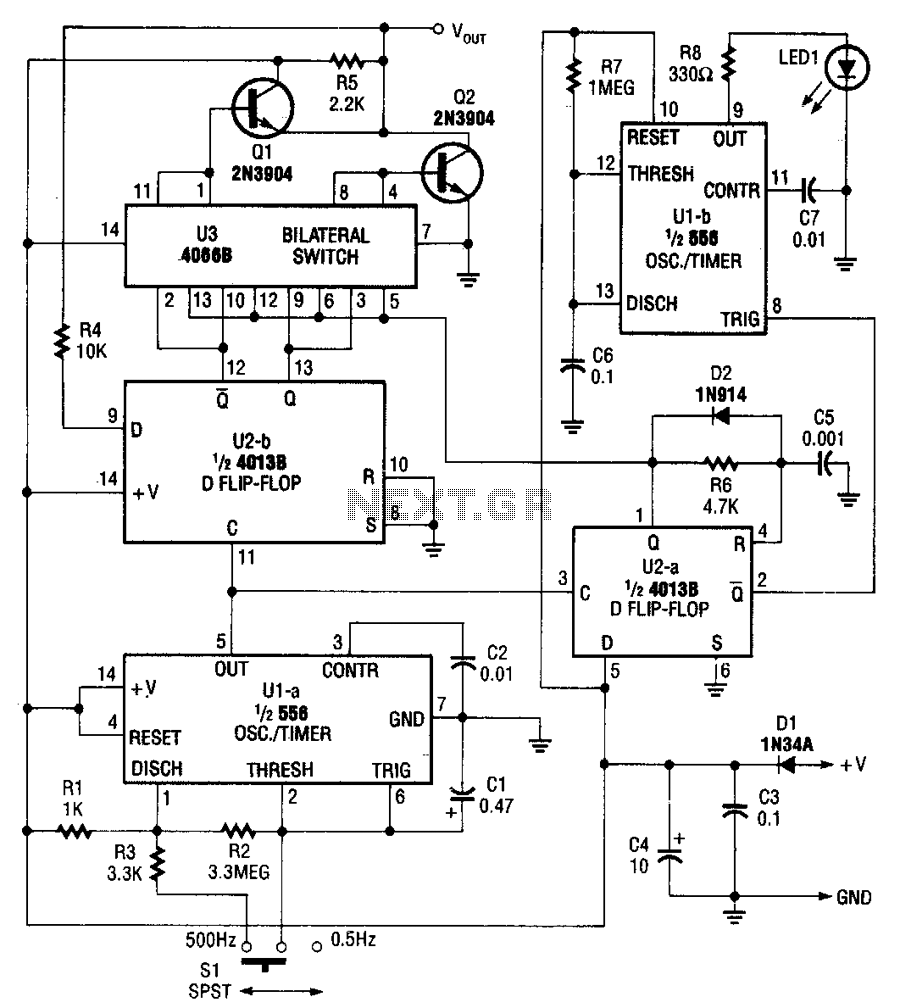
The figure illustrates the schematic for a versatile logic probe. The zener diode clamps the input signal slightly above the TTL inverter's 2.2-V trigger voltage. Zener diode D1 can be omitted if the probe is intended solely for use with TTL circuits. The logic probe primarily utilizes inverters IC1-a and IC1-b, which are components of a 7404 integrated circuit.
The versatile logic probe is designed to provide a simple and effective means for troubleshooting digital circuits. It operates by detecting and indicating the logic levels of the signals present at various points in a circuit. The core of the probe consists of two inverters from the 7404 IC, which serve to amplify the input signal and provide a clean output that can be easily interpreted.
The inclusion of a zener diode (D1) is a critical feature that protects the input of the probe by clamping the voltage to a safe level, specifically just above the 2.2-V threshold of TTL logic. This ensures that higher voltages do not damage the sensitive components of the probe when interfacing with various circuit voltages. If the probe is exclusively used with TTL circuits, the zener diode can be excluded, simplifying the design without compromising functionality.
In addition to the inverters, the schematic may include other passive components such as resistors and capacitors that help stabilize the circuit and filter out noise. The output of the logic probe is typically connected to an LED or a similar indicator, which illuminates to signify the presence of a high or low logic level. This visual feedback allows engineers and technicians to quickly assess the operational status of digital signals during testing and debugging processes.
Overall, the design of the logic probe emphasizes versatility and ease of use, making it an essential tool for anyone working with digital electronics. Its straightforward construction and effective signal detection capabilities make it suitable for a wide range of applications in both educational and professional settings.The figure shows the schematic for a versatile logic probe. The zener diode clamps the input signal just above the TTL inverter`s 2.2-V trigger voltage. Zener diode D1 can be left out if the probe is going to be used only on TTL circuits. The logic probe is based mainly on inverters IC1-a and IC1-b, which are sections of a 7404 integrated circuit. Depending.. 🔗 External reference
The versatile logic probe is designed to provide a simple and effective means for troubleshooting digital circuits. It operates by detecting and indicating the logic levels of the signals present at various points in a circuit. The core of the probe consists of two inverters from the 7404 IC, which serve to amplify the input signal and provide a clean output that can be easily interpreted.
The inclusion of a zener diode (D1) is a critical feature that protects the input of the probe by clamping the voltage to a safe level, specifically just above the 2.2-V threshold of TTL logic. This ensures that higher voltages do not damage the sensitive components of the probe when interfacing with various circuit voltages. If the probe is exclusively used with TTL circuits, the zener diode can be excluded, simplifying the design without compromising functionality.
In addition to the inverters, the schematic may include other passive components such as resistors and capacitors that help stabilize the circuit and filter out noise. The output of the logic probe is typically connected to an LED or a similar indicator, which illuminates to signify the presence of a high or low logic level. This visual feedback allows engineers and technicians to quickly assess the operational status of digital signals during testing and debugging processes.
Overall, the design of the logic probe emphasizes versatility and ease of use, making it an essential tool for anyone working with digital electronics. Its straightforward construction and effective signal detection capabilities make it suitable for a wide range of applications in both educational and professional settings.The figure shows the schematic for a versatile logic probe. The zener diode clamps the input signal just above the TTL inverter`s 2.2-V trigger voltage. Zener diode D1 can be left out if the probe is going to be used only on TTL circuits. The logic probe is based mainly on inverters IC1-a and IC1-b, which are sections of a 7404 integrated circuit. Depending.. 🔗 External reference