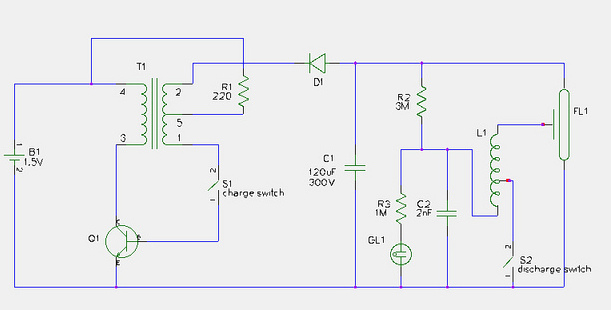
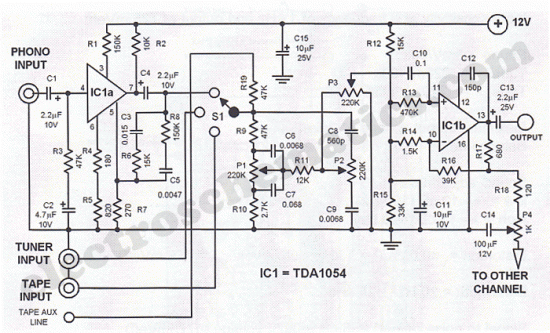
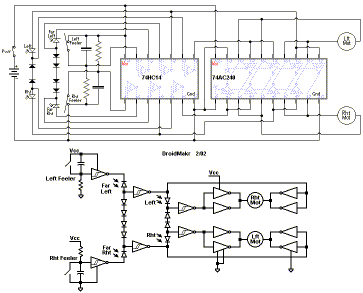
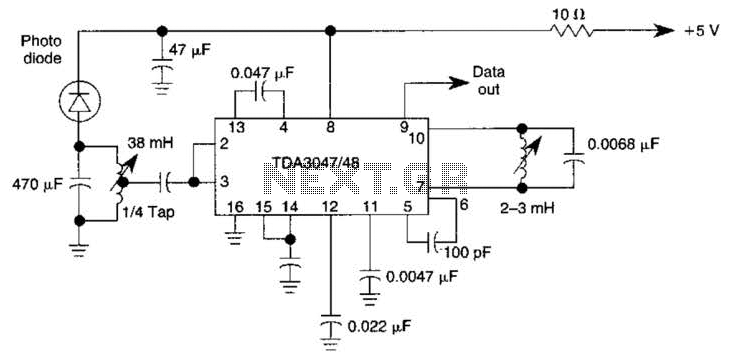
Eight PTC phase asynchronous motor protection circuit
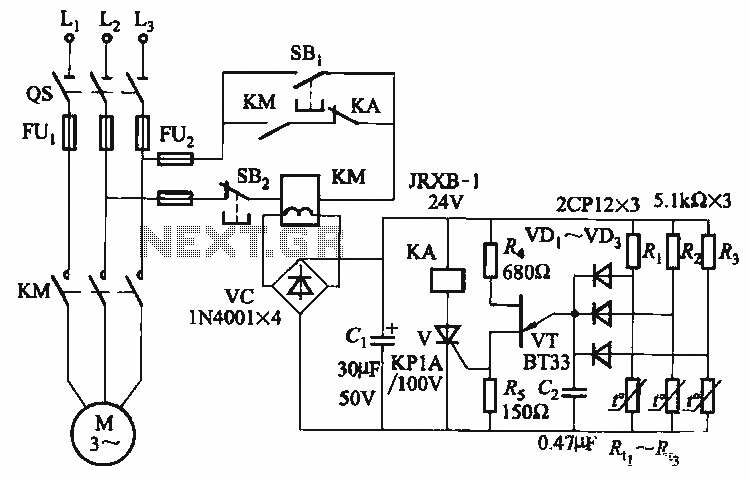
The thyristor control circuit includes a bridge circuit designed to regulate the temperature in the contactor coil KM, along with a secondary winding that functions as a power protection device. It comprises a thermistor (R:., Rt3) and a resistor (Rz, Rs) arranged in a voltage divider configuration. Additionally, the circuit features diode gates (VDi, VD2, VD3) and a unijunction transistor (VT) with its emitter connected within the bridge circuit, exhibiting specific switching characteristics.
The thyristor control circuit operates by utilizing a bridge configuration that effectively manages the temperature of the contactor coil KM. The inclusion of a secondary winding enhances the circuit's ability to provide power protection, ensuring that the system remains stable under varying load conditions. The thermistor (R:., Rt3) plays a crucial role in sensing temperature changes, allowing for real-time adjustments to the control circuit's operation.
The voltage divider, formed by the resistors (Rz, Rs), is essential for establishing the appropriate biasing conditions for the unijunction transistor (VT). This biasing allows for precise control of the switching behavior of the circuit. The diode gates (VDi, VD2, VD3) are strategically placed to facilitate the triggering of the thyristor, enabling it to turn on and off based on the thermal feedback received from the thermistor.
The unijunction transistor's emitter, connected to the bridge circuit, is pivotal in generating the necessary pulse for the thyristor control. This setup ensures that the thyristor operates within its optimal range, providing efficient control over the contactor coil's temperature. The overall design of the circuit emphasizes reliability and responsiveness, making it suitable for applications where temperature regulation is critical.The thyristor control circuit, with the bridge circuit to control the temperature in the contactor coil KM plus a secondary winding wound as a power protection device. R. thermistor , (R:., Rt3) and a resistor R. (Rz, Rs) string associated voltage divider, the diode gates (VDi, VD2, VD3) VT unijunction transistor with the emitter connected in a bridge circuit having switching characteristics.
The thyristor control circuit operates by utilizing a bridge configuration that effectively manages the temperature of the contactor coil KM. The inclusion of a secondary winding enhances the circuit's ability to provide power protection, ensuring that the system remains stable under varying load conditions. The thermistor (R:., Rt3) plays a crucial role in sensing temperature changes, allowing for real-time adjustments to the control circuit's operation.
The voltage divider, formed by the resistors (Rz, Rs), is essential for establishing the appropriate biasing conditions for the unijunction transistor (VT). This biasing allows for precise control of the switching behavior of the circuit. The diode gates (VDi, VD2, VD3) are strategically placed to facilitate the triggering of the thyristor, enabling it to turn on and off based on the thermal feedback received from the thermistor.
The unijunction transistor's emitter, connected to the bridge circuit, is pivotal in generating the necessary pulse for the thyristor control. This setup ensures that the thyristor operates within its optimal range, providing efficient control over the contactor coil's temperature. The overall design of the circuit emphasizes reliability and responsiveness, making it suitable for applications where temperature regulation is critical.The thyristor control circuit, with the bridge circuit to control the temperature in the contactor coil KM plus a secondary winding wound as a power protection device. R. thermistor , (R:., Rt3) and a resistor R. (Rz, Rs) string associated voltage divider, the diode gates (VDi, VD2, VD3) VT unijunction transistor with the emitter connected in a bridge circuit having switching characteristics.