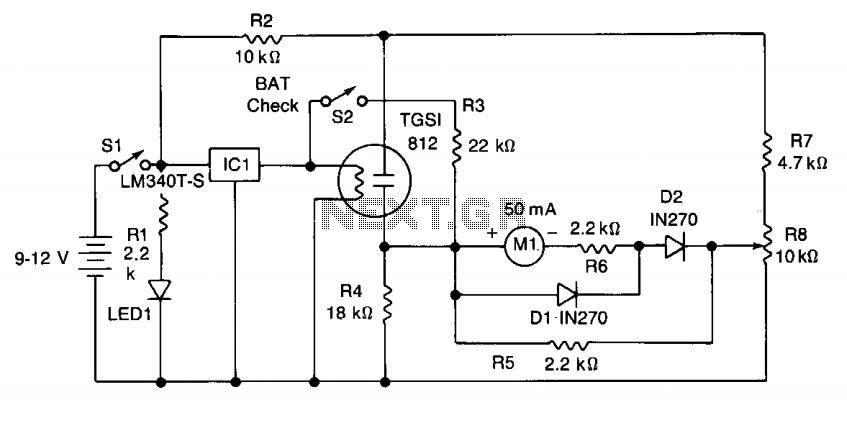
economy radar detector
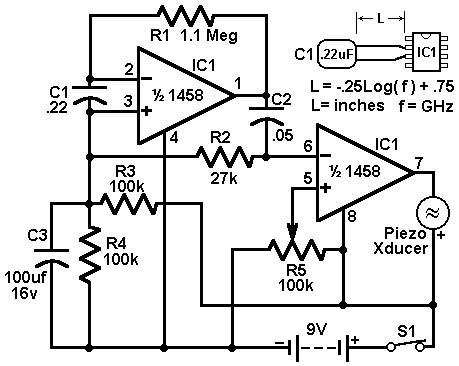
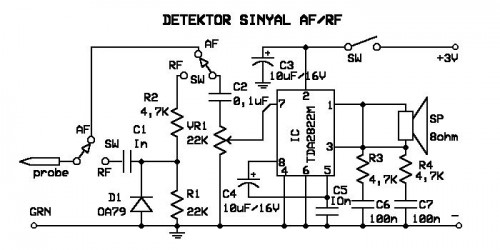
This circuit utilizes a 1458 dual op-amp to create a radar detector. C1 serves as the radar signal detector. The first op-amp functions as a current-to-voltage converter, while the second op-amp buffers the output to drive the piezo transducer. R5 determines the switching threshold of the second op-amp, which is typically adjusted to ensure the circuit triggers only on background noise, followed by a slight reduction in sensitivity. The circuit's response can be fine-tuned by modifying the length of the leads connected to C1. For standard road radar systems, the leads of the input capacitor should measure approximately 0.5 to 0.6 inches.
The radar detector circuit employs a 1458 dual operational amplifier (op-amp) to effectively detect radar signals. The first op-amp is configured as a current-to-voltage converter, which translates the incoming radar signal current into a corresponding voltage. This conversion is critical for the subsequent processing of the signal. The output from this op-amp is then fed into the second op-amp, which is configured as a buffer. The buffering stage is essential as it ensures that the output can drive a piezo transducer without loading down the previous stage, thus maintaining signal integrity.
The component C1 plays a pivotal role as the radar signal detector, and its performance can be influenced by the physical characteristics of the leads connected to it. The length of these leads is crucial; for optimal performance with typical road radar systems, they should be approximately 0.5 to 0.6 inches long. This dimension helps to tune the circuit's response to the radar frequencies of interest while minimizing interference from background noise.
Resistor R5 is a critical component for setting the switching threshold of the second op-amp. Proper adjustment of R5 allows the circuit to distinguish between actual radar signals and background noise. Initially, the threshold is set so that the circuit just begins to trigger on background noise, and then it is slightly adjusted to prevent false triggering. This careful calibration ensures that the radar detector operates effectively in different environments and under varying conditions.
Overall, this radar detector circuit demonstrates a straightforward yet effective design utilizing a dual op-amp configuration, with key components selected to optimize performance for real-world applications.This circuit uses a 1458 dual op-amp to form a radar detector. C1 is the detector of the radar signal. The first op-amp forms a current-to-voltage converter and the second op-amp buffers the output to drive the piezo transducer. R5 sets the switching threshold of the second op-amp; normally it is adjusted so that the circuit barely triggers on bac
kground noise, then it`s backed off a bit. The response of the circuit may be tuned by adjusting the length of the leads on C1. For typical road-radar systems, the input capacitor`s leads should be about 0. 5 to 0. 6 inches 🔗 External reference
The radar detector circuit employs a 1458 dual operational amplifier (op-amp) to effectively detect radar signals. The first op-amp is configured as a current-to-voltage converter, which translates the incoming radar signal current into a corresponding voltage. This conversion is critical for the subsequent processing of the signal. The output from this op-amp is then fed into the second op-amp, which is configured as a buffer. The buffering stage is essential as it ensures that the output can drive a piezo transducer without loading down the previous stage, thus maintaining signal integrity.
The component C1 plays a pivotal role as the radar signal detector, and its performance can be influenced by the physical characteristics of the leads connected to it. The length of these leads is crucial; for optimal performance with typical road radar systems, they should be approximately 0.5 to 0.6 inches long. This dimension helps to tune the circuit's response to the radar frequencies of interest while minimizing interference from background noise.
Resistor R5 is a critical component for setting the switching threshold of the second op-amp. Proper adjustment of R5 allows the circuit to distinguish between actual radar signals and background noise. Initially, the threshold is set so that the circuit just begins to trigger on background noise, and then it is slightly adjusted to prevent false triggering. This careful calibration ensures that the radar detector operates effectively in different environments and under varying conditions.
Overall, this radar detector circuit demonstrates a straightforward yet effective design utilizing a dual op-amp configuration, with key components selected to optimize performance for real-world applications.This circuit uses a 1458 dual op-amp to form a radar detector. C1 is the detector of the radar signal. The first op-amp forms a current-to-voltage converter and the second op-amp buffers the output to drive the piezo transducer. R5 sets the switching threshold of the second op-amp; normally it is adjusted so that the circuit barely triggers on bac
kground noise, then it`s backed off a bit. The response of the circuit may be tuned by adjusting the length of the leads on C1. For typical road-radar systems, the input capacitor`s leads should be about 0. 5 to 0. 6 inches 🔗 External reference