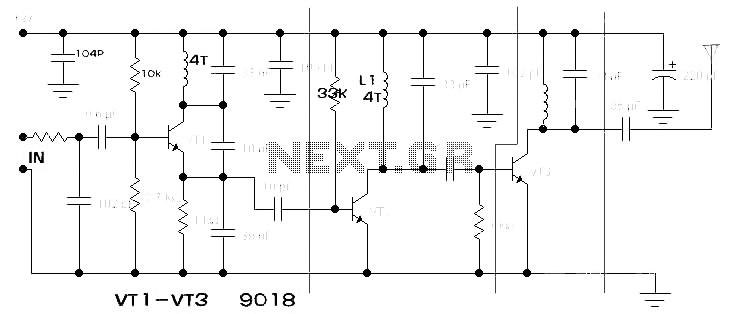
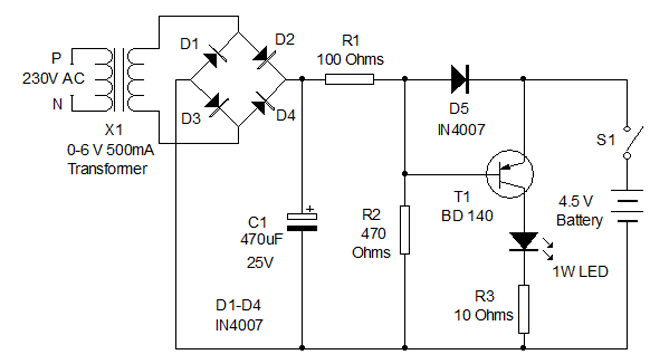
FET several basic bias circuit - self bias voltage divider circuit
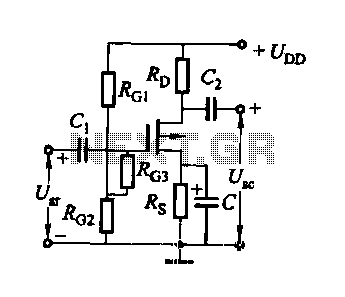
FET several basic bias circuit - self-bias voltage divider circuit
The self-bias voltage divider circuit is a fundamental configuration used in Field Effect Transistor (FET) biasing. This circuit employs two resistors to create a stable bias voltage for the transistor's gate, ensuring consistent operation across varying conditions. The voltage divider consists of two resistors connected in series across a supply voltage, with the junction of the resistors providing the bias voltage to the FET gate.
In a typical configuration, the resistors R1 and R2 are connected from the supply voltage (Vcc) to ground. The voltage at the junction point, which is the gate of the FET, can be calculated using the voltage divider formula: Vg = Vcc * (R2 / (R1 + R2)). This configuration allows the gate voltage (Vg) to remain relatively stable despite variations in the FET's characteristics or supply voltage fluctuations.
The self-biasing feature is particularly advantageous as it allows for automatic adjustment of the gate voltage based on the drain-source voltage (Vds) and the transconductance (gm) of the FET. This results in improved linearity and reduced distortion in amplifier applications. Additionally, the choice of resistor values (R1 and R2) directly influences the bias point and the overall performance of the circuit, making it crucial to select appropriate resistor values based on the desired operating point of the FET.
Overall, the self-bias voltage divider circuit is an essential component in FET amplifier design, providing a reliable and efficient means of biasing that supports consistent performance across various operational conditions.FET several basic bias circuit - self bias voltage divider circuit
The self-bias voltage divider circuit is a fundamental configuration used in Field Effect Transistor (FET) biasing. This circuit employs two resistors to create a stable bias voltage for the transistor's gate, ensuring consistent operation across varying conditions. The voltage divider consists of two resistors connected in series across a supply voltage, with the junction of the resistors providing the bias voltage to the FET gate.
In a typical configuration, the resistors R1 and R2 are connected from the supply voltage (Vcc) to ground. The voltage at the junction point, which is the gate of the FET, can be calculated using the voltage divider formula: Vg = Vcc * (R2 / (R1 + R2)). This configuration allows the gate voltage (Vg) to remain relatively stable despite variations in the FET's characteristics or supply voltage fluctuations.
The self-biasing feature is particularly advantageous as it allows for automatic adjustment of the gate voltage based on the drain-source voltage (Vds) and the transconductance (gm) of the FET. This results in improved linearity and reduced distortion in amplifier applications. Additionally, the choice of resistor values (R1 and R2) directly influences the bias point and the overall performance of the circuit, making it crucial to select appropriate resistor values based on the desired operating point of the FET.
Overall, the self-bias voltage divider circuit is an essential component in FET amplifier design, providing a reliable and efficient means of biasing that supports consistent performance across various operational conditions.FET several basic bias circuit - self bias voltage divider circuit