Direct High Voltage DC Regulator
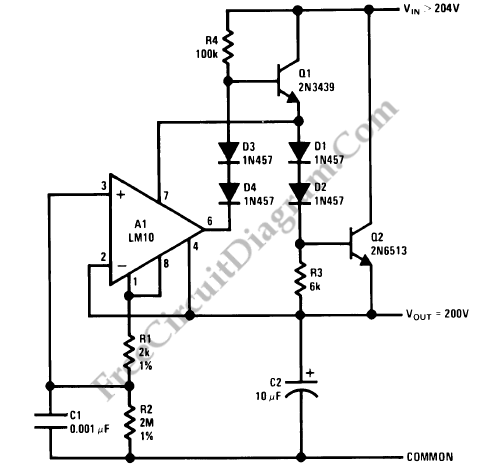
This regulator circuit stabilizes the output voltage at 200V directly (without a transformer). Although the output voltage is high, this circuit only suffers a.
The circuit in question is designed to maintain a stable output voltage of 200V without the use of a transformer, which is a notable feature, particularly in applications requiring high voltage regulation. The absence of a transformer simplifies the design and can reduce the overall size and weight of the circuit.
In this setup, a high-voltage linear voltage regulator or a switching regulator may be employed to achieve the desired output. The circuit typically consists of essential components such as a voltage reference, error amplifier, pass transistor, and feedback network.
The voltage reference provides a stable reference point, ensuring that fluctuations in input voltage do not significantly affect the output. The error amplifier compares the output voltage to the reference voltage and adjusts the control signal to the pass transistor accordingly. This transistor acts as a variable resistor, dissipating excess voltage and maintaining the output at the set level.
Additionally, the circuit may include protection features such as over-voltage protection, thermal shutdown, and current limiting to enhance reliability and safety. Capacitors are often used at the output to filter any high-frequency noise, ensuring a clean voltage supply.
The design must account for the high voltage levels, necessitating the use of components rated for at least 200V, along with careful layout considerations to prevent arcing and ensure safe operation. Overall, this regulator circuit is suitable for applications requiring precise high-voltage regulation without the bulk and complexity of transformer-based designs.This regulator circuit stabilize the output voltage at 200V directly (without a transformer). Although the output voltage is high, this circuit only suffer a. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question is designed to maintain a stable output voltage of 200V without the use of a transformer, which is a notable feature, particularly in applications requiring high voltage regulation. The absence of a transformer simplifies the design and can reduce the overall size and weight of the circuit.
In this setup, a high-voltage linear voltage regulator or a switching regulator may be employed to achieve the desired output. The circuit typically consists of essential components such as a voltage reference, error amplifier, pass transistor, and feedback network.
The voltage reference provides a stable reference point, ensuring that fluctuations in input voltage do not significantly affect the output. The error amplifier compares the output voltage to the reference voltage and adjusts the control signal to the pass transistor accordingly. This transistor acts as a variable resistor, dissipating excess voltage and maintaining the output at the set level.
Additionally, the circuit may include protection features such as over-voltage protection, thermal shutdown, and current limiting to enhance reliability and safety. Capacitors are often used at the output to filter any high-frequency noise, ensuring a clean voltage supply.
The design must account for the high voltage levels, necessitating the use of components rated for at least 200V, along with careful layout considerations to prevent arcing and ensure safe operation. Overall, this regulator circuit is suitable for applications requiring precise high-voltage regulation without the bulk and complexity of transformer-based designs.This regulator circuit stabilize the output voltage at 200V directly (without a transformer). Although the output voltage is high, this circuit only suffer a. 🔗 External reference