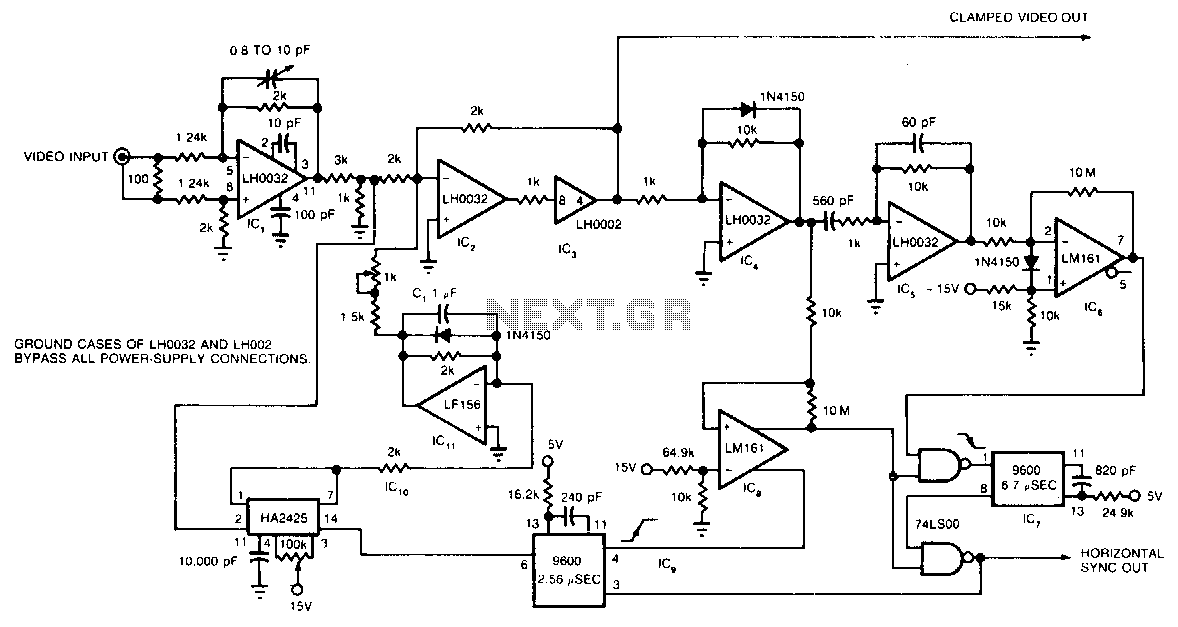
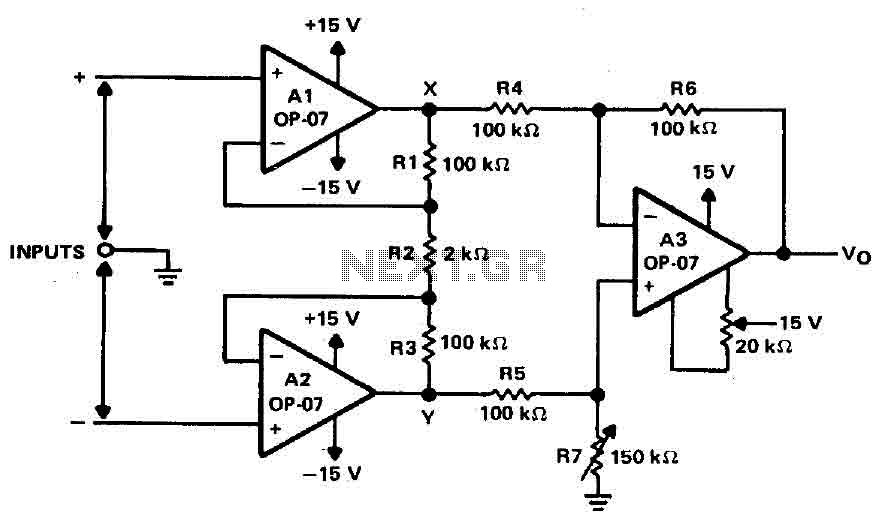
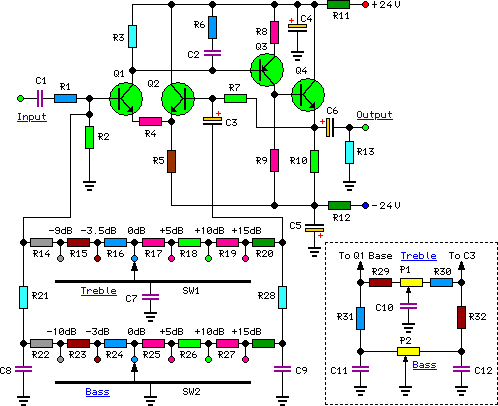
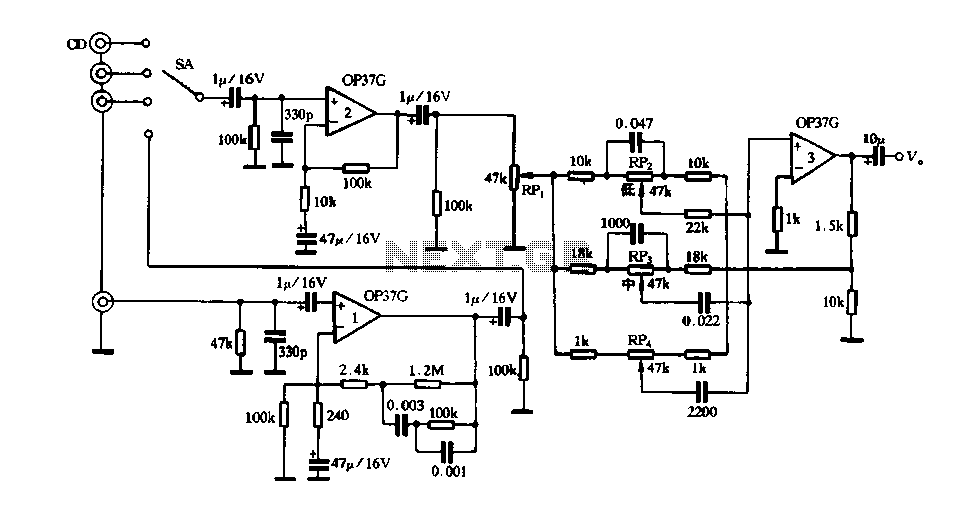
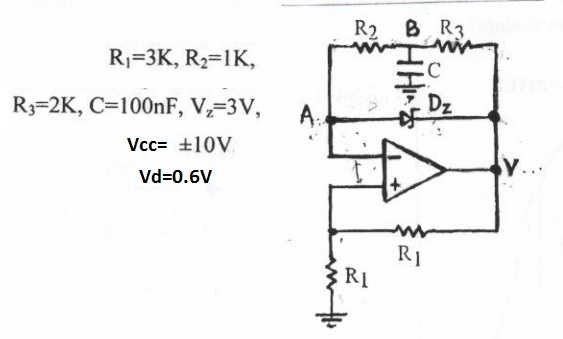
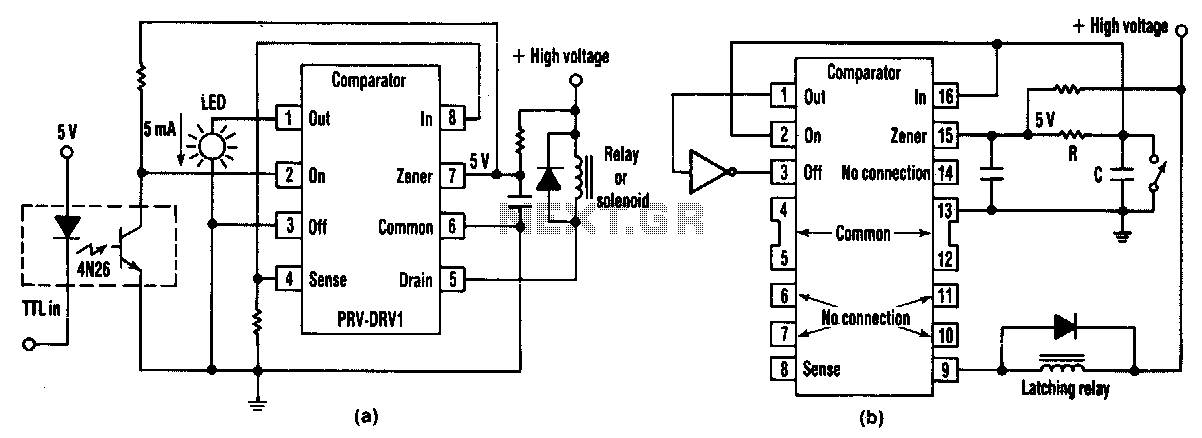
Easy and low cost IRF540/9540 amp
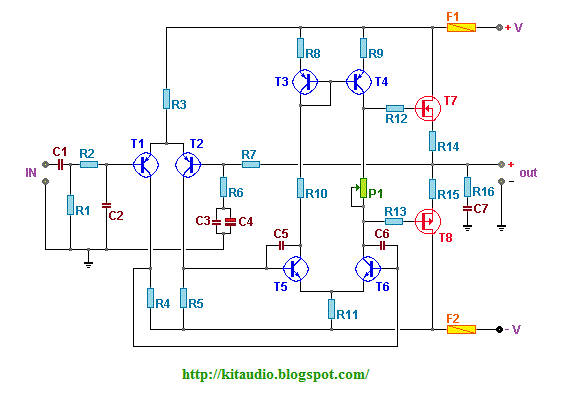
A few months ago, a first amplifier project was completed. It served primarily as a test rather than a listening device. The design utilized 9240/240 Mosfets. Future plans for enhancement or modification are being considered.
The amplifier design utilizing 9240/240 Mosfets indicates a focus on high-efficiency and high-performance amplification. The 9240 and 240 are both N-channel and P-channel MOSFETs, respectively, commonly used in audio amplification applications due to their low on-resistance and high current handling capabilities.
In a typical configuration, the amplifier could be designed using a complementary push-pull circuit topology, where the 9240 and 240 MOSFETs work together to amplify the audio signal. The circuit would include a differential input stage to ensure low distortion and high fidelity. Feedback mechanisms could be integrated to stabilize the gain and reduce any potential crossover distortion, which is crucial in audio applications.
Power supply considerations are essential for this kind of amplifier. A dual power supply design, providing both positive and negative voltages, would be ideal to ensure that the MOSFETs operate within their optimal range. Additional components such as filter capacitors would be necessary to smooth out the power supply and prevent any ripple from affecting the audio output.
Thermal management is another critical aspect of the design, as MOSFETs can generate significant heat during operation. Proper heat sinking and possibly active cooling solutions should be implemented to maintain safe operating temperatures and ensure reliability over long periods of use.
Overall, the amplifier design utilizing 9240/240 MOSFETs has the potential to deliver high-quality audio performance, and further refinements could enhance its capabilities for practical listening applications.Hi all, I completed my first amp a few months ago. It was more a test than really something to listen to. It used the 9240/240 Mosfets. Now I want to.. 🔗 External reference
The amplifier design utilizing 9240/240 Mosfets indicates a focus on high-efficiency and high-performance amplification. The 9240 and 240 are both N-channel and P-channel MOSFETs, respectively, commonly used in audio amplification applications due to their low on-resistance and high current handling capabilities.
In a typical configuration, the amplifier could be designed using a complementary push-pull circuit topology, where the 9240 and 240 MOSFETs work together to amplify the audio signal. The circuit would include a differential input stage to ensure low distortion and high fidelity. Feedback mechanisms could be integrated to stabilize the gain and reduce any potential crossover distortion, which is crucial in audio applications.
Power supply considerations are essential for this kind of amplifier. A dual power supply design, providing both positive and negative voltages, would be ideal to ensure that the MOSFETs operate within their optimal range. Additional components such as filter capacitors would be necessary to smooth out the power supply and prevent any ripple from affecting the audio output.
Thermal management is another critical aspect of the design, as MOSFETs can generate significant heat during operation. Proper heat sinking and possibly active cooling solutions should be implemented to maintain safe operating temperatures and ensure reliability over long periods of use.
Overall, the amplifier design utilizing 9240/240 MOSFETs has the potential to deliver high-quality audio performance, and further refinements could enhance its capabilities for practical listening applications.Hi all, I completed my first amp a few months ago. It was more a test than really something to listen to. It used the 9240/240 Mosfets. Now I want to.. 🔗 External reference