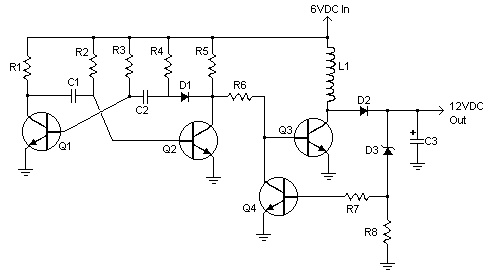
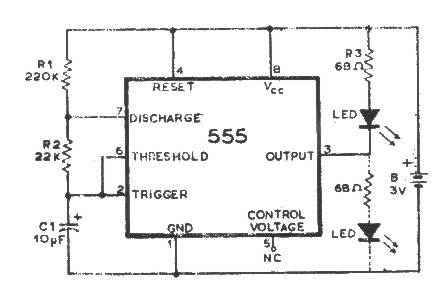
Experiments with coupled circuits
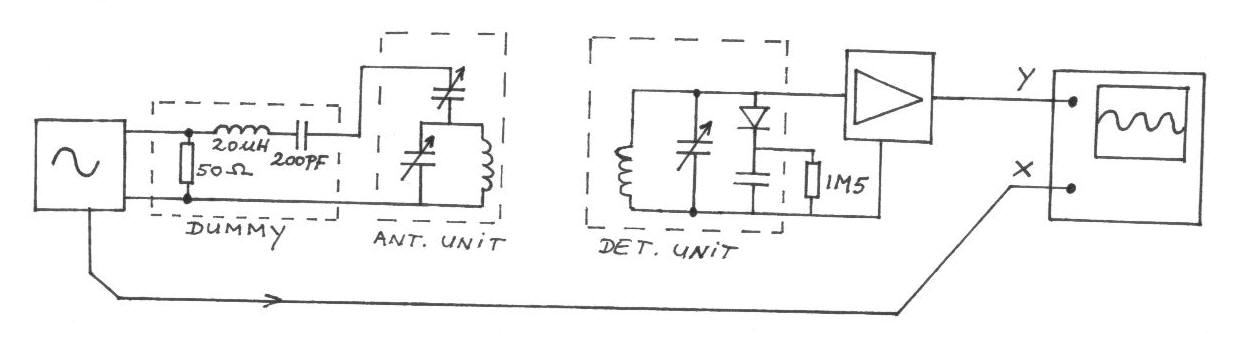
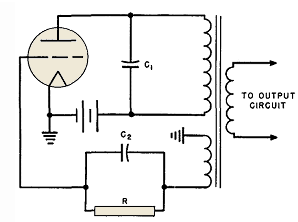
The frequency remains constant, oscillating between two predetermined values. On the oscilloscope display, a frequency spectrum is observed, showcasing the response curves of the two circuits. The input voltage of the receiver is 0.1 Volt peak-to-peak, while the voltage across the detector circuit measures approximately 5 Volts peak-to-peak, resulting in a voltage gain of 50 times.
The described circuit operates by maintaining a stable frequency that alternates between two specific values. This frequency modulation allows for the analysis of the response characteristics of two distinct circuits when visualized on an oscilloscope. The oscilloscope serves as a crucial tool in this setup, providing a visual representation of the frequency spectrum, which includes the amplitude and phase response of the circuits under test.
The receiver circuit is designed to accept a low input voltage of 0.1 Volt peak-to-peak. This low-level signal is processed and amplified by the subsequent stages of the circuit. The detector circuit, which follows the receiver, is responsible for further processing the signal. It successfully amplifies the input voltage to approximately 5 Volts peak-to-peak. This amplification results in a voltage gain of 50 times, which is significant for applications requiring enhanced signal strength for further analysis or transmission.
The design of the circuit may involve various electronic components, such as operational amplifiers for amplification, resistors for setting gain levels, and capacitors for filtering out unwanted frequencies. Proper selection of these components is essential to ensure that the circuit operates efficiently within the desired frequency range while minimizing distortion and noise.
In practical applications, this type of circuit could be utilized in communication systems, signal processing, or instrumentation, where accurate frequency response measurements are critical. The ability to visualize the response curves on an oscilloscope allows engineers to assess the performance of the circuits and make necessary adjustments to optimize their functionality.The frequency is constant varying between two set values, on the oscilloscope screen you get a frequency spectrum with the response curve of the two circuits. The input voltage of the receiver is 0. 1 Volt peak-peak, the voltage across the detector circuit is about 5 Volt peak-peak, so we have a voltage gain of 50 times.
🔗 External reference
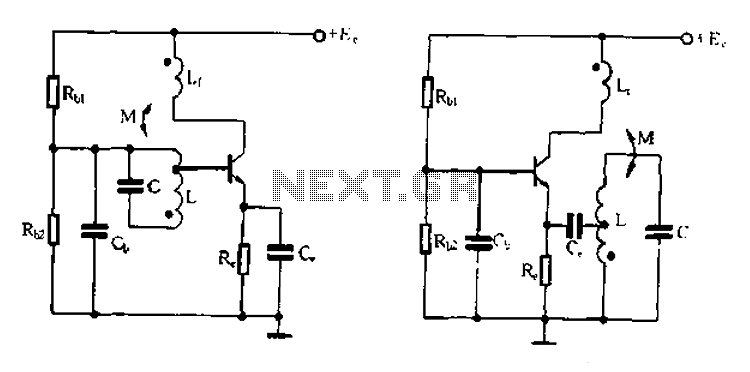
The described circuit operates by maintaining a stable frequency that alternates between two specific values. This frequency modulation allows for the analysis of the response characteristics of two distinct circuits when visualized on an oscilloscope. The oscilloscope serves as a crucial tool in this setup, providing a visual representation of the frequency spectrum, which includes the amplitude and phase response of the circuits under test.
The receiver circuit is designed to accept a low input voltage of 0.1 Volt peak-to-peak. This low-level signal is processed and amplified by the subsequent stages of the circuit. The detector circuit, which follows the receiver, is responsible for further processing the signal. It successfully amplifies the input voltage to approximately 5 Volts peak-to-peak. This amplification results in a voltage gain of 50 times, which is significant for applications requiring enhanced signal strength for further analysis or transmission.
The design of the circuit may involve various electronic components, such as operational amplifiers for amplification, resistors for setting gain levels, and capacitors for filtering out unwanted frequencies. Proper selection of these components is essential to ensure that the circuit operates efficiently within the desired frequency range while minimizing distortion and noise.
In practical applications, this type of circuit could be utilized in communication systems, signal processing, or instrumentation, where accurate frequency response measurements are critical. The ability to visualize the response curves on an oscilloscope allows engineers to assess the performance of the circuits and make necessary adjustments to optimize their functionality.The frequency is constant varying between two set values, on the oscilloscope screen you get a frequency spectrum with the response curve of the two circuits. The input voltage of the receiver is 0. 1 Volt peak-peak, the voltage across the detector circuit is about 5 Volt peak-peak, so we have a voltage gain of 50 times.
🔗 External reference