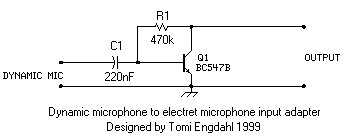
dynamic mic mid boost schematic

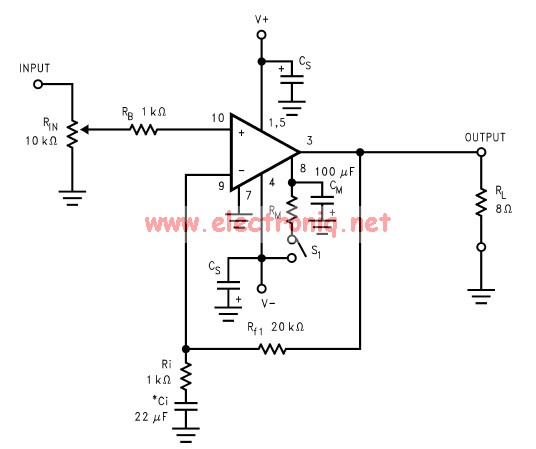
Dynamic microphone mid boost and bass rolloff schematic. This schematic is derived from the documentation of a known working prototype.
The dynamic microphone mid boost and bass rolloff circuit is designed to enhance the audio signal captured by a dynamic microphone, particularly in applications where vocal clarity and presence are essential. The schematic typically includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers to achieve the desired frequency response.
In this circuit, the mid boost is accomplished by utilizing a band-pass filter configuration that amplifies frequencies in the midrange, typically between 1 kHz and 3 kHz. This is crucial for ensuring that vocals are more pronounced in a mix, making them stand out during live performances or recordings. The selection of resistor and capacitor values will determine the exact frequency range that is boosted.
The bass rolloff feature is implemented to reduce lower frequencies that may muddy the mix or cause feedback issues. A high-pass filter is employed for this purpose, allowing higher frequencies to pass while attenuating those below a certain cutoff frequency. The cutoff frequency can be adjusted by changing the values of the capacitors and resistors in the circuit, allowing for customization based on the specific microphone and application.
Overall, this dynamic microphone mid boost and bass rolloff schematic serves as an effective tool for audio engineers and musicians seeking to optimize the performance of dynamic microphones in various sound environments. Proper implementation of this circuit can significantly enhance the quality of audio output, leading to clearer and more professional sound reproduction.Dynamic Mic Mid Boost And Bass Rolloff Schematic Photo: dynamic mic mid boost and bass rolloff schematic. taken from documentation of a known working po .. 🔗 External reference
The dynamic microphone mid boost and bass rolloff circuit is designed to enhance the audio signal captured by a dynamic microphone, particularly in applications where vocal clarity and presence are essential. The schematic typically includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers to achieve the desired frequency response.
In this circuit, the mid boost is accomplished by utilizing a band-pass filter configuration that amplifies frequencies in the midrange, typically between 1 kHz and 3 kHz. This is crucial for ensuring that vocals are more pronounced in a mix, making them stand out during live performances or recordings. The selection of resistor and capacitor values will determine the exact frequency range that is boosted.
The bass rolloff feature is implemented to reduce lower frequencies that may muddy the mix or cause feedback issues. A high-pass filter is employed for this purpose, allowing higher frequencies to pass while attenuating those below a certain cutoff frequency. The cutoff frequency can be adjusted by changing the values of the capacitors and resistors in the circuit, allowing for customization based on the specific microphone and application.
Overall, this dynamic microphone mid boost and bass rolloff schematic serves as an effective tool for audio engineers and musicians seeking to optimize the performance of dynamic microphones in various sound environments. Proper implementation of this circuit can significantly enhance the quality of audio output, leading to clearer and more professional sound reproduction.Dynamic Mic Mid Boost And Bass Rolloff Schematic Photo: dynamic mic mid boost and bass rolloff schematic. taken from documentation of a known working po .. 🔗 External reference