Dual-trace, triggered oscilloscope
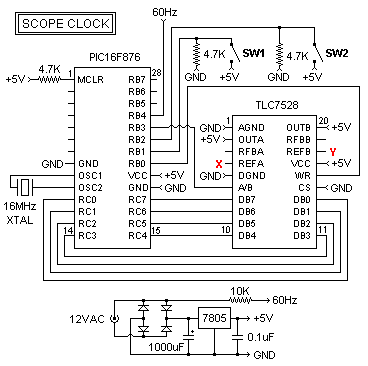
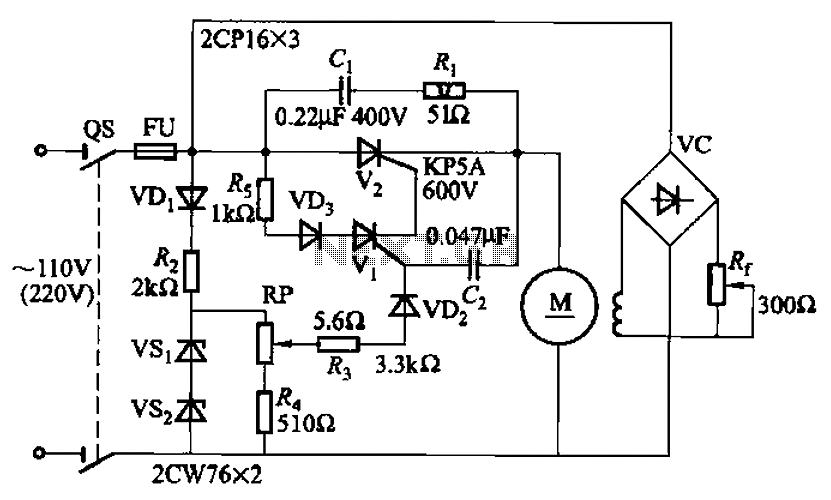
This site contains public-domain schematics for a dual-trace, triggered oscilloscope, and some theory. Click on the topic in the table below to see the schematic for that block. I designed and built this oscilloscope in 1986 using the chassis of a non-working vacuum tube oscilloscope, keeping only the original high voltage vacuum tube supply and CRT. This construction project is only for the experienced designer, since you will want to change and adapt parts of the circuit to accommodate new semiconductors and devices. I recommend that you do not build an oscilloscope from these schematics, but rather, understand the design principles and come up with a more modern design. The bandwidth can easily be extended beyond 100 MHz by using inexpensive high speed drivers and op-amps. Delayed sweep, and other features, are easy to add.
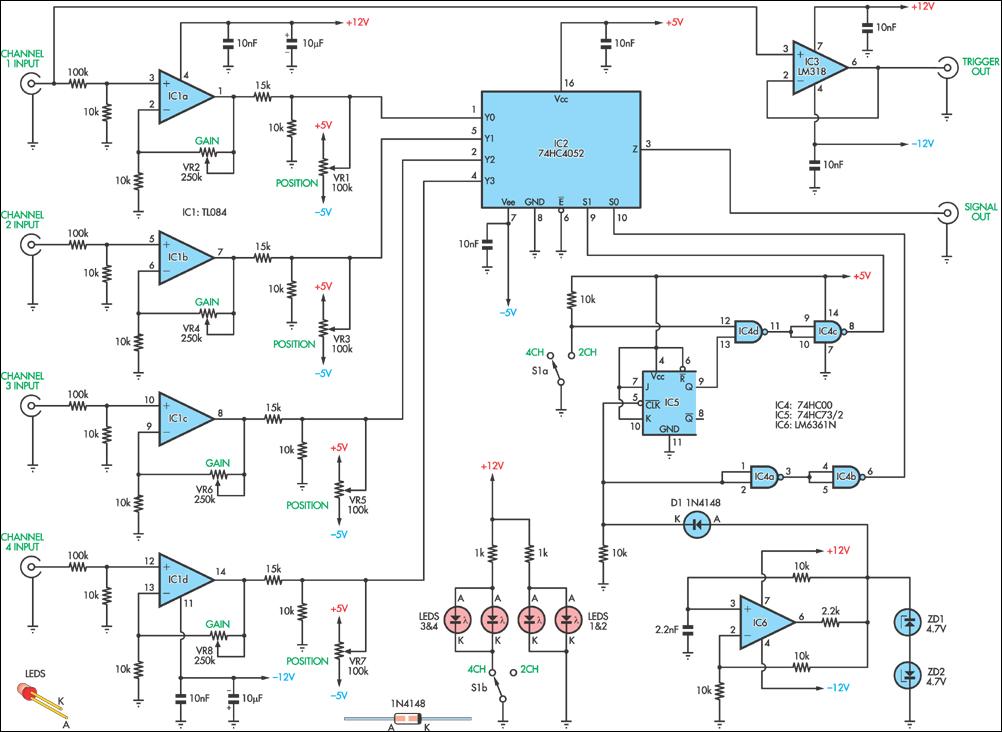
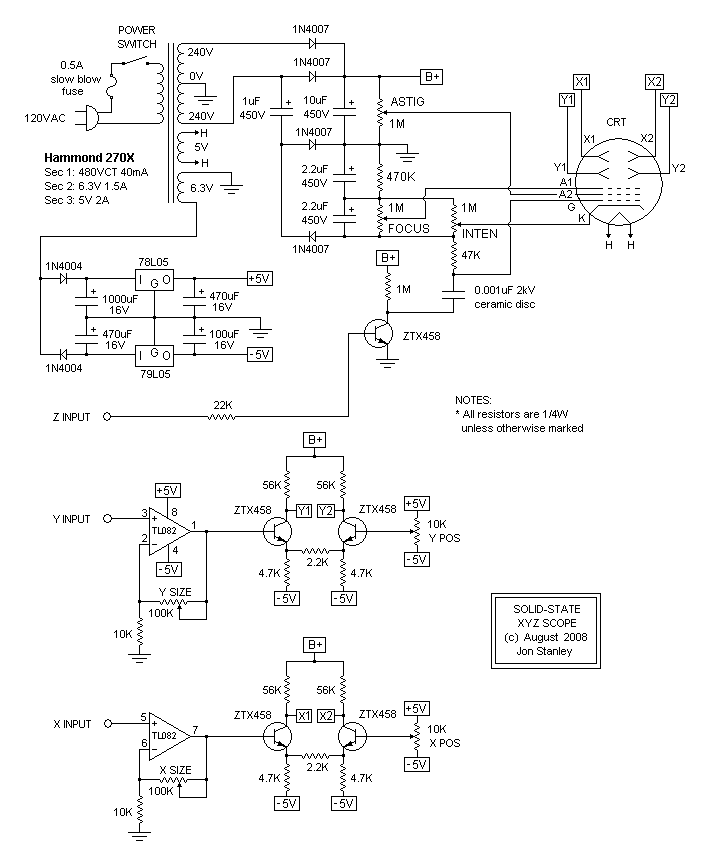
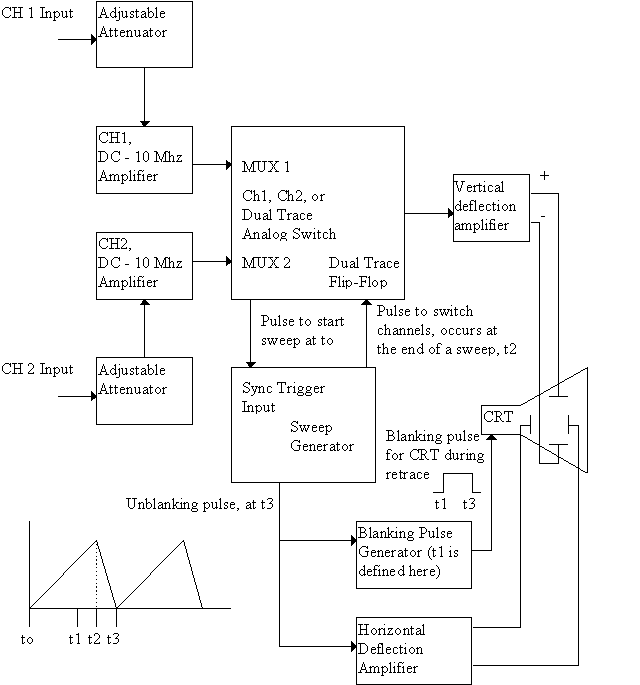
The project involves a dual-trace, triggered oscilloscope that utilizes a combination of analog and digital technologies, originally based on a vacuum tube architecture. The core of the design includes a cathode ray tube (CRT) for display, which is powered by a high voltage supply retained from the original oscilloscope chassis. The dual-trace capability allows for the observation of two signals simultaneously, which is essential for comparative analysis in various electronic applications.
The design emphasizes the importance of understanding the underlying principles of oscilloscope operation rather than strictly following the schematics. Experienced designers are encouraged to adapt the circuit to incorporate modern components such as high-speed operational amplifiers and signal drivers, which can significantly enhance performance, particularly in terms of bandwidth. The original design supports bandwidths beyond 100 MHz when modified appropriately.
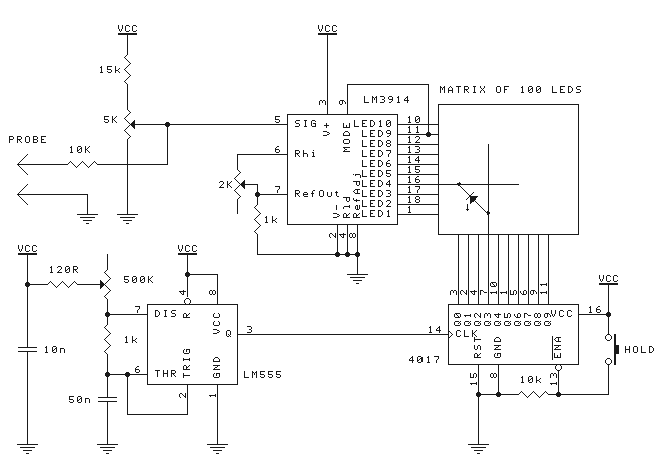
Key features of the oscilloscope include a triggered sweep mechanism that stabilizes the display of repetitive signals, enabling accurate measurements and analysis. Additionally, the design allows for the integration of delayed sweep functionality, which is advantageous for examining transient events in greater detail. The schematics provided serve as a foundational reference for designers looking to innovate and improve upon the traditional oscilloscope design, promoting a deeper understanding of both analog and digital signal processing techniques.This site contains public-domain schematics for a dual-trace, triggered oscilloscope, and some theory. Click on the topic in the table below to see the schematic for that block. I designed and built this oscilloscope in 1986 using the chassis of a non-working vacuum tube oscilloscope, keeping only the original high voltage vacuum tube supply and CRT.
This construction project is only for the experienced designer, since you will want to change and adapt parts of the circuit to accommodate new semiconductors and devices. I recommend that you do not build an oscilloscope from these schematics, but rather, understand the design principles and come up with a more modern design.
The bandwidth can easily be extended beyond 100 MHz by using inexpensive high speed drivers and op-amps. Delayed sweep, and other features, are easy to add. 🔗 External reference
The project involves a dual-trace, triggered oscilloscope that utilizes a combination of analog and digital technologies, originally based on a vacuum tube architecture. The core of the design includes a cathode ray tube (CRT) for display, which is powered by a high voltage supply retained from the original oscilloscope chassis. The dual-trace capability allows for the observation of two signals simultaneously, which is essential for comparative analysis in various electronic applications.
The design emphasizes the importance of understanding the underlying principles of oscilloscope operation rather than strictly following the schematics. Experienced designers are encouraged to adapt the circuit to incorporate modern components such as high-speed operational amplifiers and signal drivers, which can significantly enhance performance, particularly in terms of bandwidth. The original design supports bandwidths beyond 100 MHz when modified appropriately.
Key features of the oscilloscope include a triggered sweep mechanism that stabilizes the display of repetitive signals, enabling accurate measurements and analysis. Additionally, the design allows for the integration of delayed sweep functionality, which is advantageous for examining transient events in greater detail. The schematics provided serve as a foundational reference for designers looking to innovate and improve upon the traditional oscilloscope design, promoting a deeper understanding of both analog and digital signal processing techniques.This site contains public-domain schematics for a dual-trace, triggered oscilloscope, and some theory. Click on the topic in the table below to see the schematic for that block. I designed and built this oscilloscope in 1986 using the chassis of a non-working vacuum tube oscilloscope, keeping only the original high voltage vacuum tube supply and CRT.
This construction project is only for the experienced designer, since you will want to change and adapt parts of the circuit to accommodate new semiconductors and devices. I recommend that you do not build an oscilloscope from these schematics, but rather, understand the design principles and come up with a more modern design.
The bandwidth can easily be extended beyond 100 MHz by using inexpensive high speed drivers and op-amps. Delayed sweep, and other features, are easy to add. 🔗 External reference