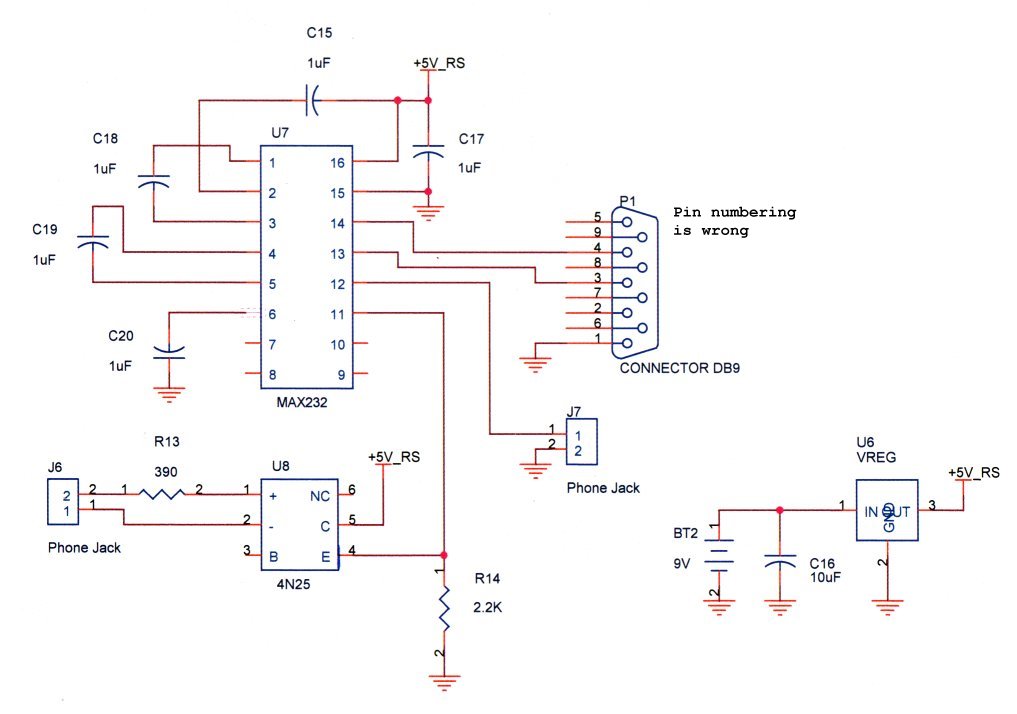
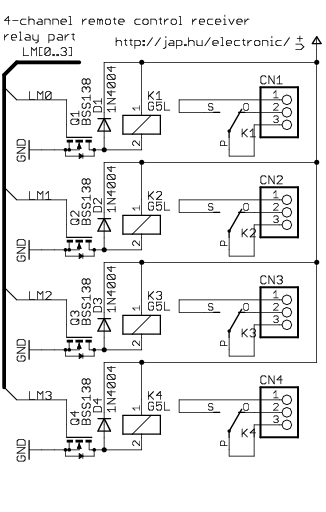
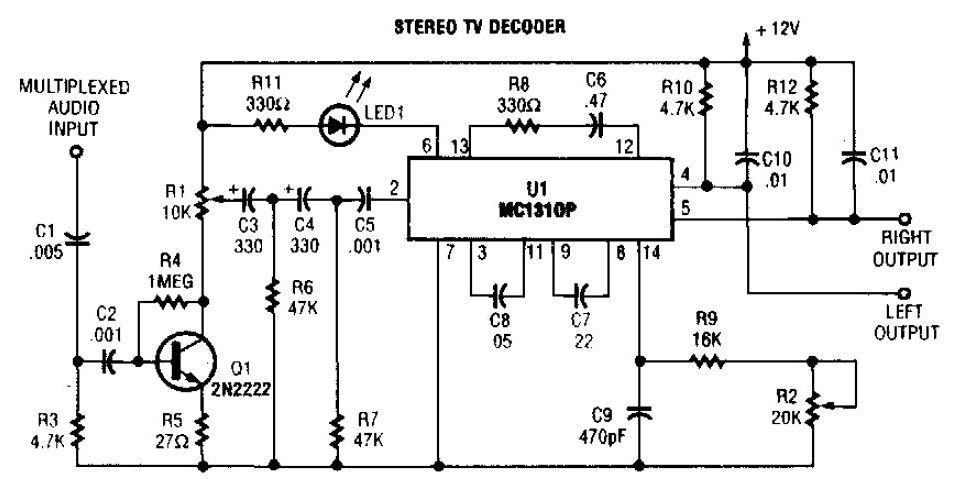
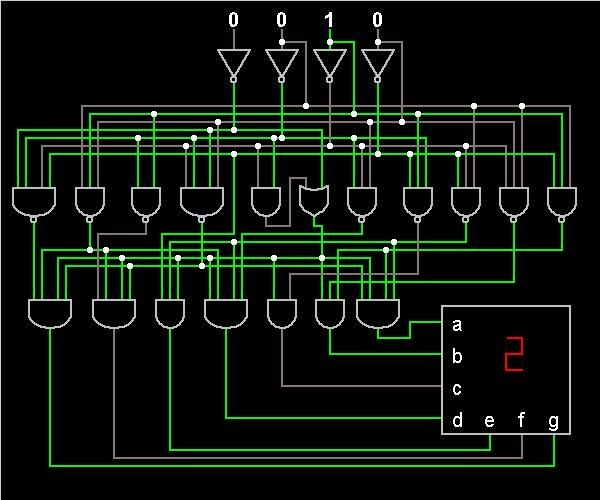
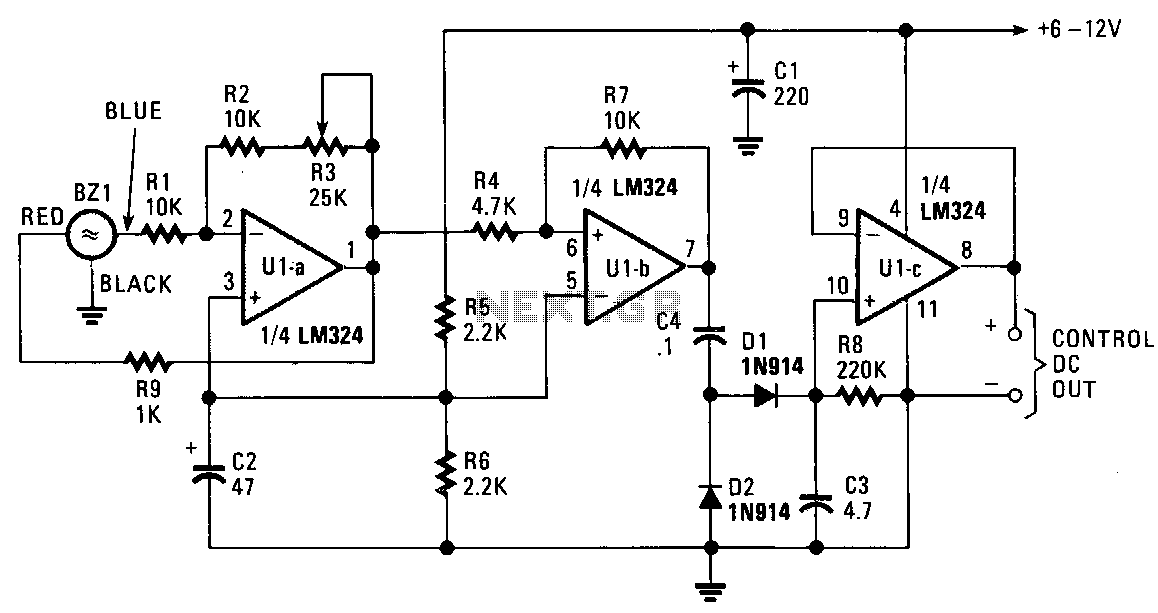
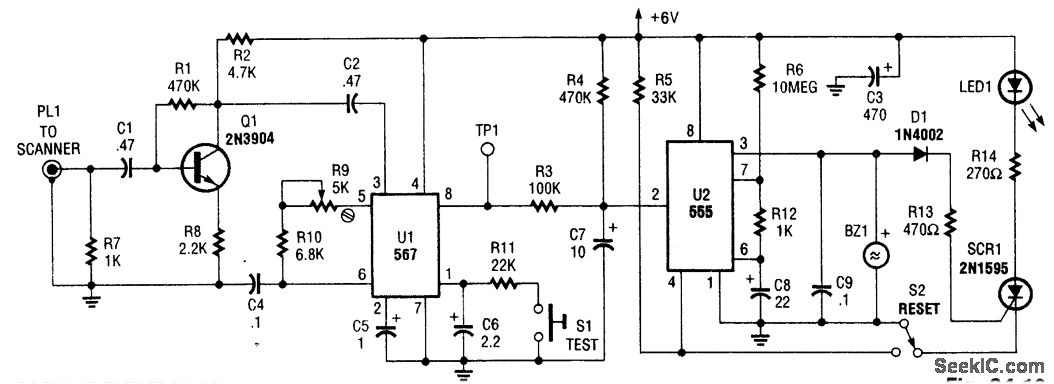
Encoder and Decoder
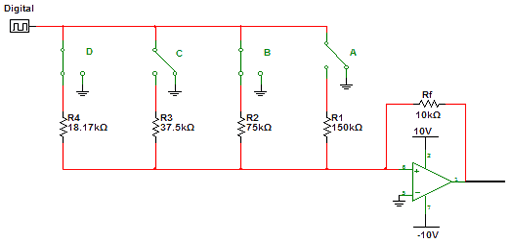
Encoders and decoders are circuits that convert analog signals to digital signals and digital signals to analog signals. The input is in digital form, while the output is a continuous sine wave or analog wave.
Encoders and decoders play a crucial role in modern electronic systems, facilitating the seamless interaction between digital and analog domains. An encoder is responsible for transforming an analog signal, such as sound or light, into a digital format, which can be processed by digital devices. This process typically involves sampling the analog signal at discrete intervals and quantizing the amplitude to a finite set of values, resulting in a binary representation.
Conversely, a decoder performs the reverse operation, taking a digital signal and converting it back into an analog form. This is essential for applications where digital processing is required, but the output needs to be in a form that can be perceived by humans or other analog systems. The output of a decoder is often a continuous sine wave or other types of analog waveforms that accurately represent the original input signal.
In practical applications, encoders and decoders can be implemented using various technologies, including integrated circuits (ICs) dedicated to signal processing. Common examples include pulse code modulation (PCM) encoders, which convert audio signals into digital data for transmission, and digital-to-analog converters (DACs), which take digital audio data and produce an analog output for speakers.
The design of these circuits requires careful consideration of factors such as sampling rate, bit depth, and noise performance, as these parameters significantly influence the fidelity of the conversion process. Additionally, various modulation techniques, such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM), can be employed to optimize the performance of the encoder and decoder in specific applications.
Overall, the integration of encoders and decoders within electronic systems enhances the versatility and functionality of devices, enabling them to operate effectively across both analog and digital environments.Encoder and Decoder are circuits which converts the analog signal to digital and digital signal into analog signal. Its input will be in digital form while the output will be a continuous sine wave or analog wave.. 🔗 External reference
Encoders and decoders play a crucial role in modern electronic systems, facilitating the seamless interaction between digital and analog domains. An encoder is responsible for transforming an analog signal, such as sound or light, into a digital format, which can be processed by digital devices. This process typically involves sampling the analog signal at discrete intervals and quantizing the amplitude to a finite set of values, resulting in a binary representation.
Conversely, a decoder performs the reverse operation, taking a digital signal and converting it back into an analog form. This is essential for applications where digital processing is required, but the output needs to be in a form that can be perceived by humans or other analog systems. The output of a decoder is often a continuous sine wave or other types of analog waveforms that accurately represent the original input signal.
In practical applications, encoders and decoders can be implemented using various technologies, including integrated circuits (ICs) dedicated to signal processing. Common examples include pulse code modulation (PCM) encoders, which convert audio signals into digital data for transmission, and digital-to-analog converters (DACs), which take digital audio data and produce an analog output for speakers.
The design of these circuits requires careful consideration of factors such as sampling rate, bit depth, and noise performance, as these parameters significantly influence the fidelity of the conversion process. Additionally, various modulation techniques, such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM), can be employed to optimize the performance of the encoder and decoder in specific applications.
Overall, the integration of encoders and decoders within electronic systems enhances the versatility and functionality of devices, enabling them to operate effectively across both analog and digital environments.Encoder and Decoder are circuits which converts the analog signal to digital and digital signal into analog signal. Its input will be in digital form while the output will be a continuous sine wave or analog wave.. 🔗 External reference