FET VOLTMETER
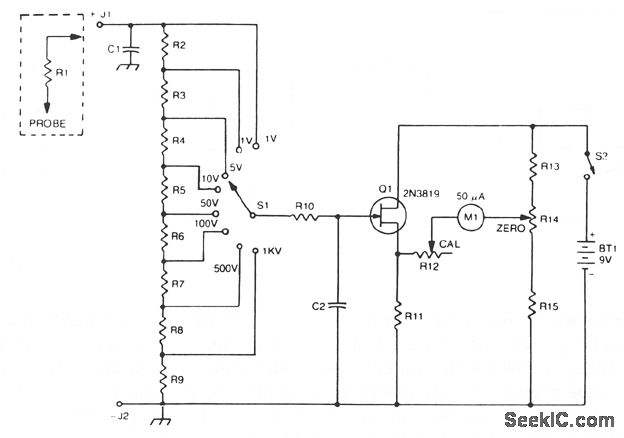
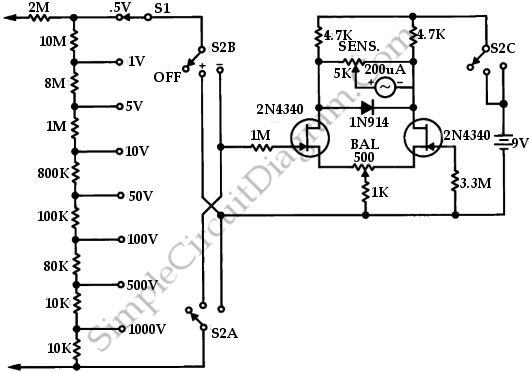
The 2N3819 FET serves as a solid-state voltage output meter (VOM). In this configuration, the 2N3819 functions as a cathode follower. The bias offset, or meter null, is achieved using resistors R14 and R12, while the full-scale calibration is set by resistors R2 through R9, which should total approximately 10 MΩ. Resistor R10 acts as a protective component, and capacitor C2 provides AC bypassing to minimize RF interference and noise pickup.
The circuit utilizes the 2N3819 field-effect transistor (FET) in a cathode follower configuration, which is advantageous for its high input impedance and low output impedance characteristics. This makes it suitable for buffering signals without significant loading effects on the preceding stage. The FET operates in the linear region, allowing for accurate voltage tracking.
The bias offset is crucial for ensuring that the meter reads correctly at zero input. Resistors R14 and R12 are strategically chosen to set the quiescent point of the FET, allowing for precise adjustments to achieve the desired meter null. The values of R2 through R9 are selected to provide a combined resistance of approximately 10 MΩ, which is necessary for the full-scale calibration of the VOM. This ensures that the meter can accurately measure a wide range of voltages.
Resistor R10 serves a protective role in the circuit, safeguarding the FET from excessive current that could lead to damage. This is particularly important in applications where the input voltage may vary significantly. Additionally, capacitor C2 is included to provide AC bypassing, which effectively filters out high-frequency noise and RF interference that could affect the accuracy of the measurements. By ensuring a clean signal is presented to the FET, the overall performance and reliability of the voltage output meter are enhanced.
In summary, the 2N3819 FET-based VOM circuit is designed for high accuracy and stability in voltage measurements, incorporating essential components for calibration, protection, and noise reduction.A2N3819 FET provides a solid state VOM ‚The 2N3819 acts as a cathodefollowerin a VOM The biasoffset(meter null) is obtained with R14 and R12 sets full scale calibration R2 through R9 should totalabout10 M © R10 is a protective resistor and C2 provides ac bypassing to limit rf and noise pickup 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the 2N3819 field-effect transistor (FET) in a cathode follower configuration, which is advantageous for its high input impedance and low output impedance characteristics. This makes it suitable for buffering signals without significant loading effects on the preceding stage. The FET operates in the linear region, allowing for accurate voltage tracking.
The bias offset is crucial for ensuring that the meter reads correctly at zero input. Resistors R14 and R12 are strategically chosen to set the quiescent point of the FET, allowing for precise adjustments to achieve the desired meter null. The values of R2 through R9 are selected to provide a combined resistance of approximately 10 MΩ, which is necessary for the full-scale calibration of the VOM. This ensures that the meter can accurately measure a wide range of voltages.
Resistor R10 serves a protective role in the circuit, safeguarding the FET from excessive current that could lead to damage. This is particularly important in applications where the input voltage may vary significantly. Additionally, capacitor C2 is included to provide AC bypassing, which effectively filters out high-frequency noise and RF interference that could affect the accuracy of the measurements. By ensuring a clean signal is presented to the FET, the overall performance and reliability of the voltage output meter are enhanced.
In summary, the 2N3819 FET-based VOM circuit is designed for high accuracy and stability in voltage measurements, incorporating essential components for calibration, protection, and noise reduction.A2N3819 FET provides a solid state VOM ‚The 2N3819 acts as a cathodefollowerin a VOM The biasoffset(meter null) is obtained with R14 and R12 sets full scale calibration R2 through R9 should totalabout10 M © R10 is a protective resistor and C2 provides ac bypassing to limit rf and noise pickup 🔗 External reference